Find Nth number in a sequence which is not a multiple of a given number
Last Updated :
30 Mar, 2023
Given four integers A, N, L and R, the task is to find the N th number in a sequence of consecutive integers from L to R which is not a multiple of A. It is given that the sequence contain at least N numbers which are not divisible by A and the integer A is always greater than 1.
Examples:
Input: A = 2, N = 3, L = 1, R = 10
Output: 5
Explanation:
The sequence is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10. Here 5 is the third number which is not a multiple of 2 in the sequence.
Input: A = 3, N = 6, L = 4, R = 20
Output: 11
Explanation :
11 is the 6th number which is not a multiple of 3 in the sequence.
Naive Approach: The naive approach is to iterate over the range [L, R] in a loop to find the Nth number. The steps are:
- Initialize the count of non-multiple number and current number to 0.
- Iterate over the range [L, R] until the count of the non-multiple number is not equal to N.
- Increment the count of the non-multiple number by 1, If the current number is not divisible by A.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void count_no (int A, int N, int L, int R)
{
int count = 0;
int i = 0;
for(i = L; i < R + 1; i++)
{
if (i % A != 0)
count += 1;
if (count == N)
break;
}
cout << i;
}
int main()
{
int A = 3, N = 6, L = 4, R = 20;
count_no (A, N, L, R);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class GFG{
static void count_no (int A, int N,
int L, int R)
{
int count = 0;
int i = 0;
for(i = L; i < R + 1; i++)
{
if (i % A != 0)
count += 1;
if (count == N)
break;
}
System.out.println(i);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int A = 3, N = 6, L = 4, R = 20;
count_no (A, N, L, R);
}
}
|
Python3
def count_no (A, N, L, R):
count = 0
for i in range ( L, R + 1 ):
if ( i % A != 0 ):
count += 1
if ( count == N ):
break
print ( i )
A, N, L, R = 3, 6, 4, 20
count_no (A, N, L, R)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static void count_no (int A, int N,
int L, int R)
{
int count = 0;
int i = 0;
for(i = L; i < R + 1; i++)
{
if (i % A != 0)
count += 1;
if (count == N)
break;
}
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
public static void Main()
{
int A = 3, N = 6, L = 4, R = 20;
count_no (A, N, L, R);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function count_no (A, N, L, R)
{
let count = 0;
let i = 0;
for(i = L; i < R + 1; i++)
{
if (i % A != 0)
count += 1;
if (count == N)
break;
}
document.write(i);
}
let A = 3, N = 6, L = 4, R = 20;
count_no (A, N, L, R);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(R – L)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Efficient Approach:
The key observation is that there are A – 1 numbers that are not divisible by A in the range [1, A – 1]. Similarly, there are A – 1 numbers not divisible by A in range [A + 1, 2 * A – 1], [2 * A + 1, 3 * A – 1] and so on.
With the help of this observation, the Nth number which is not divisible by A will be:
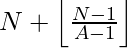
To find the value in the range [ L, R ], we need to shift the origin from ‘0’ to ‘L – 1’, thus we can say that the Nth number which is not divisible by A in the range will be :
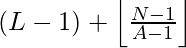
However there is an edge case, when the value of ( L – 1 ) + N + floor( ( N – 1 ) / ( A – 1 ) ) itself turns out to be multiple of a ‘A’, in that case Nth number will be :
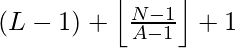
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void countNo(int A, int N, int L, int R)
{
int ans = L - 1 + N + floor((N - 1) /
(A - 1));
if (ans % A == 0)
{
ans = ans + 1;
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main()
{
int A = 5, N = 10, L = 4, R = 20;
countNo(A, N, L, R);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
static void countNo(int A, int N, int L, int R)
{
int ans = L - 1 + N + (int)Math.floor((N - 1) / (A - 1));
if (ans % A == 0)
{
ans = ans + 1;
}
System.out.println(ans);
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
int A = 5, N = 10, L = 4, R = 20;
countNo(A, N, L, R);
}
}
|
Python3
import math
def countNo (A, N, L, R):
ans = L - 1 + N \
+ math.floor( ( N - 1 ) / ( A - 1 ) )
if ans % A == 0:
ans = ans + 1;
print(ans)
A, N, L, R = 5, 10, 4, 20
countNo(A, N, L, R)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void countNo(int A, int N, int L, int R)
{
int ans = L - 1 + N + ((N - 1) / (A - 1));
if (ans % A == 0)
{
ans = ans + 1;
}
Console.WriteLine(ans);
}
static void Main()
{
int A = 5, N = 10, L = 4, R = 20;
countNo(A, N, L, R);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function countNo(A, N, L, R)
{
var ans = L - 1 + N +
Math.floor((N - 1) / (A - 1));
if (ans % A == 0)
{
ans = ans + 1;
}
document.write(ans);
}
var A = 5, N = 10, L = 4, R = 20;
countNo(A, N, L, R);
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...