Expression Tree
Last Updated :
10 Mar, 2023
The expression tree is a binary tree in which each internal node corresponds to the operator and each leaf node corresponds to the operand so for example expression tree for 3 + ((5+9)*2) would be:
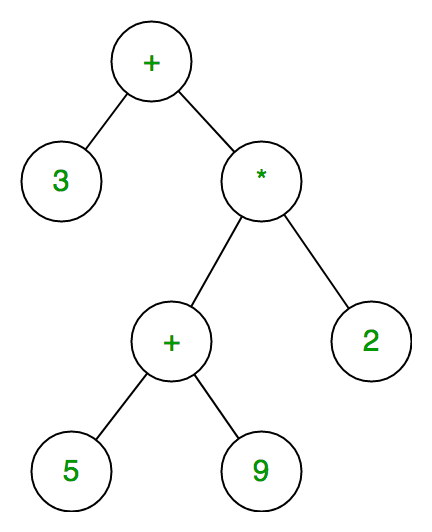
Inorder traversal of expression tree produces infix version of given postfix expression (same with postorder traversal it gives postfix expression)
Evaluating the expression represented by an expression tree:
Let t be the expression tree
If t is not null then
If t.value is operand then
Return t.value
A = solve(t.left)
B = solve(t.right)
// calculate applies operator 't.value'
// on A and B, and returns value
Return calculate(A, B, t.value)
Construction of Expression Tree:
Now For constructing an expression tree we use a stack. We loop through input expression and do the following for every character.
- If a character is an operand push that into the stack
- If a character is an operator pop two values from the stack make them its child and push the current node again.
In the end, the only element of the stack will be the root of an expression tree.
Examples:
Input: A B C*+ D/
Output: A + B * C / D
The first three symbols are operands, so create tree nodes and push pointers to them onto a stack as shown below.

In the Next step, an operator ‘*’ will going read, so two pointers to trees are popped, a new tree is formed and a pointer to it is pushed onto the stack

In the Next step, an operator ‘+’ will read, so two pointers to trees are popped, a new tree is formed and a pointer to it is pushed onto the stack.
A3f.png
Similarly, as above cases first we push ‘D’ into the stack and then in the last step first, will read ‘/’ and then as previous step topmost element will pop out and then will be right subtree of root ‘/’ and other nodes will be right subtree.
Final Constructed Expression Tree is:
A4f.png
Below is the code of the above approach:
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class node {
public:
char value;
node* left;
node* right;
node* next = NULL;
node(char c)
{
this->value = c;
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
node()
{
left = NULL;
right = NULL;
}
friend class Stack;
friend class expression_tree;
};
class Stack {
node* head = NULL;
public:
void push(node*);
node* pop();
friend class expression_tree;
};
class expression_tree {
public:
void inorder(node* x)
{
if (x == NULL)
return;
else {
inorder(x->left);
cout << x->value << " ";
inorder(x->right);
}
}
};
void Stack::push(node* x)
{
if (head == NULL) {
head = x;
}
else {
x->next = head;
head = x;
}
}
node* Stack::pop()
{
node* p = head;
head = head->next;
return p;
}
int main()
{
string s = "ABC*+D/";
Stack e;
expression_tree a;
node *x, *y, *z;
int l = s.length();
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-' || s[i] == '*'
|| s[i] == '/' || s[i] == '^') {
z = new node(s[i]);
x = e.pop();
y = e.pop();
z->left = y;
z->right = x;
e.push(z);
}
else {
z = new node(s[i]);
e.push(z);
}
}
cout << " The Inorder Traversal of Expression Tree: ";
a.inorder(z);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
char data;
struct node* left;
struct node* right;
struct node* next;
};
struct node *head=NULL;
struct node* newNode(char data)
{
struct node* node
= (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
node->data = data;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
node->next = NULL;
return (node);
}
void printInorder(struct node* node)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
else{
printInorder(node->left);
printf("%c ", node->data);
printInorder(node->right);
}
}
void push(struct node* x)
{
if(head==NULL)
head = x;
else
{
(x)->next = head;
head = x;
}
}
struct node* pop()
{
struct node* p = head;
head = head->next;
return p;
}
int main()
{
char s[] = {'A','B','C','*','+','D','/'};
int l = sizeof(s) / sizeof(s[0]) ;
struct node *x, *y, *z;
for (int i = 0; i < l; i++) {
if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-' || s[i] == '*'
|| s[i] == '/' || s[i] == '^') {
z = newNode(s[i]);
x = pop();
y = pop();
z->left = y;
z->right = x;
push(z);
}
else {
z = newNode(s[i]);
push(z);
}
}
printf(" The Inorder Traversal of Expression Tree: ");
printInorder(z);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.Stack;
class Node{
char data;
Node left,right;
public Node(char data){
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class Main {
public static boolean isOperator(char ch){
if(ch=='+' || ch=='-'|| ch=='*' || ch=='/' || ch=='^'){
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static Node expressionTree(String postfix){
Stack<Node> st = new Stack<Node>();
Node t1,t2,temp;
for(int i=0;i<postfix.length();i++){
if(!isOperator(postfix.charAt(i))){
temp = new Node(postfix.charAt(i));
st.push(temp);
}
else{
temp = new Node(postfix.charAt(i));
t1 = st.pop();
t2 = st.pop();
temp.left = t2;
temp.right = t1;
st.push(temp);
}
}
temp = st.pop();
return temp;
}
public static void inorder(Node root){
if(root==null) return;
inorder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data);
inorder(root.right);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String postfix = "ABC*+D/";
Node r = expressionTree(postfix);
inorder(r);
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, value=None, left=None, right=None, next=None):
self.value = value
self.left = left
self.right = right
self.next = next
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def push(self, node):
if not self.head:
self.head = node
else:
node.next = self.head
self.head = node
def pop(self):
if self.head:
popped = self.head
self.head = self.head.next
return popped
else:
raise Exception("Stack is empty")
class ExpressionTree:
def inorder(self, x):
if not x:
return
self.inorder(x.left)
print(x.value, end=" ")
self.inorder(x.right)
def main():
s = "ABC*+D/"
stack = Stack()
tree = ExpressionTree()
for c in s:
if c in "+-*/^":
z = Node(c)
x = stack.pop()
y = stack.pop()
z.left = y
z.right = x
stack.push(z)
else:
stack.push(Node(c))
print("The Inorder Traversal of Expression Tree: ", end="")
tree.inorder(stack.pop())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Node{
public char data;
public Node left,right;
public Node(char data){
this.data = data;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class GFG {
public static bool isOperator(char ch){
if(ch=='+' || ch=='-'|| ch=='*' || ch=='/' || ch=='^'){
return true;
}
return false;
}
static Node expressionTree(String postfix){
Stack<Node> st = new Stack<Node>();
Node t1, t2, temp;
for(int i = 0; i < postfix.Length; i++)
{
if(!isOperator(postfix[i])){
temp = new Node(postfix[i]);
st.Push(temp);
}
else{
temp = new Node(postfix[i]);
t1 = st.Pop();
t2 = st.Pop();
temp.left = t2;
temp.right = t1;
st.Push(temp);
}
}
temp = st.Pop();
return temp;
}
static void inorder(Node root){
if(root == null) return;
inorder(root.left);
Console.Write(root.data);
inorder(root.right);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
String postfix = "ABC*+D/";
Node r = expressionTree(postfix);
inorder(r);
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(value = null, left = null, right = null, next = null) {
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.next = next;
}
}
class Stack {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
}
push(node) {
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node;
}
else
{
node.next = this.head;
this.head = node;
}
}
pop() {
if (this.head) {
let popped = this.head;
this.head = this.head.next;
return popped;
} else {
throw new Error("Stack is empty");
}
}
}
class ExpressionTree {
inorder(x) {
if (!x) {
return;
}
this.inorder(x.left);
console.log(x.value+" ");
this.inorder(x.right);
}
}
let s = "ABC*+D/";
let stack = new Stack();
let tree = new ExpressionTree();
for (let c of s) {
if (c === "+" || c === "-" || c === "*" || c === "/" || c === "^") {
let z = new Node(c);
let x = stack.pop();
let y = stack.pop();
z.left = y;
z.right = x;
stack.push(z);
} else {
stack.push(new Node(c));
}
}
console.log("The Inorder Traversal of Expression Tree: ");
tree.inorder(stack.pop());
|
Output
The Inorder Traversal of Expression Tree: A + B * C / D
Time complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary space: O(n)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...