Dispersion Patterns in Nature
Last Updated :
30 Apr, 2024
Dispersion patterns in nature describe how plants and animals spread out in their environment. Understanding the types of patterns in nature helps scientists understand how species interact with each other and their habitats. In this article, we will learn about dispersion patterns in nature including uniform, clumped and random dispersion types in detail.
Dispersion Patterns in Nature
Dispersion patterns in nature describe how plants, animals, and other organisms are spread across different habitats. Each species has its unique way of spreading out or clustering together. These patterns help scientists learn more about how species interact with each other and their surroundings.
- This depends on many factors like the type of resources available, the behaviour of the species, and the layout of the landscape.
- Dispersion has specific reasons and patterns. It is not random.
- For example, some plants release seeds that do not travel far. This can cause many new plants to grow close to each other.
- Wind or water might spread seeds over a wide area. This can lead to a more spread-out arrangement.
- Animals also show different dispersion patterns based on their social structures and survival strategies.
- Some animals prefer to live in groups for protection or to hunt more effectively. Others might spread out to claim their own space and resources.
Types of Dispersion Patterns in Nature
Based on how individuals are spaced relative to each other in their environment, there are three types of dispersion patterns. They are:
- Uniform Dispersion
- Clumped Dispersion
- Random Dispersion
Now let’s see each one of them in detail.
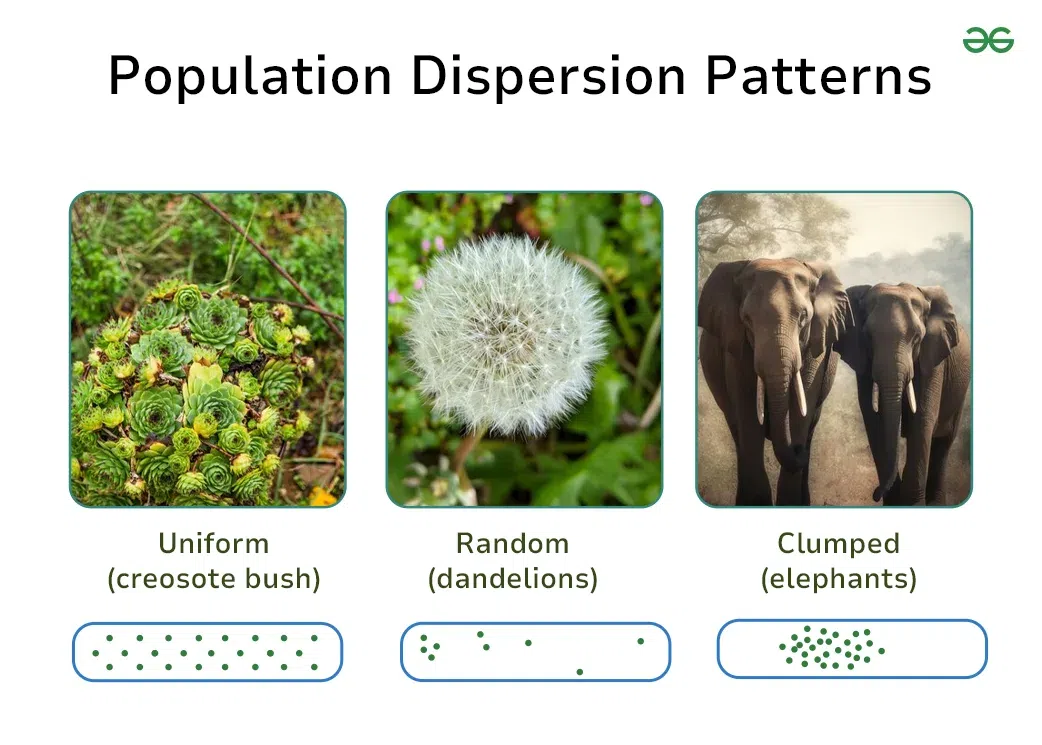
Uniform dispersion is when each individual in a population is spaced evenly from the others. This type of pattern is less common in nature but can be found in certain species. Trees in an orchard are a good example. Farmers plant them at specific distances to promote growth and fruit production.
- In uniform dispersion, each organism has its own space. This can reduce competition for resources like sunlight, water, and nutrients. It can also prevent disease from spreading quickly through a population.
- This spacing might be due to social behaviors in animals. For example, territorial birds like swans often maintain a fixed distance between nests.
- This pattern can be seen in environments where resources are evenly distributed.
- It also appears where individuals can actively maintain their spacing.
- In some cases, plants produce toxins to keep other plants from growing too close. This ensures that they have enough room to grow.
Clumped Dispersion
Clumped dispersion is where individuals group together in patches. This is the most common dispersion pattern in nature. It is often seen in environments where resources are unevenly distributed. Animals and plants form groups where conditions are best for survival.
- Many factors drive clumped dispersion.
- Plants might cluster where soil nutrients are rich.
- Animals might group together for protection or to increase their chances of finding food.
- For instance, wolves hunt in packs to take down larger prey. This makes hunting more efficient.
- In some cases, clumped dispersion is driven by social or reproductive needs.
- Penguins huddle together for warmth in cold environments. This behavior helps them conserve heat and protect each other from predators.
Random Dispersion
Random dispersion occurs when the position of each individual is independent of the others. This pattern is rare in nature because environmental conditions and resource availability usually influence how organisms are distributed.
- In random dispersion, individuals do not form a recognizable pattern.
- They are spread out in an unpredictable way. This can happen in habitats where resources like food and water are abundant and uniformly available.
- It might also occur in disturbed environments where traditional patterns have been disrupted.
- Examples of random dispersion are harder to pinpoint because of its unpredictable nature.
- However, it can sometimes be seen in plants that grow from seeds scattered by the wind.
- These seeds land randomly and grow wherever they happen to fall, provided conditions are suitable.
Here’s a breakdown of the differences between uniform, clumped, and random dispersion patterns:
| Feature |
Uniform Dispersion |
Clumped Dispersion |
Random Dispersion |
| Distribution |
Even spacing between individuals |
Individuals clustered together in groups |
Individuals scattered unpredictably |
| Causes |
Limited resources, territoriality, competition |
Social behavior, resource availability, environmental factors |
Lack of interaction, random environmental factors |
| Example |
Trees in an orchard |
Penguins in a colony |
Dandelion seeds dispersed by wind |
| Consistency |
Stable over time |
Can vary seasonally or with resource availability |
May change over time |
| Impact on Ecology |
Resource competition can be intense |
Facilitates cooperation and social behavior |
May lead to a mix of ecological interactions |
Factors Influencing Dispersion Pattern in Nature
Here are some key factors that influence dispersion patterns in nature:
Resource Availability
- When resources like food and water are plentiful in a specific area, organisms might clump together.
- If resources are spread out evenly, organisms are likely to be more evenly dispersed.
Environmental Conditions
- Harsh conditions may lead certain species to cluster in safer or more favorable microhabitats.
- Milder environments might allow a more random or uniform spread of organisms.
Predation Pressure
- High risk of predation can lead animals to group together as a defensive strategy.
- Lower predation risks might encourage a more dispersed arrangement to reduce competition.
Reproductive Strategies
- Species whose survival strategy involves staying hidden might disperse widely to avoid detection.
- Others might gather in groups to increase the chances of mating and protection of the young.
Social Interactions
- Some species are naturally more social and form groups, influencing a clumped dispersion.
- Solitary species tend to spread out, each individual maintaining its own territory.
Conclusion – Dispersion Patterns in Nature
In conclusion, understanding dispersion patterns in nature is important for ecological science. These patterns—uniform, clumped, and random—show how plants and animals interact with their environment. They help us see how species use space and resources. This knowledge is important for conservation and management. It helps in protecting ecosystems and ensuring biodiversity thrives.
Also Read:
FAQs on Dispersion Patterns in Nature
Which Dispersion Pattern is Most Common in Nature?
The most common dispersion pattern in nature is clumped dispersion, where individuals gather in groups.
What are the Types of Pattern in Nature?
Patterns in nature include clumped, uniform, and random distributions, each reflecting different arrangements of organisms in their environment.
What are Dispersion Patterns in Nature?
Dispersion patterns refer to the way individuals in a population are spaced within their habitat. The main types are uniform, clumped, and random, each describing a specific arrangement and spacing of individuals in an ecosystem.
How do Uniform Dispersion Patterns Occur in Nature?
Uniform dispersion patterns occur when individuals are evenly spaced from each other. This often happens due to direct interactions among individuals, such as competition for resources like light, water, or space, leading to an evenly distributed population.
Give Examples of Clumped Dispersion Patterns in Nature.
Clumped dispersion is the most common pattern in nature, often seen in plants like mushrooms that grow in clusters due to favorable growing conditions or in animals like elephants that group for social or protective reasons.
What causes Random Dispersion Patterns in Nature?
Random dispersion patterns occur when the position of each individual is independent of others, often due to homogeneous environmental conditions where resources are uniformly available, and there are minimal interactions among individuals.
Why is Studying Dispersion Patterns Important for Conservation?
Studying dispersion patterns helps ecologists understand population dynamics, habitat preferences, and ecological interactions, which are crucial for effective conservation planning and management of wildlife and natural resources.
What Impact do Human Activities have on Natural Dispersion Patterns?
Human activities can alter natural dispersion patterns by disrupting habitats and introducing invasive species, leading to shifts in biodiversity and ecosystem dynamics.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...