Difference Between sum of degrees of odd and even degree nodes in an Undirected Graph
Last Updated :
01 Nov, 2023
Given an undirected graph with N vertices and M edges, the task is to find the absolute difference Between the sum of degrees of odd degree nodes and even degree nodes in an undirected Graph.
Examples:
Input: N = 4, edges[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 }, { 1, 4 }, { 2, 3 }, { 2, 4 }, { 3, 4 } }
Output: 12
Explanation:
Below is the graph for the above information:
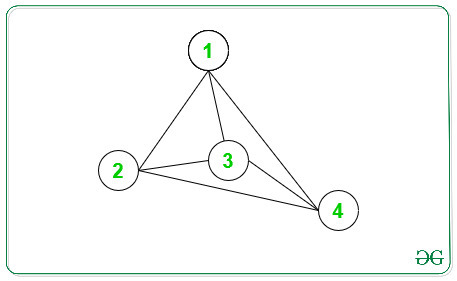
Node -> Degree
1 -> 3
2 -> 3
3 -> 3
4 -> 3
Sum of odd degree node = 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 12
Sum of even degree node = 0
Difference = 12
Input: N = 5, edges[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 }, { 2, 4 }, { 2, 5 } }
Output: 4
Approach:
- For each vertex, the degree can be calculated by the length of the Adjacency List of the given graph at the corresponding vertex.
- Count the sum of degrees of odd degree nodes and even degree nodes and print the difference.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int OddEvenDegree(int N, int M,
int edges[][2])
{
vector<int> Adj[N + 1];
int EvenSum = 0;
int OddSum = 0;
for (int i = 0 ; i < M ; i++) {
int x = edges[i][0];
int y = edges[i][1];
Adj[x].push_back(y);
Adj[y].push_back(x);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
int x = Adj[i].size();
if (x % 2 != 0)
{
OddSum += x;
}
else
{
EvenSum += x;
}
}
return abs(OddSum - EvenSum);
}
int main()
{
int N = 4, M = 6;
int edges[M][2] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 }, { 1, 4 },
{ 2, 3 }, { 2, 4 }, { 3, 4 } };
cout<< OddEvenDegree(N, M, edges);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
static int OddEvenDegree(int N, int M,
int edges[][])
{
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Vector<Integer> []Adj = new Vector[N + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < N + 1; i++)
{
Adj[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
}
int EvenSum = 0;
int OddSum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
int x = edges[i][0];
int y = edges[i][1];
Adj[x].add(y);
Adj[y].add(x);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
int x = Adj[i].size();
if (x % 2 != 0)
{
OddSum += x;
}
else
{
EvenSum += x;
}
}
return Math.abs(OddSum - EvenSum);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, M = 6;
int edges[][] = { { 1, 2 }, { 1, 3 }, { 1, 4 },
{ 2, 3 }, { 2, 4 }, { 3, 4 } };
System.out.print(OddEvenDegree(N, M, edges));
}
}
|
Python3
def OddEvenDegree(N, M, edges):
Adj = [[] for i in range(N + 1)]
EvenSum = 0;
OddSum = 0;
for i in range(M):
x = edges[i][0];
y = edges[i][1];
Adj[x].append(y);
Adj[y].append(x);
for i in range(1, N + 1):
x = len(Adj[i])
if (x % 2 != 0):
OddSum += x;
else:
EvenSum += x;
return abs(OddSum - EvenSum);
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 4
M = 6
edges = [[1, 2], [1, 3],
[1, 4], [2, 3],
[2, 4], [3, 4]]
print(OddEvenDegree(N, M,
edges));
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static int OddEvenDegree(int N, int M,
int [,]edges)
{
List<int> []Adj = new List<int>[N + 1];
for(int i = 0; i < N + 1; i++)
{
Adj[i] = new List<int>();
}
int EvenSum = 0;
int OddSum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
int x = edges[i, 0];
int y = edges[i, 1];
Adj[x].Add(y);
Adj[y].Add(x);
}
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
{
int x = Adj[i].Count;
if (x % 2 != 0)
{
OddSum += x;
}
else
{
EvenSum += x;
}
}
return Math.Abs(OddSum - EvenSum);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 4, M = 6;
int [,]edges = {{1, 2}, {1, 3}, {1, 4},
{2, 3}, {2, 4}, {3, 4}};
Console.Write(OddEvenDegree(N, M, edges));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function OddEvenDegree(N, M, edges)
{
var Adj = Array.from(Array(N+1), ()=>Array());
var EvenSum = 0;
var OddSum = 0;
for (var i = 0 ; i < M ; i++) {
var x = edges[i][0];
var y = edges[i][1];
Adj[x].push(y);
Adj[y].push(x);
}
for (var i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
var x = Adj[i].length;
if (x % 2 != 0)
{
OddSum += x;
}
else
{
EvenSum += x;
}
}
return Math.abs(OddSum - EvenSum);
}
var N = 4, M = 6;
var edges = [ [ 1, 2 ], [ 1, 3 ], [ 1, 4 ],
[ 2, 3 ], [ 2, 4 ], [ 3, 4 ] ];
document.write( OddEvenDegree(N, M, edges));
</script>
|
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...