The diagram of human organs in body helps us see how different organs work together, making it easier to understand how our bodies function. Organs are groups of tissues that perform specific functions necessary for survival. The diagram of human organs shows 78 organs in our body.
The labelled diagram of human organs is given below:

What is an Organ?
An organ is a group of similar tissues that perform specific functions to help the body operate and survive. Organs are anatomically distinct structures composed of multiple tissue types organized in a way that enables them to carry out their specialized roles, such as pumping blood (heart) and breathing (lungs). They have a dedicated blood supply and nerve connections, which work interdependently with other organs as part of larger body systems. The diagram of human organs shows the arrangement of various organs in the body.
List of Organ System in Human Body Diagram and Functions
The human body is comprised of various types of organs, which together form organ system. Each system has specific functions essential for maintaining life. These organs can be broadly categorized into several systems:
Digestive System Organs
The digestive system is responsible for processing food and extracting nutrients. The diagram of human organs shows this system including organs such as the mouth, esophagus, stomach, intestines (small and large), liver, gallbladder, and pancreas.

Human Digestive System
Respiratory System Organs
This system is involved in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. It comprises of organs including the lungs, nose, trachea, and diaphragm.

Respiratory System
Circulatory System Organs
This sysrem is responsible for transporting oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. The diagram of human organs shows this system includes the heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries), and blood.

Circulatory System
Nervous System Organs
This system facilitate communication within the body and responses to external stimuli and this system includes the brain, spinal cord and nerves.
.jpg)
Nervous System
Endocrine System Organs
Regulating various bodily functions through hormone secretion, this system comprises organs such as the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, and reproductive organs (ovaries and testes).
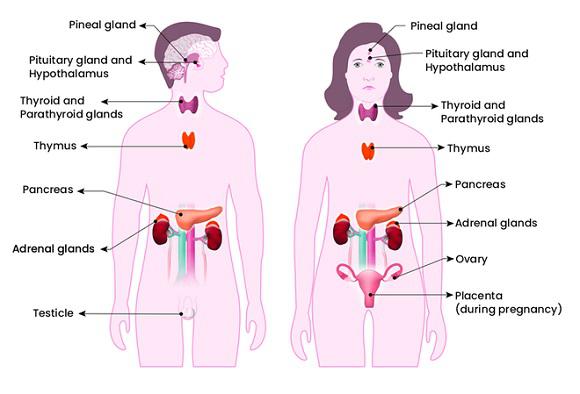
Endocrine System
Urinary System Organs
This system is involved in the elimination of waste products and regulation of fluid balance. The human organs diagram shows this system includes organs like the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.

Urinary System
Reproductive System Organs
Responsible for reproduction and the production of sex hormones, this system includes organs such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, vagina (in females), and testes, epididymis, vas deferens, and prostate (in males).

Reproductive System
Musculoskeletal System Organs
Supporting the body, enabling movement, and protecting internal organs, this system comprises bones, muscles, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage.
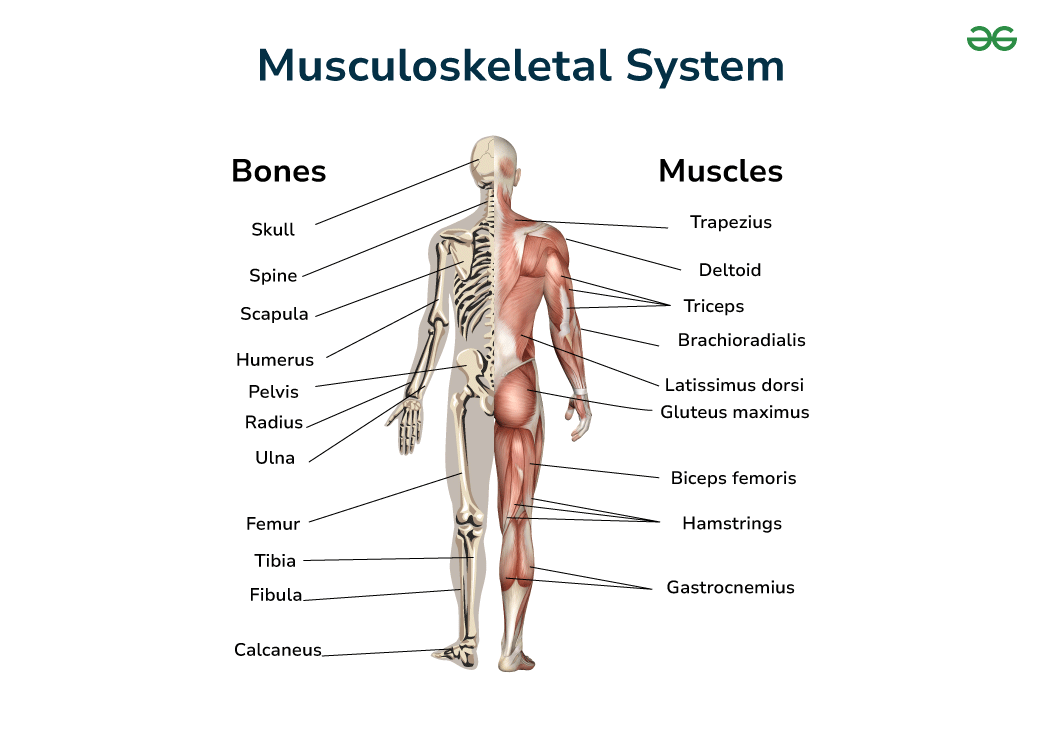
Musculoskeletal System
Integumentary System Organs
Serving as a protective barrier against pathogens and environmental factors, this system includes the skin, hair, nails, and sweat glands.

Integumentary System
Lymphatic and Immune System Organs
This system is responsible for defending the body against infections and maintaining fluid balance. The human organs diagram shows this system includes organs such as the lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, bone marrow, and lymphatic vessels.

Lymphatic System
Sensory Organs
The sensory organs are specialized structures that detect various stimuli from the environment and transmit this information to the brain for interpretation. These organs are crucial for perception, allowing organisms to interact with their surroundings. The primary sensory organs include:

Sense Organs
It is important to note that some organs may have multiple functions and may be involved in more than one body system, highlighting the interconnectedness of the human body.
Conclusion – Diagram of Human Organs
In conclusion, the human body has highly interconnected organs functioning to sustain life. There are approximately 78 recognized organs, each serving specific roles. The diagram of human organs shows the structural arrangements of all the organs that help in understanding our body better.
Also Read:
FAQs on Diagram of Human Organs
What are Organs, and How do they Function?
An organ is a self-contained group of tissues that perform specific functions necessary for the body’s operation and survival.
Can Organs have Multiple Functions?
Yes, many organs in the human body have multiple functions and may be involved in more than one body system. For instance, the pancreas is not only involved in digestion by producing digestive enzymes but also plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels by producing insulin and glucagon.
What are the Major Organ Systems in the Human Body?
The major organ systems include the digestive system, respiratory system, circulatory system, nervous system, endocrine system, urinary system, reproductive system, musculoskeletal system, integumentary system, lymphatic system, and sensory organs.
Name Three Major Organ Systems in the Human Body.
Three major organ systems include the circulatory system, nervous system, and digestive system.
What is the Role of Organs Within the Body?
Organs perform specialized functions crucial for the body’s operation and survival, contributing to processes such as digestion, circulation, and sensory perception.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...