Decorators with parameters in Python
Last Updated :
03 Jan, 2023
Prerequisite: Decorators in Python, Function Decorators
We know Decorators are a very powerful and useful tool in Python since it allows programmers to modify the behavior of function or class. In this article, we will learn about the Decorators with Parameters with help of multiple examples.
Python functions are First Class citizens which means that functions can be treated similarly to objects.
- Function can be assigned to a variable i.e they can be referenced.
- Function can be passed as an argument to another function.
- Function can be returned from a function.
Decorators with parameters is similar to normal decorators.
The syntax for decorators with parameters :
@decorator(params)
def func_name():
''' Function implementation'''
The above code is equivalent to
def func_name():
''' Function implementation'''
func_name = (decorator(params))(func_name)
"""
As the execution starts from left to right decorator(params) is called which returns a function object fun_obj. Using the fun_obj the call fun_obj(fun_name) is made. Inside the inner function, required operations are performed and the actual function reference is returned which will be assigned to func_name. Now, func_name() can be used to call the function with decorator applied on it.
How Decorator with parameters is implemented
Python3
def decorators(*args, **kwargs):
def inner(func):
return func
return inner
@decorators(params)
def func():
|
Here params can also be empty.
Observe these first :
Python3
def decorator_fun(func):
print("Inside decorator")
def inner(*args,**kwargs):
print("Inside inner function")
print("Decorated the function")
func()
return inner()
@decorator_fun
def func_to():
print("Inside actual function")
func_to
|
Another Way:
Python3
def decorator_fun(func):
print("Inside decorator")
def inner(*args, **kwargs):
print("Inside inner function")
print("Decorated the function")
func()
return inner
def func_to():
print("Inside actual function")
decorator_fun(func_to)()
|
Output:
Inside decorator
Inside inner function
Decorated the function
Inside actual function
Let’s move to another example:
Example #1:
Python3
def decorator(*args, **kwargs):
print("Inside decorator")
def inner(func):
print("Inside inner function")
print("I like", kwargs['like'])
func()
return inner
@decorator(like = "geeksforgeeks")
def my_func():
print("Inside actual function")
|
Output:
Inside decorator
Inside inner function
I like geeksforgeeks
Inside actual function
Example #2:
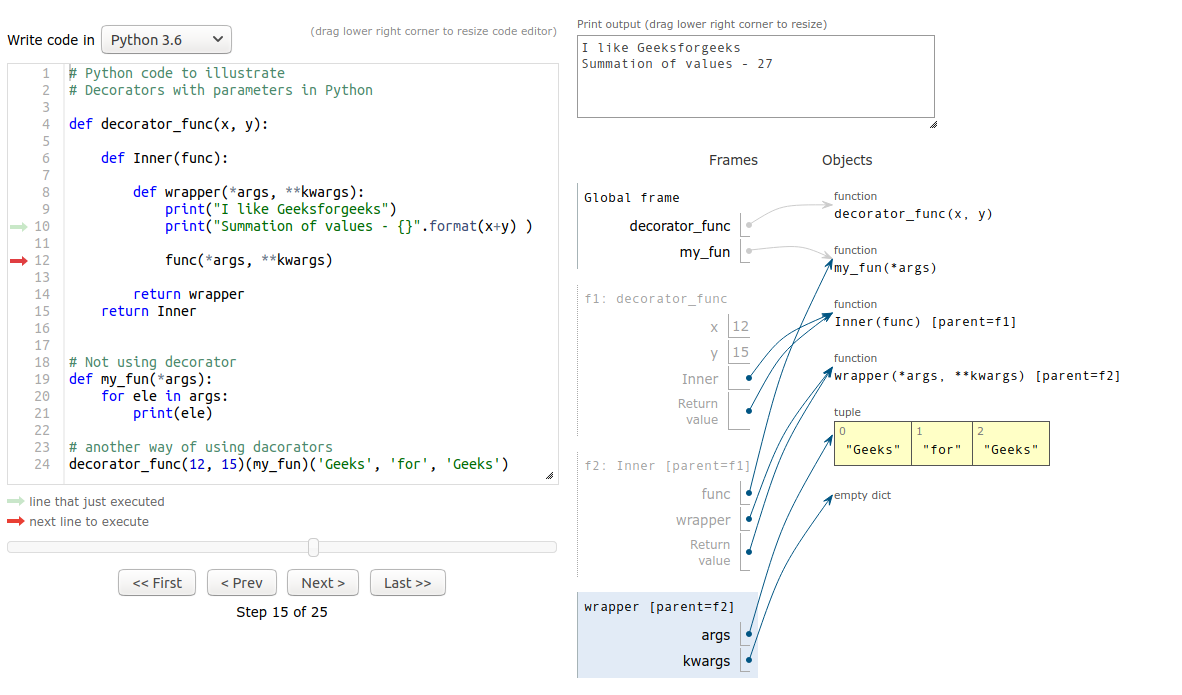
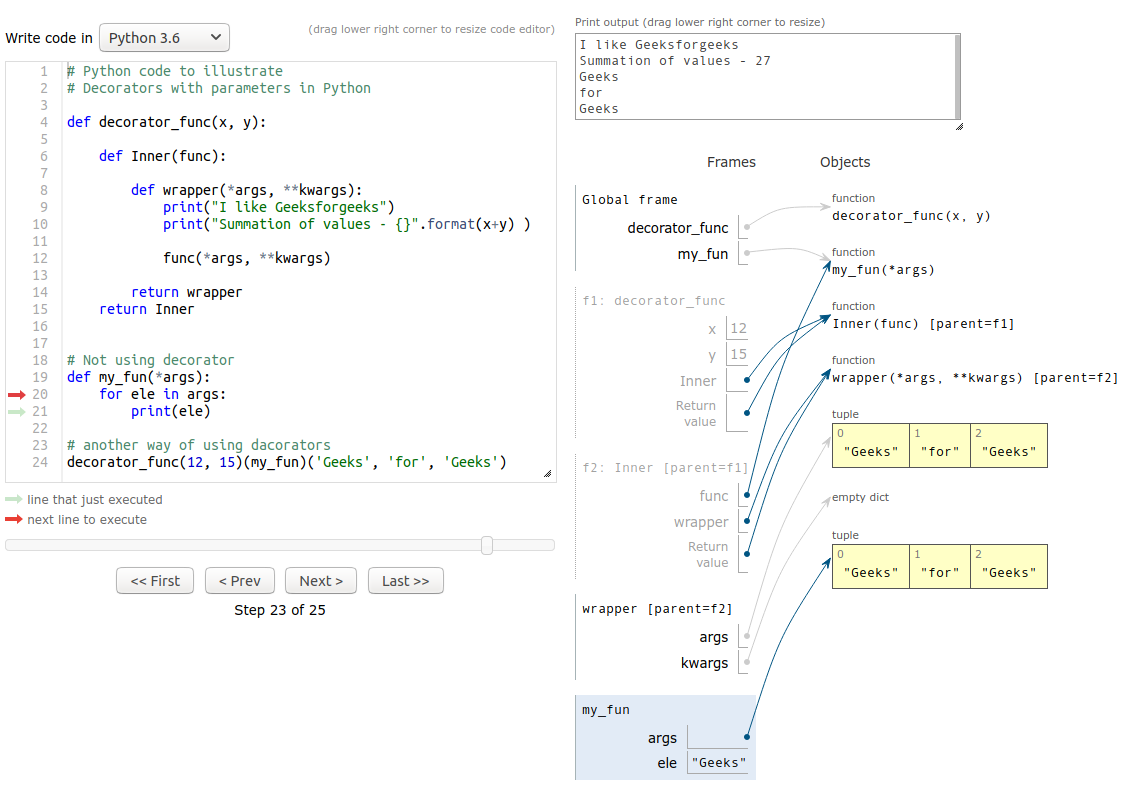
Python3
def decorator_func(x, y):
def Inner(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print("I like Geeksforgeeks")
print("Summation of values - {}".format(x+y) )
func(*args, **kwargs)
return wrapper
return Inner
def my_fun(*args):
for ele in args:
print(ele)
decorator_func(12, 15)(my_fun)('Geeks', 'for', 'Geeks')
|
Output:
I like Geeksforgeeks
Summation of values - 27
Geeks
for
Geeks
This example also tells us that Outer function parameters can be accessed by the enclosed inner function.
Example #3:
Python3
def decodecorator(dataType, message1, message2):
def decorator(fun):
print(message1)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
print(message2)
if all([type(arg) == dataType for arg in args]):
return fun(*args, **kwargs)
return "Invalid Input"
return wrapper
return decorator
@decodecorator(str, "Decorator for 'stringJoin'", "stringJoin started ...")
def stringJoin(*args):
st = ''
for i in args:
st += i
return st
@decodecorator(int, "Decorator for 'summation'\n", "summation started ...")
def summation(*args):
summ = 0
for arg in args:
summ += arg
return summ
print(stringJoin("I ", 'like ', "Geeks", 'for', "geeks"))
print()
print(summation(19, 2, 8, 533, 67, 981, 119))
|
Output:
Decorator for 'stringJoin'
Decorator for 'summation'
stringJoin started ...
I like Geeksforgeeks
summation started ...
1729
1. Inside the Decorator
2. Inside the function
Note: Image snapshots are taken using PythonTutor.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...