Count of Root to Leaf Paths consisting of at most M consecutive Nodes having value K
Last Updated :
19 Jan, 2022
Given an Acyclic Undirected Graph in the form of a Binary Tree with the root at vertex 1 and values at each vertex [1, N] denoted by the array arr[], the task is to find the number of root to leaf paths that contain at most m consecutive nodes with value K.
Example:
Input: arr[] = {1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0}, K = 1, M = 2
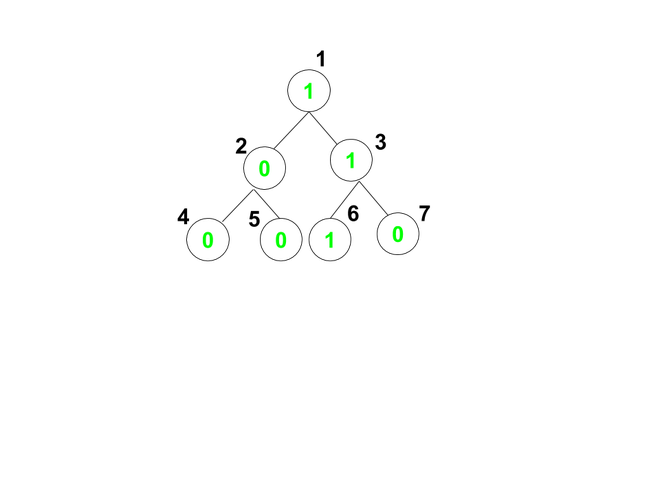
Output: 3
Explanation:
Path 1 : 1 -> 2 -> 4 contains maximum 1 consecutive K
Path 2 : 1 -> 2 -> 5 contains maximum 1 consecutive K
Path 3 : 1 -> 3 -> 6 contains maximum 3 consecutive K
Path 4 : 1 -> 3 -> 7 contains maximum 2 consecutive K
Since the given value of M is 2, therefore there are 3 paths that contains atmost 2 consecutive K.
Input: arr[] = {2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1, 4, 3, 5, 2}, K = 2, M = 2
2
/ \
1 3
/ \ / \
2 1 2 1
/ \ / \
4 3 5 2
Output: 3
Approach:
The problem can be solved using the Depth First Search approach:
- Depth First Search can be used to traverse all the paths from the root vertex.
- Every time, if the value at the present node is K, increment the count.
- Otherwise, set the count to 0.
- If the count exceeds M, then return.
- Otherwise, traverse its neighboring nodes and repeat the above steps.
- Finally, print the value of the count obtained.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
vector<int> adj[100005];
int visited[100005] = { 0 };
int ans = 0;
void dfs(int node, int count, int m,
int arr[], int k)
{
visited[node] = 1;
if (arr[node - 1] == k) {
count++;
}
else {
count = 0;
}
if (count > m) {
return;
}
if (adj[node].size() == 1 && node != 1) {
ans++;
}
for (auto x : adj[node]) {
if (!visited[x]) {
dfs(x, count, m, arr, k);
}
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int N = 7, K = 2, M = 2;
adj[1].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(1);
adj[1].push_back(3);
adj[3].push_back(1);
adj[2].push_back(4);
adj[4].push_back(2);
adj[2].push_back(5);
adj[5].push_back(2);
adj[3].push_back(6);
adj[6].push_back(3);
adj[3].push_back(7);
adj[7].push_back(3);
int counter = 0;
dfs(1, counter, M, arr, K);
cout << ans << "\n";
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG{
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
static Vector<Integer> []adj = new Vector[100005];
static int []visited = new int[100005];
static int ans = 0;
static void dfs(int node, int count, int m,
int arr[], int k)
{
visited[node] = 1;
if (arr[node - 1] == k)
{
count++;
}
else
{
count = 0;
}
if (count > m)
{
return;
}
if (adj[node].size() == 1 && node != 1)
{
ans++;
}
for(int x : adj[node])
{
if (visited[x] == 0)
{
dfs(x, count, m, arr, k);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int N = 7, K = 2, M = 2;
for(int i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = new Vector<Integer>();
adj[1].add(2);
adj[2].add(1);
adj[1].add(3);
adj[3].add(1);
adj[2].add(4);
adj[4].add(2);
adj[2].add(5);
adj[5].add(2);
adj[3].add(6);
adj[6].add(3);
adj[3].add(7);
adj[7].add(3);
int counter = 0;
dfs(1, counter, M, arr, K);
System.out.print(ans + "\n");
}
}
|
Python3
adj = [[] for i in range(100005)]
visited = [ 0 for i in range(100005)]
ans = 0;
def dfs(node, count, m, arr, k):
global ans
visited[node] = 1;
if (arr[node - 1] == k):
count += 1;
else:
count = 0;
if (count > m):
return;
if (len(adj[node]) == 1 and node != 1):
ans += 1
for x in adj[node]:
if (not visited[x]):
dfs(x, count, m, arr, k);
if __name__ == "__main__":
arr = [2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1]
N = 7
K = 2
M = 2
adj[1].append(2);
adj[2].append(1);
adj[1].append(3);
adj[3].append(1);
adj[2].append(4);
adj[4].append(2);
adj[2].append(5);
adj[5].append(2);
adj[3].append(6);
adj[6].append(3);
adj[3].append(7);
adj[7].append(3);
counter = 0;
dfs(1, counter, M, arr, K);
print(ans)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG{
static List<int> []adj = new List<int>[100005];
static int []visited = new int[100005];
static int ans = 0;
static void dfs(int node, int count, int m,
int []arr, int k)
{
visited[node] = 1;
if (arr[node - 1] == k)
{
count++;
}
else
{
count = 0;
}
if (count > m)
{
return;
}
if (adj[node].Count == 1 && node != 1)
{
ans++;
}
foreach(int x in adj[node])
{
if (visited[x] == 0)
{
dfs(x, count, m, arr, k);
}
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []arr = { 2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 };
int K = 2, M = 2;
for(int i = 0; i < adj.Length; i++)
adj[i] = new List<int>();
adj[1].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(1);
adj[1].Add(3);
adj[3].Add(1);
adj[2].Add(4);
adj[4].Add(2);
adj[2].Add(5);
adj[5].Add(2);
adj[3].Add(6);
adj[6].Add(3);
adj[3].Add(7);
adj[7].Add(3);
int counter = 0;
dfs(1, counter, M, arr, K);
Console.Write(ans + "\n");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let adj = new Array(100005);
let visited = new Array(100005);
visited.fill(0);
let ans = 0;
function dfs(node, count, m, arr, k)
{
visited[node] = 1;
if (arr[node - 1] == k)
{
count++;
}
else
{
count = 0;
}
if (count > m)
{
return;
}
if (adj[node].length == 1 && node != 1)
{
ans++;
}
for(let x = 0; x < adj[node].length; x++)
{
if (visited[adj[node][x]] == 0)
{
dfs(adj[node][x], count, m, arr, k);
}
}
}
let arr = [ 2, 1, 3, 2, 1, 2, 1 ];
let K = 2, M = 2;
for(let i = 0; i < adj.length; i++)
adj[i] = [];
adj[1].push(2);
adj[2].push(1);
adj[1].push(3);
adj[3].push(1);
adj[2].push(4);
adj[4].push(2);
adj[2].push(5);
adj[5].push(2);
adj[3].push(6);
adj[6].push(3);
adj[3].push(7);
adj[7].push(3);
let counter = 0;
dfs(1, counter, M, arr, K);
document.write(ans + "</br>");
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(V + E)
Auxiliary Space: O(V)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...