Cladding in Fiber Optics
Last Updated :
24 Jun, 2022
Cladding is a layer of material with a lower refractive index that covers the core of a fiber optic cable. The core of the fiber optic cable is of a higher refractive index than the cladding around it.
Refractive Index of a Medium:
The Refractive Index of a Medium is a ratio between the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in the medium.
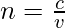
where c is the speed of light in a vacuum, v is the speed of light in the medium, and n is the Refractive Index of the medium.
The principle of data transfer through optic fiber cables is based on the phenomenon of Total Internal Reflection. When a light ray moves from a medium of higher refractive index into a medium of lower refractive index, it bends away from the normal. The normal is a perpendicular dropped to the surface boundary of the two media at the point at which the light ray meets the surface boundary. Visually:
Here, α is the Angle of Incidence and β is the Angle of Refraction. They are mathematically related as follows:
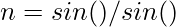
As the value of angle of incidence increases, the value of angle of refraction also increases. This phenomenon continues until the angle of refraction (β) becomes 90 degrees. If the angle of incidence is increased any further, the light ray reflects back into the same medium it emerged from. This is the phenomenon of Total Internal Reflection.
The condition for Total Internal Reflection is given by 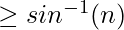
When 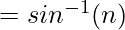 the light ray grazes the Surface Boundary, this angle α, is called the Critical Angle. But when
the light ray grazes the Surface Boundary, this angle α, is called the Critical Angle. But when 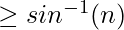 the light gets reflected back into the medium with a higher Refractive Index, as shown in the figure below:
the light gets reflected back into the medium with a higher Refractive Index, as shown in the figure below:
The cladding ensures that the optical signals being transmitted by the optical fiber cable remain confined to the core and do not get dissipated when the signal travels a long distance. This is how the cladding helps the optical signals be confined to the core:
Advantages:
- Glass fiber, the typical material from which the core of the Optical Fiber Cable is made may have some irregularities which dissipate the optical signal and lessen the travel distance of the signal. Cladding reduces this dissipation to the minimum.
- It provides added strength and durability to the Optical Fiber Cable.
- With the use of cladding, the diameter of the cores can be reduced to a great extent.
Disadvantages:
- Professional aid might be needed for splicing and joining two Optical Fiber Cables together.
- Optical Fibre may fail if the cladding is damaged to a certain extent.
So, Cladding is the optically rarer material surrounding the optically denser core of the Optical Fiber Cable in order to exploit the phenomena of Total Internal Reflection for better signal transmission over long distances.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...