Check if a number N starts with 1 in b-base
Last Updated :
20 Feb, 2023
Given a number N and base b if N in base b representation starts with 1 print Yes else print No
Examples :
Input : n = 6, b = 4
Output : Yes
6 can be written as 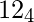 in base 4so answer is Yes as it starts with 1Input : n = 24, b = 2Output : Yes24 can be written as
in base 4so answer is Yes as it starts with 1Input : n = 24, b = 2Output : Yes24 can be written as 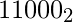 in base 2so answer is Yes as it starts with 1Input : n = 24, b = 7Output : No24 can be written as
in base 2so answer is Yes as it starts with 1Input : n = 24, b = 7Output : No24 can be written as 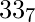 in base 7so answer is No as it starts with 3
in base 7so answer is No as it starts with 3
When a number N is represented in base ‘b’ it gets converted to m+1 length sequence 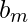 [Tex]b_{m-1} [/Tex]…..
[Tex]b_{m-1} [/Tex]…..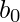 which implies
which implies 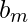 *
*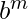 +
+ 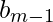 *
*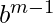 …..+
…..+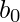 *
*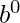 = N
= N
The smallest number in base b and starting with ‘1’ i.e. 100..00 and m+1 digits in base is 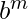
and largest number is 2*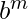 -1.So N should lie in this range.
-1.So N should lie in this range.
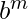 <= N <= 2*
<= N <= 2*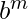 -1
-1
Now another thing to notice is that m cannot exceed floor(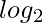 (N)) because when we represent any number in base-2 it gets converted into a sequence of only 1s and 0s so the length of this sequence will always be greater than any other base representation and its length will be equal to floor(
(N)) because when we represent any number in base-2 it gets converted into a sequence of only 1s and 0s so the length of this sequence will always be greater than any other base representation and its length will be equal to floor(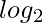 (N))+1.
(N))+1.
So to check for a given base ‘b’ if N starts with 1 or not we will traverse from m = 1 to m = floor(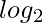 (N)) and check if for any m N lies in the range
(N)) and check if for any m N lies in the range 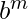 <= N <= 2*
<= N <= 2*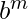 -1 or not and accordingly print “Yes” or “No”.
-1 or not and accordingly print “Yes” or “No”.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
bool CheckIfstartsWithOne(int n, int b)
{
int m = log2(n);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
if (n >= pow(b, i) && n <= 2 * pow(b, i) - 1)
return true;
}
return false;
}
void printYesORno(int n, int b)
{
if (CheckIfstartsWithOne(n, b) == true)
cout << "Yes" << endl;
else if (CheckIfstartsWithOne(n, b) == false)
cout << "No" << endl;
}
int main()
{
printYesORno(6, 4);
printYesORno(24, 2);
printYesORno(24, 7);
printYesORno(24, 15);
}
|
Java
class GFG {
static boolean CheckIfstartsWithOne(int n, int b)
{
int m = (int)(Math.log10(n) / Math.log10(2));
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
if (n >= (int)Math.pow(b, i) &&
n <= 2 * (int)Math.pow(b, i) - 1)
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println(
CheckIfstartsWithOne(6, 4) ? "Yes" : "No");
System.out.println(
CheckIfstartsWithOne(24, 2) ? "Yes" : "No");
System.out.println(
CheckIfstartsWithOne(24, 7) ? "Yes" : "No");
System.out.println(
CheckIfstartsWithOne(24, 15) ? "Yes" : "No");
}
}
|
Python3
import math
def CheckIfstartsWithOne(n, b):
m = (int)(math.log2(n));
for i in range (1, m + 1):
x = (int)(math.pow(b, i));
if n >= x and n <= 2 * x - 1:
return 1;
return 0;
def printYesORno(n, b):
if CheckIfstartsWithOne(n, b) == 1:
print("Yes");
if CheckIfstartsWithOne(n, b) == 0:
print("No");
printYesORno(6, 4);
printYesORno(24, 2);
printYesORno(24, 7);
printYesORno(24, 15);
|
C#
using System;
class GFG{
static bool CheckIfstartsWithOne(int n, int b)
{
int m = (int)(Math.Log10(n) / Math.Log10(2));
for(int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
if (n >= (int)Math.Pow(b, i) &&
n <= 2 * (int)Math.Pow(b, i) - 1)
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void Main(String []args)
{
Console.WriteLine(
CheckIfstartsWithOne(6, 4) ? "Yes" : "No");
Console.WriteLine(
CheckIfstartsWithOne(24, 2) ? "Yes" : "No");
Console.WriteLine(
CheckIfstartsWithOne(24, 7) ? "Yes" : "No");
Console.WriteLine(
CheckIfstartsWithOne(24, 15) ? "Yes" : "No");
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function CheckIfstartsWithOne($n, $b)
{
$m = log($n, 2);
for ($i = 1; $i <= $m; $i++)
{
if ($n >= pow($b, $i) &&
$n <= 2 * pow($b, $i) - 1)
return true;
}
return false;
}
function printYesORno($n, $b)
{
if (CheckIfstartsWithOne($n, $b) == true)
echo "Yes" ,"\n";
else if (CheckIfstartsWithOne($n, $b) == false)
echo "No" ,"\n";
}
printYesORno(6, 4);
printYesORno(24, 2);
printYesORno(24, 7);
printYesORno(24, 15);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function CheckIfstartsWithOne(n, b)
{
let m = parseInt(Math.log10(n) / Math.log10(2), 10);
for (let i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
if (n >= Math.pow(b, i) && n <= 2 * Math.pow(b, i) - 1)
return true;
}
return false;
}
document.write(CheckIfstartsWithOne(6, 4) ? "Yes" + "</br>" : "No" + "</br>");
document.write(CheckIfstartsWithOne(24, 2) ? "Yes" + "</br>" : "No" + "</br>");
document.write(CheckIfstartsWithOne(24, 7) ? "Yes" + "</br>" : "No" + "</br>");
document.write(CheckIfstartsWithOne(24, 15) ? "Yes" : "No");
</script>
|
Output :
Yes
Yes
No
Yes
Time Complexity: O(m), where m is calculated as log2(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1), as no extra space is required
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...