Check if an integer can be expressed as a sum of two semi-primes
Last Updated :
16 Feb, 2023
Given a positive integer N, check if it can be expressed as a sum of two semi-primes or not.
Semi-primes A number is said to be a semi-prime if it can be expressed as product of two primes number ( not necessarily distinct ).
Semi-primes in the range 1 -100 are:
4, 6, 9, 10, 14, 15, 21, 22, 25, 26, 33, 34, 35, 38, 39, 46, 49, 51, 55, 57, 58, 62, 65, 69, 74, 77, 82, 85, 86, 87, 91, 93, 94, 95.
Examples:
Input : N = 30
Output: YES
Explanation: 30 can be expressed as '15 + 15'
15 is semi-primes as 15 is a product of two primes 3 and 5.
Input : N = 45
Output : YES
Explanation: 45 can be expressed as '35 + 10'
35 and 10 are also semi-primes as it can a be expressed
as product of two primes:
35 = 5 * 7
10 = 2 * 5
Prerequisite:
A Simple Solution is to traverse from i=1 to 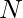 and check if i and N-i are semi-primes or not. If yes, print i and n-i.
and check if i and N-i are semi-primes or not. If yes, print i and n-i.
An Efficient Solution is to pre-compute semi-primes in an array up to the given range and then traverse the semi-prime array and check if n-arr[i] is semi-prime or not. As, arr[i] is already a semi-prime if n-arr[i] is also a semi-prime, then n can be expressed as sum of two semi-primes.
Below is the implementation of above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 1000000
vector<int> arr;
bool sprime[MAX];
void computeSemiPrime()
{
memset(sprime, false, sizeof(sprime));
for (int i = 2; i < MAX; i++) {
int cnt = 0;
int num = i;
for (int j = 2; cnt < 2 && j * j <= num; ++j) {
while (num % j == 0) {
num /= j, ++cnt;
}
}
if (num > 1)
++cnt;
if (cnt == 2) {
sprime[i] = true;
arr.push_back(i);
}
}
}
bool checkSemiPrime(int n)
{
int i = 0;
while (arr[i] <= n / 2) {
if (sprime[n - arr[i]]) {
return true;
}
i++;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
computeSemiPrime();
int n = 30;
if (checkSemiPrime(n))
cout << "YES";
else
cout << "NO";
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static final int MAX = 1000000;
static Vector<Integer> arr = new Vector<>();
static boolean[] sprime = new boolean[MAX];
static void computeSemiPrime()
{
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
sprime[i] = false;
for (int i = 2; i < MAX; i++) {
int cnt = 0;
int num = i;
for (int j = 2; cnt < 2 && j * j <= num; ++j) {
while (num % j == 0) {
num /= j;
++cnt;
}
}
if (num > 1)
++cnt;
if (cnt == 2) {
sprime[i] = true;
arr.add(i);
}
}
}
static boolean checkSemiPrime(int n)
{
int i = 0;
while (arr.get(i) <= n / 2) {
if (sprime[n - arr.get(i)]) {
return true;
}
i++;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
computeSemiPrime();
int n = 30;
if (checkSemiPrime(n))
System.out.println("YES");
else
System.out.println("NO");
}
}
|
Python3
MAX = 10000
arr = []
sprime = [False] * (MAX)
def computeSemiPrime():
for i in range(2, MAX):
cnt, num, j = 0, i, 2
while cnt < 2 and j * j <= num:
while num % j == 0:
num /= j
cnt += 1
j += 1
if num > 1:
cnt += 1
if cnt == 2:
sprime[i] = True
arr.append(i)
def checkSemiPrime(n):
i = 0
while arr[i] <= n // 2:
if sprime[n - arr[i]] == True:
return True
i += 1
return False
if __name__ == "__main__":
computeSemiPrime()
n = 30
if checkSemiPrime(n) == True:
print("YES")
else:
print("NO")
|
C#
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int MAX = 1000000;
static List<int> arr = new List<int>();
static bool[] sprime = new bool[MAX];
static void computeSemiPrime()
{
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
sprime[i] = false;
for (int i = 2; i < MAX; i++)
{
int cnt = 0;
int num = i;
for (int j = 2; cnt < 2 && j * j <= num; ++j)
{
while (num % j == 0)
{
num /= j;
++cnt;
}
}
if (num > 1)
++cnt;
if (cnt == 2)
{
sprime[i] = true;
arr.Add(i);
}
}
}
static bool checkSemiPrime(int n)
{
int i = 0;
while (arr[i] <= n / 2)
{
if (sprime[n - arr[i]])
{
return true;
}
i++;
}
return false;
}
public static void Main()
{
computeSemiPrime();
int n = 30;
if (checkSemiPrime(n))
System.Console.WriteLine("YES");
else
System.Console.WriteLine("NO");
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var MAX = 1000000;
var arr = [];
var sprime = Array(MAX).fill(false);
function computeSemiPrime()
{
for (var i = 2; i < MAX; i++) {
var cnt = 0;
var num = i;
for (var j = 2; cnt < 2 && j * j <= num; ++j) {
while (num % j == 0) {
num /= j, ++cnt;
}
}
if (num > 1)
++cnt;
if (cnt == 2) {
sprime[i] = true;
arr.push(i);
}
}
}
function checkSemiPrime(n)
{
var i = 0;
while (arr[i] <= parseInt(n / 2)) {
if (sprime[n - arr[i]]) {
return true;
}
i++;
}
return false;
}
computeSemiPrime();
var n = 30;
if (checkSemiPrime(n))
document.write( "YES");
else
document.write( "NO");
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(MAX*log(log(MAX)))
Auxiliary Space: O(MAX)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...