Heat engines are those engines that convert thermal energy into mechanical work and enhance many aspects of modern life. Heat engines works on the principle of thermodynamics. Heat engines are used in power plants, cars, trains etc. In this article, we will learn in detail about the different functions of heat engine in real life.
What are Heat Engines?
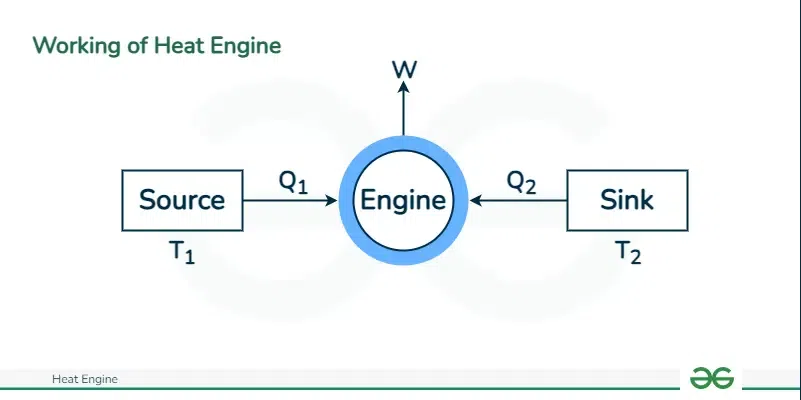
Heat engines are devices that convert heat energy into mechanical work. They operate by transferring thermal energy from a heat source to a heat sink, utilizing the temperature difference between the two. The heat input causes a working fluid, such as gas or steam, to expand and perform work on a piston or turbine, which can then be used to drive machinery or generate electricity. Heat engines play a crucial role in various applications, including power generation, transportation, and industrial processes.
Characteristics of Heat engines
Some characteristics of heat engines are:
- Heat engines require a temperature difference between a heat source and a heat sink to operate. Thermal energy is taken in from the heat source and waste heat is released to the heat sink.
- Working fluids like air, gases, or steam transfer heat energy into mechanical work in heat engines, chosen based on factors like application needs and operating conditions.
- Thermodynamic cycles describe how working fluids convert heat to mechanical work in heat engines.
- Heat engine efficiency, the ratio of useful work output to heat input, depends on the working fluid’s properties, engine design, and operating conditions.
- Heat engines primarily produce mechanical work used for powering equipment, generating electricity, and propelling vehicles, influenced by factors like engine size, design, temperature differences, and cycle efficiency.
Applications of Heat Engines in Real-Life
Heat engines are devices that convert thermal energy (heat) into mechanical work through a cyclic process. They play a crucial role in various real-life applications, powering many devices and systems that we rely on daily. Here are some common applications of heat engines:
Power Generation
Power generation is one of the main uses for heat engines. One kind of heat engine that is essential to the production of energy in power plants is the steam turbine. These turbines use the steam created when water boils to power generators, which generate electricity.
Steam Turbines in Coal-Fired Power Plants: The heat engine used to produce electricity is the steam turbine, which is mostly seen in coal-fired power stations. These plants use the energy generated by burning coal to heat water and create steam. Turbines that generate electricity under high pressure from steam power electrical generators. Through the conversion of heat energy from the burning of coal into mechanical work and eventually electrical energy, the process demonstrates the basic ideas of thermodynamics.
Gas Turbines in Combined Cycle Power Plants: Compressing air, combining it with fuel, and igniting the combination results in high-pressure exhaust gases that turn turbine blades to provide mechanical energy. Combined cycle facilities combine steam and gas turbines, producing steam for additional power by using waste heat from gas turbine exhaust, thereby increasing total efficiency.
Automotive Engines
Another major use for heat engines is in internal combustion engines, which are found in Automotive Engines like cars, motorbikes, and other vehicles. Through combustion, the chemical energy contained in fuel is transformed into mechanical energy in these engines, which powers pistons to produce motion. The ability to move around and travel is what makes modern society run.
Internal Combustion Engines in Passenger Vehicles: The operation of passenger cars requires internal combustion engines. In order to produce power, these engines burn a mixture of fuel and air inside cylinders. The pistons descend in a predetermined order as a result of the fuel-air mixture’s quick expansion during combustion. There are several types of internal combustion engines, such as petrol and diesel engines.
Hybrid Powertrains in Modern Automobiles: In a hybrid car, two engines cooperate to generate power. The two engines run on petrol, as in a real car and the other one’s powered by electricity just like that toy car. When the car is started, or has to be accelerated, the power of the electricity engine will give you a boost that makes driving smooth and comfortable. But in order to maintain proper operation, while driving quickly or carrying large objects, the petrol engine come into effect.
Aircraft Propulsion
Heat engines used in most Airplane are called jet engines. They are made for propulsion. In order to produce thrust, these engines take in air, compress it, combine it with fuel, light the mixture, and then quickly release the exhaust gases that follow.
Jet Engines in Commercial Aircraft: The main source of aircraft control in commercial aviation is the fly engines. These engines pull in air, compress it, combine it with fuel, fire the blend, and at that point quickly discharge the coming about exhaust gasses to create pushed. The drive moves the flying machine forward, allowing it to break through the discussion of resistance and continue to fly. Commercial air carriers are able to carry passengers and cargo across long distances at fast speed due to the viability and limited capacity of jet engines.
Turbofan Engines in Modern Jets: Turbofan engines are the most popular type of jet engine used in modern aircraft, especially for commercial Airplane and certain military planes. The enormous fan in the front of these engines creates two streams of airflow: one stream enters the engine’s core for combustion and another exits to produce more thrust. This double airflow arrangement is improving overall performance, reducing noise levels and increasing fuel efficiency.
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
Air conditioning and refrigeration systems also use heat engines. One kind of heat engine that effectively cools a target space is a heat pump, which transfers heat from a colder environment to a warmer one. These systems are essential for controlling industrial processes that require precise temperatures, preserving food, and keeping buildings comfortable.
Vapor Compression Refrigeration : Vapor compression technique, which is found in home refrigerators, is frequently used in air conditioning and refrigeration systems. In order to absorb and release heat, these systems work by pumping a refrigerant through a closed loop and passing through phase shifts. Condensation coils at the back or bottom of the appliance are where the heat is released from the refrigerator after the refrigerant cools the contents by absorbing heat from the interior.
Air Conditioning Systems in Commercial Buildings: Air conditioning equipment plays a major role in maintaining interior comfort and temperature control in offices, commercial buildings, and other big spaces. Typically, these systems employ vapor compression technology, which uses refrigerants to transport heat from the inside air outside while cooling the inside space.
Marine Propulsion
Heat engines are a common propulsion method used by marine vessels to navigate across expanses of water. Although gas turbines or diesel engines are more frequently found in modern ships, steam engines were previously very common in ships. By converting heat energy from the combustion of fuel into mechanical work, these engines enable the vessel to move ahead by powering propellers.
Diesel Engines in Cargo Ships: Diesel engines are common in marine drive frameworks, which are used for moving ships over expansive bodies of water. Diesel engines are broadly utilized by cargo ships to move items and commodities over oceans and seas since of their steadfastness, proficiency, and flexibility. Diesel fuel is burned in barrels by diesel motors that powers the ship’s propeller. These motors are perfect for the huge weights and long trips of cargo ships since they give impressive torque at direct speeds.
Gas Turbines in Naval Vessels: Another well-known example of a marine propulsion system is a gas turbine, which is often found in naval ships like cruisers and destroyers. For military and defensive activities, these vessels need propulsion systems that can give high speeds. Gas turbines provide notable power-to-weight ratios and quick acceleration, enabling naval ships to move quickly in a variety of marine conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heat engines play a vital role across various sectors, providing mechanical work from heat energy. They are integral to power generation, facilitating electricity supply to infrastructure, businesses, and homes. Automotive engines enable mobility and transportation, while jet engines power commercial flights, fostering global connectivity and trade. Also, heat engines support air conditioning and refrigeration systems, crucial for food preservation, comfort, and industrial processes.
Also, Check
FAQs on Applications of Heat Engines
How do heat engines differ from other types of engines?
Heat engines differ from other types of engines such as electric motors or hydraulic engines in that they particularly use the principles of thermodynamics to turn heat energy into mechanical work.
What factors affect the efficiency of a heat engine?
Heat engine efficiency is influenced by a number of variables, such as the working fluid type, engine component design and material composition, and the temperature differential between the heat source and sink.
Are heat engines environmental friendly?
Heat engines are useful devices, but they also release pollutants and greenhouse gases into the atmosphere since they frequently burn fossil fuels. The development of greener, more sustainable substitutes, like enhanced engine technologies and renewable energy sources, is now under progress.
Can Heat engines operate without external heat sources?
Since heat engines rely on the transfer of heat from a high-temperature reservoir to a low-temperature reservoir in order to operate, they need a heat source. But because to developments in thermoelectric materials, waste heat may now be converted into energy without burning.
How do heat engines contribute to energy efficiency?
Heat engines are essential to energy conversion processes because they make it possible to use heat energy effectively for a variety of purposes, including power generation, transportation, and heating and cooling systems. Energy efficiency can be improved, lowering resource consumption and environmental effect, by optimising their design and operation.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...