What is Net Promoter Score in Product Management?
Last Updated :
02 Feb, 2024
The Net Promoter Score (NPS) is an important component of that serves as a growth indicator. This metric, which serves as a measure of customer loyalty, is incorporated into the process of developing new products. Let’s look at how Net Promoter Score and Product Management interact, and how customer feedback can be used to create products that connect.
.jpg)
What is Net Promoter Score
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a metric used to assess a company’s customer loyalty, satisfaction, and enthusiasm. It is calculated by asking customers one question: “On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend this product/company to a friend or colleague?” Aggregate NPS scores assist businesses in improving service, customer support, delivery, and so on to increase customer loyalty. However, organizations must ensure that NPS surveys do not feel forced, and they should not be the only metric used to determine customer loyalty.
Fred Reichheld, a Bain & Company consultant, developed the Net Promotor Score (NPS) in 2003.

NPS Score
NPS can be used to forecast business growth. When your company’s NPS is high (or, at the very least, higher than the industry average), you know you have a healthy relationship with customers who are likely to act as brand evangelists, fuel word of mouth, and create a positive growth cycle.
On a strategic level, NPS is a valuable metric, but the score alone is insufficient to be useful or paint a complete picture. The NPS system as a whole is important because it enables businesses to:
- As part of the standard NPS survey, ask follow-up questions. Organizations of any size can learn what they’re doing well and where they can improve by asking customers why they gave a specific score.
- Create internal benchmarks by tracking and quantifying a score over time.
- Gather all employees around a single mission-critical goal: gaining more enthusiastic customers.
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a valuable metric for businesses of all sizes, but it is particularly important for product managers.
Here are some of the reasons why NPS is so important for product management:

Importance of Net Promoter Score
- Measures customer loyalty: Net Promoter Score is a quick and easy approach for evaluating how devoted your clients are to your service or product. While detractors are more inclined to spread unfavourable rumours, promoters are more likely to tell others about your goods. may identify patterns in customer loyalty and enhance the product by monitoring NPS over time.
- Provides insights into customer satisfaction: Customer satisfaction may also be obtained through the Net Promoter Score. It is common for detractors to be unhappy with your goods, whereas promoters are usually happy. Product managers might find opportunities for product enhancement by analysing the reasons behind customer’s low NPS rankings.
- Helps prioritise product development efforts: Product managers may focus their efforts on developing new products by using NPS. Product managers may maximise their time and resources by concentrating on products and enhancements that are most likely to raise NPS.
- Measures the impact of marketing campaigns: Net Promoter Score is a useful metric for evaluating marketing campaign effectiveness. Product managers may determine whether a promotion has a beneficial effect on customer loyalty by monitoring NPS before and after the campaign.
- Improves communication between product and marketing teams: The product and marketing teams can communicate more effectively thanks to NPS. Teams may collaborate to make sure the product is fulfilling consumer demands by exchanging NPS data.
How to calculate NPS?
The percentage of detractors is subtracted from the percentage of promoters to get the NPS score. The NPS score might be 50, for example, if 60% of consumers are promoters and 10% are detractors.
Here is the formula for calculating NPS:
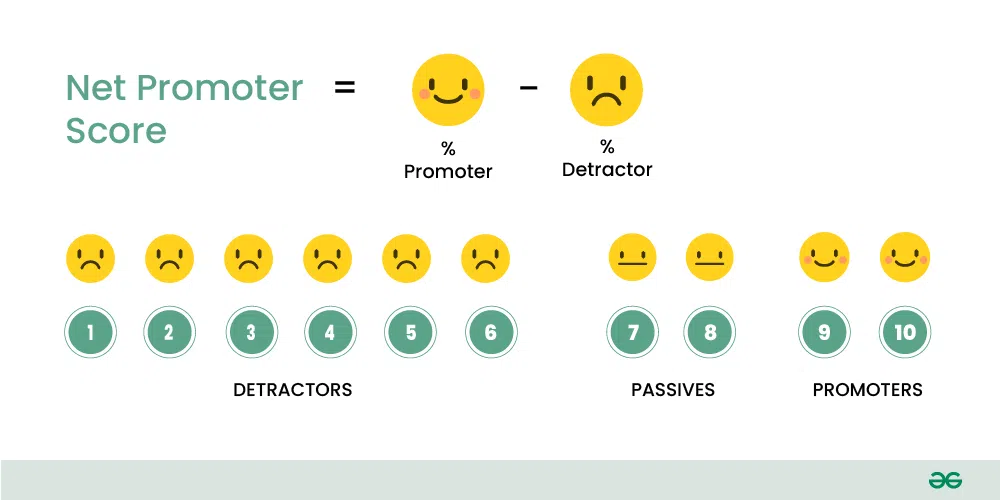
formula for calculating NPS
NPS = % Promoters – % Detractors
NPS scores can range from -100 to 100. A score of 100 would mean that all customers are promoters, while a score of -100 would mean that all customers are detractors. A score of 0 would mean that the number of promoters and detractors is equal.
Here is a table that shows how NPS scores are interpreted:
|
Excellent
|
|
Good
|
|
Neutral
|
|
Poor
|
|
Very poor
|
The Net Promoter Score (NPS) scale categorizes respondents into three groups based on their ratings to the “How likely is it that you would recommend our product/service/company to a friend or colleague?” question. Here are the three segments:

Net Promoter Score scale
- Promoters (Score 9-10):
- Customers who are highly satisfied with the product or service.
- They are likely to be loyal customers and enthusiastic advocates.
- Promoters are crucial for positive word-of-mouth marketing and can contribute to the growth of the customer base.
- Passives (Score 7-8):
- Customers who are moderately satisfied but not overly enthusiastic.
- They may not actively promote the product or service but are also not likely to actively discourage others.
- Passives are considered neutral and may be susceptible to competitive offerings.
- Detractors (Score 0-6):
- Customers who are dissatisfied with the product or service.
- Detractors may express negative opinions, potentially harming the brand’s reputation.
- Identifying and addressing the concerns of detractors is crucial for preventing customer churn and negative impact on the business.
Analyzing Net Promoter Score (NPS) involves a comprehensive approach that goes beyond simply calculating the overall score. NPS responses can be analyzed by tracking changes to the score over time, tagging and classifying responses that are undefined, visualizing the data on a dashboard, and doing a root cause analysis.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to effectively analyzing NPS:
- Determine and monitor your NPS rating: Find out what proportion of your responses are promoters (scores 9–10), passives (scores 7-8), and critics (scores 0-6). To find your NPS score, subtract the percentage of critics from the percentage of supporters. Monitor trends in consumer sentiment by tracking this score over time.
- Divide up your data: Sort your NPS data by customer demographics, product usage trends, or acquisition methods, for example. This segmentation aids in locating possible problems or targeted areas for improvement within certain clientele.
- Examine input from supporters and detractors: Examine the open-ended comments from supporters and critics with great attention. To determine the underlying causes of their ratings, look for recurring themes and patterns in their answers.
- Determine the main reasons and motivators: Examine the comments made by supporters and critics to ascertain the main factors affecting their NPS ratings. Investigate further to identify the underlying factors influencing these drivers, such as particular product attributes, negative customer service encounters, or price problems.
How to create a NPS survey?
The simplest NPS survey would simply ask, “On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend us to a friend or colleague?” Surveys, on the other hand, can be supplemented with additional questions that provide greater insight into customer motivations.
Typical additional survey questions include the following:
- Age and gender demographic questions. Because scores may differ across demographics, asking these questions can help a company better understand customer loyalty across audience segments.
- A question asking the “Reason for your score.” This is normally an open-ended question asking the individual the reason behind why they gave that numerical score.
- Ask “How could we improve?”
- A question asking for permission to follow up with the customer as needed.
The survey can be emailed to a customer or displayed on a webpage or in a popup. NPS can be tracked by organizations using customer experience management or NPS software, which should be updated on a regular basis.
How to run surveys and collect NPS feedback?
- Website Survey: If you’re considering running a survey on your website, it can be a valuable tool for gathering feedback, understanding user preferences, and improving the overall user experience.
- Email Survey: Running email surveys to collect Net Promoter Score (NPS) feedback involves a few key steps. Clearly outline the goals of your survey. What specific information are you trying to gather? Whether it’s product feedback, customer satisfaction, or insights for improvement, having clear objectives will guide your survey design. Choose a reliable survey platform to create and distribute your email survey. Create a survey that includes the Net Promoter Score question along with any additional questions you may have. Consider the template provided in a previous response for the NPS email survey.
NPS analysis is a crucial step to gauge customer loyalty, identify improvement areas, and foster customer satisfaction. By carefully analyzing feedback, prioritizing initiatives, and incorporating NPS into the customer experience journey, businesses can effectively leverage NPS to drive growth.
What is a good NPS score?
An NPS score above 0 is considered good, but above 20 is excellent, and above 50 is remarkable, according to Bain & Company, the company that developed the NPS metric. The top percentile is anywhere above 80. It’s crucial to remember that a high NPS score varies depending on whether the absolute or relative NPS approach is being used.
What is NPS and CSAT?
The primary difference between Net Promoter Score (NPS) and Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) is that NPS is used to assess long-term customer happiness and loyalty, whereas CSAT is typically used to measure short-term customer loyalty.
Who has the highest NPS score?
- Princeton Mortgage, NPS score = 98
- Tesla, NPS score = 97
- Nutanix, NPS score = 92
- Loanboox, NPS score = 90
- Nimble, NPS score = 85
Is CSAT better than NPS?
While CSAT assists in highlighting important, targeted areas for development, NPS provides a broad overview of customer satisfaction. CSAT is more effective in identifying interest areas, while NPS provides an overall business measurement.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...