Product strategy in product management is a strategic plan that aligns the product with overall business objectives. This article will examine the complexities of product design, including its definition, importance, characteristics, and critical factors. It will also discuss where product management fits into the development process and examine some effective business models.

What is Product Strategy?
What is a Product Strategy?
A product strategy is a comprehensive plan that outlines the long-term vision and direction for a product. It involves making informed decisions about what to build, for whom, and why. A well-crafted product strategy aligns with the company’s overall goals, market dynamics, and customer needs, providing a roadmap for successful product development and lifecycle management.
Types of Product Strategies
Product strategies can take various forms, depending on business goals and market conditions. Common types include:
1. Market Expansion Strategy:
This strategy involves the identification and entry into new markets or the expansion of the product’s footprint within existing markets. It aims to capitalize on untapped opportunities, broaden the customer base, and increase market share. By strategically positioning the product in diverse markets, companies can mitigate risks associated with dependence on single market segment foster overall business growth.
2. Innovation Strategy:
An innovation strategy centres around differentiating the product through groundbreaking technologies or unique features. By staying at the forefront of technological advancements, companies can create a competitive edge, attract early adopters, and continually captivate the market’s attention. This strategy not only addresses current market needs but also positions the product as a pioneer, driving long-term success.
3. Cost Leadership Strategy:
A cost leadership strategy focuses on becoming a low-cost provider, appealing to price-sensitive customers. By optimizing operational efficiency, reducing production costs, and offering competitive pricing, companies employing this strategy aim to capture a significant market share. This approach requires a meticulous focus on cost management while maintaining product quality to meet customer expectations.
4. Cost Intimacy Strategy:
The customer intimacy strategy prioritizes the establishment of robust relationships with customers. By understanding individual customer needs and preferences, companies can tailor products and services to create a personalized experience. This strategy fosters customer loyalty, repeat business, and positive word-of-mouth, ultimately differentiating the brand in a saturated market through a strong emotional connection with the customer.
5. Product Lifecycle Strategy:
Addressing the various stages of a product’s life, from introduction to decline, this strategy involves tailoring specific approaches for each phase. In the introduction phase, the focus may be on building awareness and establishing a market presence. During growth, efforts shift to maximizing market share, followed by maturity where emphasis turns to product differentiation. Finally, in the decline phase, strategies may include product diversification or gradual phasing out, ensuring a strategic response to the product’s lifecycle dynamics.
Why is Product Strategy Important?
1. Alignment with Business Goals:
- Ensures that the product development aligns with overall business objectives, fostering a cohesive organization vision.
2. Clarity and Direction:
- Provides a clear roadmap, guiding decision-making processes and ensuring a focused direction for the product.
3. Resource Optimization:
- Facilitates efficient resource allocation by prioritizing features and initiatives that align with strategic goals.
4. Risk Mitigation:
- Identifies potential risks and challenges, allowing teams to proactively develop strategies for risk mitigation.
5. Innovation and Adaptability:
- Encourages innovation and adaptability to changing market conditions, fostering a proactive and responsive approach.
A Product Strategy Template
1. Mission and Vision Statements:
Clearly articulate the overarching purpose (mission) and the long-term aspirations (vision) of the product, providing a guiding framework for development.
2. Target Market identification:
Define the specific market segments the product aims to serve, including demographics, psychographics, and any relevant characteristics that influence the target audience.
3. Competitive Analysis:
Understand the competitive landscape by analyzing key competitors, their strengths, weakness, market positioning, and any distinctive features they offer.
4. Value Proposition:
Clearly define what makes the product unique and valuable to customers. Highlight the key benefits that set it apart from alternatives in the market.
5. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs):
Identify measurable metrics that will gauge the success and performance of the product strategy. These could include sales targets, customer satisfaction scores, or market share percentages.
How to Create a Product Strategy?
Creating a product strategy involves several key steps:
1. Define Objectives: Clearly articulate the specific objectives and goals of the product. Objectives should be SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound) and closely aligned with the broader goals. This step sets the foundation for a focused and purpose-driven product strategy.
2. Market Analysis: Conduct a deep understanding of the target market. Understand customer demographics, preferences, and behaviors. Analyze the competitive landscape to identify key players, market trends, and potential opportunities or challenges. This step ensures the product strategy is informed by a deep understanding of the market dynamics.
3. SWOT Analysis: Perform a SWOT analysis to evaluate the internal Strengths and Weaknesses of the product and the external Opportunities and Threats in the market. This analysis provides a holistic view, guiding strategic decision-making by leveraging strengths, addressing weaknesses, seizing opportunities, and mitigating threats.
4. Value Proposition: Clearly define the unique that the product brings to customers. Identify what sets it apart from competitors and articulate the key benefits that resonate with the target audience. A compelling value proposition forms the core messaging that shapes the product’s positioning in the market.
5. Roadmap: Develop a roadmap outlines the product’s evolution overtime. Consider the phased release of features, enhancements, and improvements. This roadmap serves as a visual guide, aligning the team and stakeholders on the planned trajectory of the product. It incorporates feedback loops for continuous improvement.
6. KPIs: Identify key performance indicators (KPIs) that align with defined objectives. These metrics should be quantifiable and measurable, providing insights into the product’s success. KPIs could include sales figures, customer satisfaction scores, user adoption rates, or any other relevant metrics that gauge performance and impact.
Key Components of a Product Strategy
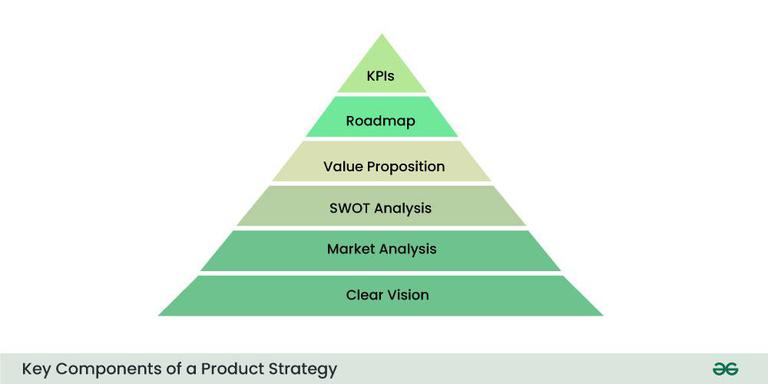
key components of product strategy
The key components of a product strategy are as follows:
1. Clear Vision: A concise and inspiring vision statement that defines the product’s purpose and direction. This overarching vision serves as a north star, guiding the team and aligning their efforts with the product’s long-term goals.
2. Target Market: Identification of the specific market segments the product aims to serve. Understanding the target audience’s needs, preferences, and behaviors is crucial for tailoring the product to meet customer expectations.
3. Value Proposition: Articulation of the unique value the product delivers to customers. The value proposition communicates why customers should choose the product over alternatives and highlights the key benefits that set it apart.
4. Competitive Analysis: Understanding the competitive landscape and positioning the product effectively. Analyzing competitors’ strengths and weaknesses helps in identifying opportunities for differentiation and crafting strategies that capitalize on the product’s unique selling points.
5. Execution Plan: A detailed plan outlining how the strategy will be implemented over time. This includes a roadmap that specifies the sequence of activities, milestones, and timelines for development, marketing, and other key aspects.
6. Risk Mitigation: Identification of potential risks and strategies to mitigate them. This component involves anticipating challenges that could impact the product’s success and developing contingency plans to address or minimize those risks.
Where Does Product Strategy in the Development Plan?
Product strategy is an integral part of the development plan, guiding decision-making from ideation to launch and beyond. It influences the product roadmap, features prioritization, and resource allocation at every stage of the development lifecycle. By aligning the product strategy with the development plan, teams ensure a cohesive and focused approach, maximizing the chances of success in the market.
Effective Product Strategy Business Models
Several business models complement effective product strategies:
1. Subscription Model: Generates recuring revenue through subscription-based access to the product or service. This model fosters customer loyalty and ensures a predictable stream of income, often incorporating tiered plans to cater to different user needs.
2. Freemium Model: Offers a basic product for free, enticing users to upgrade to a premium version with additional features or enhances capabilities. This model attracts a wide user base while monetizing through premium offerings.
3. Ecosystem Model: Builds an interconnected ecosystem of products or services that enhance each other value. This model encourages customer retention by providing a seamless experience across various offerings, creating brand stickiness.
4. Platform Model: Provides a platform for third-party developers to create complementary products or features. This model leverages network effects, allowing the platform to grow exponentially as more developers contribute to its ecosystem.
5. Agile Model: Embraces an iterative and flexible approach to product development. This model emphasizes rapid iterations, constant feedback loops, and responsiveness to changing market dynamics, ensuring adaptability and continuous improvement.
Product Strategy Examples
To illustrate these concept in practice, let’s examine a real-world product strategy examples.
1. Tesla
- Business Model: Ecosystem Model
- Tesla, the electric vehicle(EV) manufacturer, provides a compelling example an innovative and disruptive product strategy. Tesla’s strategy revolves around combining cutting-edge technology, sustainability, and a unique customer experience. By focusing on premium electric vehicles, Tesla has redefined the automotive industry. The company’s commitment to continuous innovation, such as the development of self-driving technology and energy solutions, sets it apart.
- Tesla’s product strategy isn’t just about creating cars; it’s about creating an ecosystem that includes energy products like solar panels and energy storage. The emphasis on direct-to-consumer sales, over-the-sir software updates, and a network of charging stations contributes to a holistic customer experience. Tesla’s success showcases the power of a product strategy that not only meets current market needs but anticipates and shapes future trends, illustrating how a well-crafted strategy can redefine industries and captivate consumers.
2. Microsoft office 365:
- Business Model : Subscription Model
- Explanation: Microsoft Office 365 offers a suite of productivity tools on a subscription basis, providing user with regular updates and cloud-based collaboration features.
3. Spotify:
- Business Model : Freemium Model
- Explanation : Spotify offers free access to its music streaming service with ads, encouraging users to subscribe to the premium version for an ad-free experience and additional feature.
4. Amazon Web Services (AWS):
- Business Model: Platform Model
- Explanation: AWS provides a cloud computing platform where developers can build, deploy, and scale applications, fostering innovation within its extensive developer community.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, A well-defined product strategy is the backbone of successful product management. It serves as the guiding force that aligns product development with business objectives, fosters innovation, and ensures adaptability in dynamic markets.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...