What is an Expression and What are the types of Expressions?
Last Updated :
02 Aug, 2019
Expression: An expression is a combination of operators, constants and variables. An expression may consist of one or more operands, and zero or more operators to produce a value.
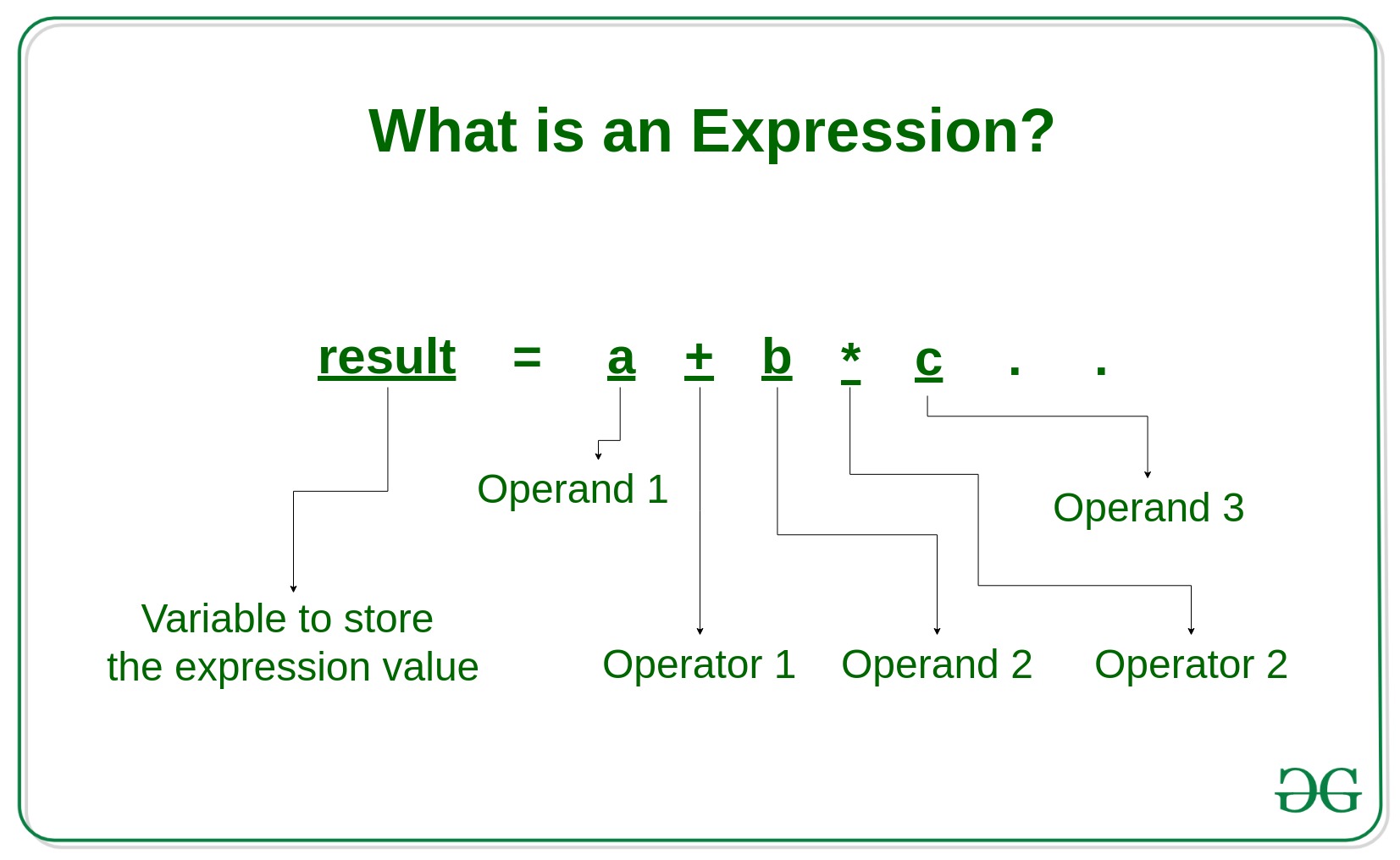
Example:
a+b
c
s-1/7*f
.
.
etc
Types of Expressions:
Expressions may be of the following types:
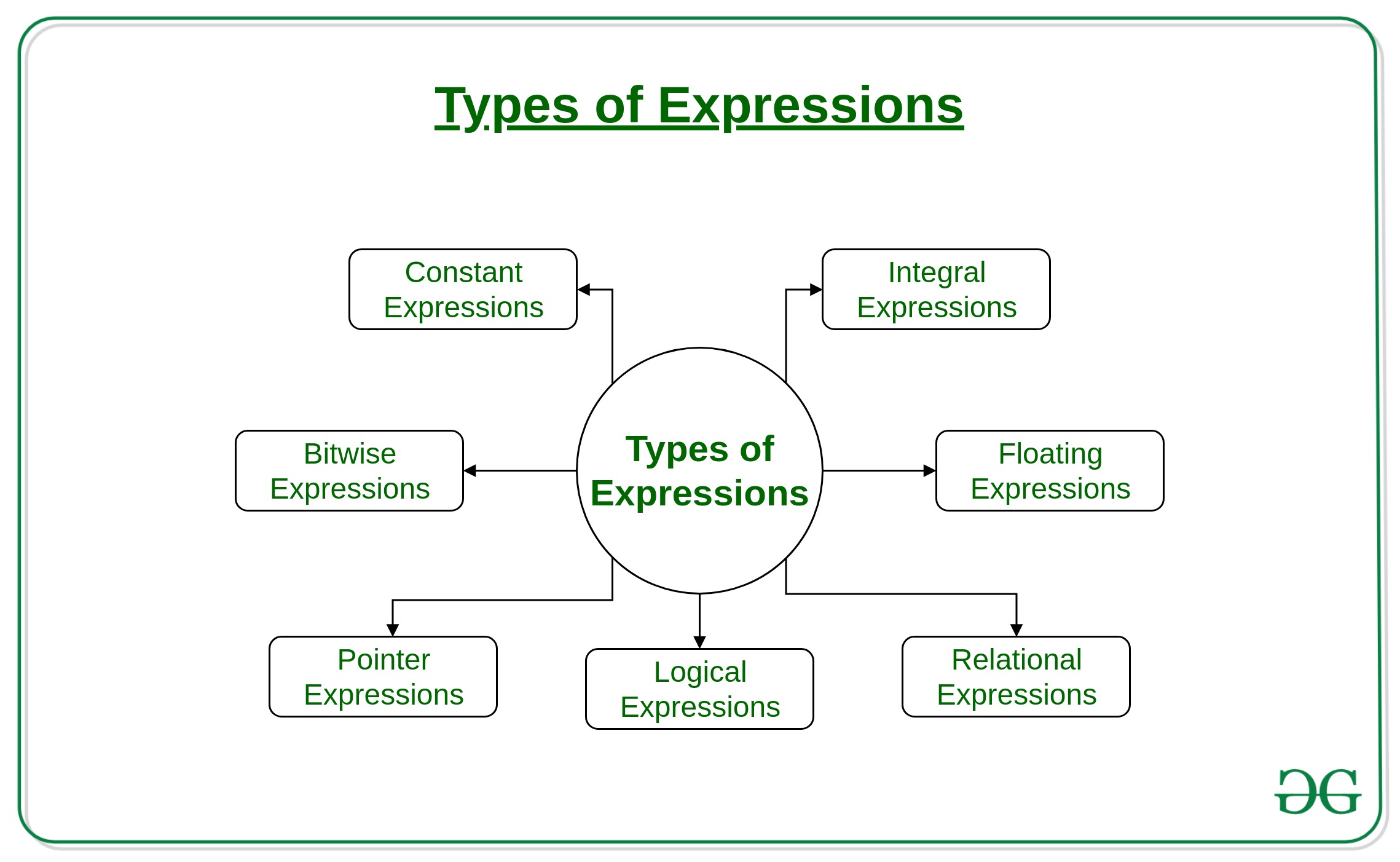
- Constant expressions: Constant Expressions consists of only constant values. A constant value is one that doesn’t change.
Examples:
5, 10 + 5 / 6.0, 'x’
- Integral expressions: Integral Expressions are those which produce integer results after implementing all the automatic and explicit type conversions.
Examples:
x, x * y, x + int( 5.0)
where x and y are integer variables.
- Floating expressions: Float Expressions are which produce floating point results after implementing all the automatic and explicit type conversions.
Examples:
x + y, 10.75
where x and y are floating point variables.
- Relational expressions: Relational Expressions yield results of type bool which takes a value true or false. When arithmetic expressions are used on either side of a relational operator, they will be evaluated first and then the results compared. Relational expressions are also known as Boolean expressions.
Examples:
x <= y, x + y > 2
- Logical expressions: Logical Expressions combine two or more relational expressions and produces bool type results.
Examples:
x > y && x == 10, x == 10 || y == 5
- Pointer expressions: Pointer Expressions produce address values.
Examples:
&x, ptr, ptr++
where x is a variable and ptr is a pointer.
- Bitwise expressions: Bitwise Expressions are used to manipulate data at bit level. They are basically used for testing or shifting bits.
Examples:
x << 3
shifts three bit position to left
y >> 1
shifts one bit position to right.
Shift operators are often used for multiplication and division by powers of two.
Note: An expression may also use combinations of the above expressions. Such expressions are known as compound expressions.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...