What Are the Objectives of Project Management?
Last Updated :
01 May, 2024
Project management is crucial for guiding projects from inception to completion, however, what are its primary objectives? Understanding those objectives is critical to guaranteeing fruitful project results and optimizing organizational effectiveness.
What are Project Objectives?
Project objectives of Project Management outline what a project is meant to achieve and are defined as clean, measurable, attainable, applicable, and time-bound goals. They provide the project a distinct purpose and course, directing the team’s selections and actions all through the project’s lifecycle. Typically, project objectives specify the deliverables, success criteria, and intended results. They serve as a foundation for planning, carrying out, overseeing, and evaluating the project and aid in the understanding of its goal by stakeholders.
What are the Objectives of Project Management?
- Successfully Accomplishing All Project Goals: Making sure that all project objectives, such as deliverables, deadlines, and quality standards, are fulfilled or surpassed.
- Providing instructions and supervision for team members: Throughout the project lifetime, team members should receive clear instructions, assistance, and advice to ensure tasks are executed effectively and efficiently.
- Promoting Cooperation and Communication: To improve the efficacy and efficiency of a project, team members, stakeholders, and other pertinent parties should be encouraged to collaborate and maintain open lines of communication.
- Implementing all Safety Procedures and Protocols: Ensuring that all essential safety measures are followed in order to safeguard the health and safety of project participants and stakeholders.
- Optimizing Budge and Resources: Budget and resource optimization refers to the effective management of project resources, such as funds, supplies, and labor, in order to achieve project goals while maximizing value and reducing waste.
- Managing Changes and Risks: Actively detecting, evaluating, and controlling risks at every stage of the project’s lifetime in order to minimize dangers and take advantage of opportunities. In order to keep the project in line with its goals, it is also important to manage changes to the project’s scope, schedule, or resources successfully.
- Ensuring Client Satisfaction: Throughout the project, giving the needs and expectations of the client first priority, making sure that deliverables meet or surpass the client’s expectations; and aggressively requesting feedback to resolve any issues and improve client satisfaction.
- Attaining Cost Efficiency: Keeping an eye fixed on and handling project charges to ensure that spending remains inside economic limits whilst optimizing value.
- Continuous Improvement: Promoting a tradition of non-stop development via the use of best practices, identity of lesson learnt from preceding projects, and learning from them.
What are the types of Project Objectives?
- Time-based Objectives: These goals outline when certain project phases must be finished. To reveal improvement and ensure the project remains on time, they incorporate milestones and cut-off dates.
- Strategic Objectives: High-level objectives that complement the organization’s broad mission and vision are known as strategic objectives. They are often long-term in nature and give the project direction and emphasis.
- Tactical Objectives: These goals concentrate on the project’s short- to medium-term objectives and are more precise than strategic goals. They help in directing daily operations and decision-making and are frequently derived from strategic objectives.
- Cost Objectives: Cost objectives delineate the project’s budget and resource allocation strategy. They make sure that sources are spent correctly and that the project is completed inside the allocated budget.
- Functional Objectives: These goals are related to the particular departments or functions which can be a part of the project. They make sure that everybody is operating toward the identical goals and delineate the jobs and obligations of various team members.
Project Management Phases
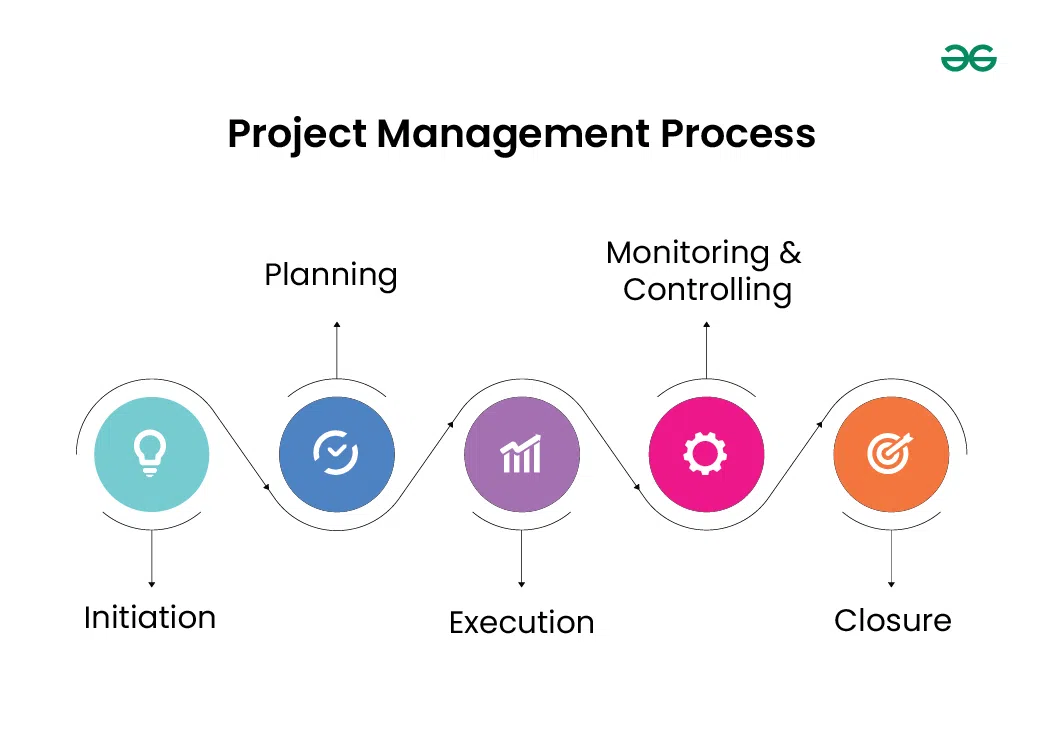
Project Management Phases
- Initiation: The project’s goal, scope, objectives, and early feasibility evaluation are all defined during the early phase. A project charter might also want to be created, stakeholders must be identified, a initial threat assessment should be done, and approval to move forward should be acquired.
- Planning: Detailed plans are created during this stage to direct the project’s implementation. This comprises determining the needs for the project, putting together a work breakdown structure (WBS), making timelines, estimating the resources needed, outlining roles and duties, and setting aside money. During this stage, techniques for risk management are also devised.
- Execution: Members of the project team assign tasks, distribute resources, and carry out their individual responsibilities. To keep the project moving forward throughout this phase, team member’s and stakeholder’s cooperation and communication are essential.
- Monitoring and Controlling: Throughout the path of the project, the plan, timeline, finances, and excellent standards are used to gauge how well the work goes. Any deviations or problems are found and fixed right away with corrective measures. Monitoring performance indicators, holding frequent status meetings, handling changes, and managing risks are all part of this phase.
- Closing: The project is officially closed out once all deliverables have been finished and authorized. This entails getting the client’s or stakeholder’s final approval, recording lessons learned, allocating project resources, and preserving project records.
Essential Skills to become a Project Manager
Below are some essential skills to become a Project Manager:
- Team Building: Effective project managers have to recognize how to create a collaborative environment, capitalize on each team member’s specific skills, and develop strong teams.
- Technical Skills: Project managers can also require know-how specifically disciplines, together with engineering, IT, creation, or finance, relying on the nature of the project.
- Negotiation: Project managers frequently have to negotiate in order to settle disputes, come to an agreement, and accomplish project goals with stakeholders, team members, and vendors.
- Problem-Solving: During the course of a project, managers face a variety of difficulties and roadblocks. To effectively identify the sources of these issues, weigh their choices, and put solutions in place, project managers need to possess excellent problem-solving abilities.
- Communication: Team members, stakeholders, and clients must be informed of project goals, expectations, and progress through effective communication. This involves communicating effectively, listening carefully, and changing up communication tactics when necessary.
How to Set Effective Project Management Objectives?
- Understand Project Requirements: To start, make sure you have a clear understanding of the project’s requirements, which include its objectives, deliverables, scope, budget, schedule, and stakeholders’ expectations. A solid grasp of these elements serves as the basis for goal-setting.
- Communicate Objectives Clearly: Make sure that all parties involved in the project—team members, sponsors, and clients—are aware of the goals. Make certain that everyone is aware of the goals, how they fit into the bigger picture, and how success will be determined.
- Divide Your Goals Into Milestones: Divide more ambitious goals into more doable deadlines or tasks. This facilitates monitoring development, early detection of possible problems, and project momentum maintenance.
- Review and update goals on a regular basis: Throughout the course of the project, continuously review and, if necessary, update the project objectives. This enables adaptability to shifting project needs, objectives, and outside circumstances.
- Set Project Objectives in Order of Priority: Set project objectives in order of significance, influence on project success, and alignment with organizational objectives. This aids in concentrating resources and efforts on the most important goals.
Related Articles:
Conclusion: Objectives of Project Management
The goals of project management encompass controlling risks, promoting the cooperation, and gratifying stakeholders similarly to finishing initiatives on agenda, inside price range, and to the required first-rate requirements. Accepting these goals gives project managers the ability to successfully negotiate challenges and manage a constantly changing project and initiative landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Objectives of Project Management
1. How may the goals of project management be modified as the project progresses?
Throughout the course of a project, it may be necessary to modify the project management objectives in response to shifting priorities, conditions, or stakeholder demands. Timely modifications are facilitated when there is efficient communication and collaboration among stakeholders, as well as regular review and assessment of objectives.
2. What order should the objectives of project management be put in?
Project management objectives are prioritized based on how important they are, how they affect the project’s outcome, and how well they correspond with organizational priorities. Prioritizing objectives based on their direct impact on project goals and level of value delivery is recommended.
3. What tactics are available to project managers to guarantee the accomplishment of project management goals?
To guarantee that project management goals are met, project managers can utilize a number of tactics, such as efficient planning, resource distribution, risk control, stakeholder involvement, and communication. Success also requires keeping an eye on developments, anticipating problems, and making required adjustments to plans.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...