What Are The 22 Bones Of The Skull?
Last Updated :
19 Oct, 2023
Bones of the skull form the cavity of the brain and support the structure of the face. It consists of 22 bones, categorized into cranial and facial bones, along with the mandible and hyoid bones. The cranial bones are 8, and the facial bones are 14 in number, which shape the facial features. The skull forms the anterior-most portion of the skeleton, which includes both the brain and various sensory organs like the eyes, ears, nose, and mouth.
Human Skull
The human skull is the bony structure that forms the head in the human skeleton. It is made up of 22 bones, ligaments, and cartilage. The skull consists of three parts: the neurocranium, the sutures, and the facial skeleton, each part having different embryological origin. The neurocranium, also known as the braincase, encloses the brain and brainstem and protect the brain from injury. The upper regions of the cranial bones form the skullcap, or calvaria. The membranous viscerocranium consists of the mandible. The sutures forms the joints between neurocranial bones, while the facial skeleton consists of the supporting bones of the face.
At birth, the human skull consists of 44 separate bony structures. Initially, the bones of the skull’s roof are separated by dense connective tissue areas known as fontanelles. As development progresses, many of these bony elements gradually fuse into solid bone structures, such as the frontal bone.
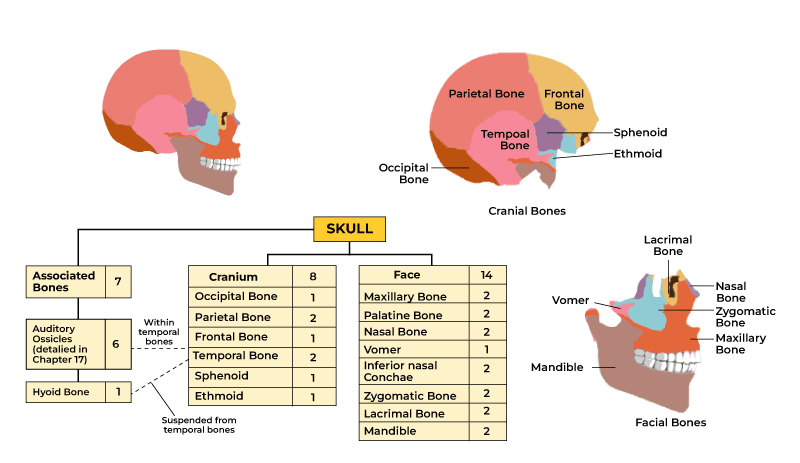
Skull Bone Anatomy
The skull is a complex structure formed through a combination of intramembranous and endochondral ossification processes. The facial skeleton and the sides and roof of the neurocranium, are dermal bones created by intramembranous ossification. However, the temporal bones undergo endochondral ossification. The bones of the skull are categorized into 2 main parts:
- Cranial bones (8)
- Facial skeletal bones (14)
Cranial Bones
Cranial bones are the bones that make up the top and sides of the human skull, forming the protective enclosure for the brain. These bones can be categorized into two main groups: the neurocranium and the viscerocranium.
Also Read: Cranial Nerve
Neurocranium
The neurocranium surrounds and protects the brain. It protects the brain from injury. It consists of eight bones:
- Frontal bone: It forms the forehead and the upper part of the eye sockets. It is the largest bone in the skull.
- Parietal bones (2): The parietal bones are two bones in number, when joined at a fibrous joint, they form the sides and roof of the cranium.
- Temporal bones (2):These bones are present on each side of the skull and contains the temples and ear structures.
- Occipital bone: It is located at the back and base of the skull. The occipital bone forms the posterior part of the cranium.
- Sphenoid bone: The sphenoid bone is located deep within the skull. It contributes to the base of the cranium and the sides of the eye sockets.
- Ethmoid bone: The ethmoid bone is located in the anterior part of the cranium. It forms the roof of the nasal cavity and part of the eye sockets.
Facial Bones
Facial bones also known as viscerocranium, supports the face and contains various sensory organs, such as the eyes, nose, and mouth. The facial skeleton consists of 14 individual bones, which include:
- Nasal Bones (2): These are two small, rectangular bones that form the bridge of the nose.
- Maxilla (2): The maxillae are the upper jawbones and are the largest bones of the facial skeleton. They form the upper jaw and contribute to the hard palate, the floor of the orbits (eye sockets), and the sides of the nasal cavity.
- Zygomatic Bones (2): The zygomatic bones, also known as the cheekbones, form the prominence of the cheeks and part of the orbital rim.
- Lacrimal Bones (2): The lacrimal bones are thin, fragile bones located near the nasal region. They contribute to the medial wall of the orbits and contain small openings for tear ducts.
- Palatine Bones (2): The palatine bones form the posterior part of the hard palate (roof of the mouth).
- Inferior Nasal Conchae (2): These are thin, scroll-shaped bones that are part of the nasal cavity. They help humidify and filter the air we breathe.
- Vomer: The vomer is a single bone that forms the lower and posterior part of the nasal septum, separating the nasal passages.
- Mandible: The mandible, or lower jawbone, is the only movable bone in the facial skeleton. It houses the lower teeth and forms the chin.
- Hyoid Bone: While not part of the facial skeleton, the hyoid bone is often associated with it because it is located in the neck and supports the base of the tongue and the muscles of the throat.
If the auditory ossicles or the bones in the ears are also included, then the total number of bones in the skull becomes 28.
Ear Bones (Auditory Ossicles)
The ear bones, also known as auditory ossicles, are the three tiny bones in the middle ear that transmit sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. These bones are named as follows:
- Malleus (Hammer)
- Incus (Anvil)
- Stapes (Stirrup)
Function of the Skull
The functions of the skull includes:
- Skull protects the brain from the external injury or trauma.
- It enables stereoscopic vision, by fixing the distance between the eyes.
- The upper jawbone (maxilla) and lower jawbone (mandible) provide support for teeth, facilitating biting and chewing.
- It aids in sound localisation as it fixes the position of the ears that pinpoints the direction and distance of sounds.
- Skull supports the face and contains various sensory organs, such as the eyes, nose, and mouth.
- The shape and structure of the skull contribute to facial aesthetics, giving each person a unique appearance.
FAQs on Bones of Human Skull
1. Are there 28 or 22 Bones in the Skull?
There are 22 skull bone with 8 cranial bones and 14 facial bones. If the auditory ossicles or the bones in the ears are also included, then the total number of bones in the skull becomes 28.
2. What are the Cranial Bones of the Skull?
The cranial bones forms the top and back of the skull. There are 8 cranial bones that include the frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital, sphenoid, and ethmoid bones.
3. Which is the Largest Bone in the Skull?
The largest bone in the skull is the frontal bone. It forms the forehead and the upper part of the eye sockets. It provides protection to the frontal lobe of the brain and to the eye socket.
4. Which Bone in the Skull is responsible for Chewing?
The mandible bone, also known as the lower jawbone, is responsible for chewing and articulating with the upper jawbone (maxilla). Mandible is the only bone in the skull that is moveable.
5. What is the Purpose of the Fontanelles in a Newborn’s skull?
Fontanelles are soft spots on a newborn’s skull where the cranial bones have not yet fully fused. They allow for some flexibility during childbirth and rapid brain growth during early infancy.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...