Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP)
Last Updated :
11 Dec, 2023
Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) is a network protocol that is connection-oriented and used for transmitting multiple streams of data simultaneously between any two endpoints that have established a connection in a computer network. SCTP is a transport layer of Internet Protocol (IP).
SCTP support telephone connection over the internet.
History of SCTP Protocol
SCTP is a standard protocol that was coined by The Transport Area Working Group (TSVWG) of the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force). The reason for the development of the protocol is to develop a system that is similar to the telephone Signaling System 7 (SS7) switching network for carrying call control signals using networks.

TSVWG and IETF developed SCTP as a standard protocol
The SCTP is similar to TCP protocol but the advantage is that it also provides message oriented data transfer like User Datagram Protocol (UDP) which makes it useful for end to end communication over internet. Both TCP and UPD protocol are based on the concept that made SCTP possible. Unlike TCP SCTP make ensure that it complete the concurrent transmission over several streams of data in units called message between the end points which are connected to each other.
Understanding Stream Control Transmission Protocol
As we know SCTP is an transport layer protocol it exist at an equivalent level with UDP and TCP which provides the transport layer functions properties to many other Internet applications. As it is a reliable transport protocol which operates on top of connectionless packet networks like IP and supports transfer of data over the network in single or multiple Ip cases.
It transport the signaling message to and from Signaling System (SS7) for 3G mobiles networks with help of M3UA, M2Ua or SUA. It is a packet based transport protocol. It is both reliable and secure transport which minimize the end to end delay.
This protocol is optimized to :-
- It avoids problem related to he multithread infrastructure during the high traffic.
- It also improves the SCTP association searching rate by SCTP hash table optimization on the SPU(Services Processing Unit ).
- It improves the FSM for retransmission of cases.
What is Multihoming in SCTP?
First we will understand multihoming so multihoming is the process of connecting a network or a host to multiple network simultaneously which is done due to increase reliability or performance.
Telecommunication systems are highly prone to time delays. Multihoming system enables with multiple interfaces to use one over the other without waiting. SCTP multihoming means that the endpoints which are connected can have different IP addresses associated to it. In simpler way multihoming refers to sending data to an alternate IP address if in case due to any issue the primary or original IP address is unreachable. Therefore the SCTP can connect or establish multiple connection paths between two endpoints.
In this there is a original or primary interface or secondary interfaces. So during establishment of connections a acknowledgment process validates the IP address and manages the round trip time (RTT) for each individual address. The RTT calculation enables the communication to migrate to a secondary interface.
SCTP Packet
SCTP protocol packet consist of two main parts Header and Payload. The Header is common but Payload have variable chunks.
The Common SCTP header is 12 byte long and made of the 4 parts
- Port Number (Source): shows the sending port
- Port Number (Destination): shows the receiving port
- Verification tag: a 32 bit random value which differentiate the packets from the previous connection
- Checksum: a CRC32 algorithm for detection of error.
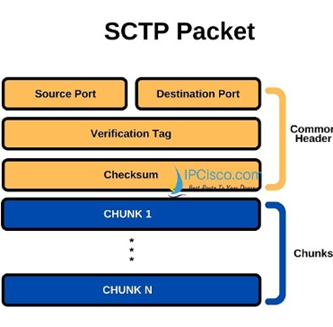
SCTP Packet
Security
This protocol provides certain security features related to transport such as resistance against blind DOS attack (Denial of Service), masquerades and monopolization of any type of service during operation. SIGTRAN (Signaling Transport) protocols does not define any type of new security mechanism as current available security protocols provide necessary steps for securing the transmission of SS7 message over IP networks
SCTP Services
- Aggregate Server Access Protocol (ASAP)
- Bearer-independent Call Control (BICC)
- Direct Data Placement Segment chunk (DDP-segment)
- Direct Data Placement Stream session control (DDP-stream)
- Diameter in a DTLS/SCTP DATA chunk (Diameter-DTLS)
Understanding Central Point Architecture Support for SCTP
As we know that the SCTP association is a connection between two SCTP endpoints. Each endpoint identifies it’s association with a tag. During it’s setup the SCTP endpoints exchange their tags for receiving packets. So during the exchange f packets between two SCTP endpoints the both source and destination address can change in the association life cycle.
Before the release of Junos OS 15.1X49-D40 all the sessions of the SCTP association are hashed to the same SPU with the help of the fixed per association SCTP port pair. In many of the cases multiple SCTP association use the same port pair, which results a bad load balancing with all the traffic handled by single SPU. When the version Junos OS release 15.1X49-D40 and Junos OS Release 17.3R1 to handle load balancing issue, the tag based hash distribution is used to ensure the even distribution of the traffic of SCTP from various associations among all the SPU’s. It’s flow session utilizes a connection tag to more finely distribute SCTP traffic across all the SPU’s on the SRX1500, SRX4100, SRX4200, SRX5400, SRX600, and SRX800 devices that supports the SCTP ALG. The decoding of connection tag is from SCTP vtag.
Advantages of SCTP
As SCTP is a full duplex connection, it enables the data to be sent and receive simultaneously. The data is delivered in chunks and in a ordered way which are independent to each stream this help in isolating the data from other streams.
Like TCP and unlike UDP the SCTP provides the following advantage
- Flow control: It adjust the data transmission in a particular order and quantity.
- Congestion control: It checks for network prior transmission to prevent the congestion over the links.
- Fault tolerance: It uses the IP address from different internet services providers. So, if in case ISP fails another connection can be used for establishing the connection.
- It is a message oriented rather than byte oriented as of UDP.
- It provides a path selection functionality to select the primary data transmission and a monitoring function to test the connectivity of transmission path.
Limitation and Constraints of SCTP Protocol
- IP address
- In this protocol a maximum of eight IP address and eight destination IP address are used in communication.
- In this only static IP NAT is supported.
- SCTP Payload Protocol Blocking
- If there is any change in the protocol blocking configuration it immediately impacts the traffic of existing associations.
- The protocol which is supported is in decimal value ranging from 0 to 63, which includes 48 IANA protocol and 16 unassigned protocols.
- All the static NAT the interfaces packets (client or server side) should belong from the same zone.
- The sessions of SCTP are not deleted with associations they have a time out of 30 min (default).
- Only the Static NAT is supported for SCTP protocol.
Application Of SCTP Protocol
- Telephone Communication: It was developed foe the communication of telephony over the internet.
- Multihoming Support: It provides multihoming support, in which both endpoints of the connection can have multiple IP address which help helps in detection of failure in between the communication path.
- Transport for various Application: It is used in transport signaling messages to and from SS7(Signaling System 7) on the devices supporting 3G networks through M3UA , M2UA.
- Roaming Security and RAN Security: In mobile infrastructure it is used in roaming security and RAN (Radio Access Network) security.
- Reliable and Secure Transport: This protocol provides reliable and highly secure transport or communication which minimizes the end to end delay.
Conclusion
Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) is a connection oriented protocol which allows transmission of multiple data streams. SCTP was first coined by the Transport Area Working Group (TSVWG) of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to create a system similar to the telephone Signaling System 7 (SS7) switching network for carrying call control signals using IP networks. SCTP make sure that it completes transmission of several streams of data in units called messages between the connected endpoints. It supports the multihoming concept, , which increases the reliability and performance. it is a reliable and very secure and trustworthy transport protocol which minimizes end to end delay and provides security features like, resistance against blind DOS attacks, masquerades, and monopolization of services during operation. It is used in various applications such as Aggregate Server Access Protocol (ASAP), Bearer-independent Call Control (BICC), and others. It’s advantages include full duplex connection, message oriented data transfer, flow control, congestion control, and fault tolerance. It has limitations of a maximum of eight IP addresses and the eight destination IP addresses in the communication process, and it only supports static IP NAT . Changes in the protocol blocking configuration immediately, it impacts the traffic.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the header if the SCTP protocol ?
SCTP header includes
- Source and Destination Port
- verification tag
- Checksum
2. What are the application of SCTP protocol
The assigned protocol number for SCTP on IP is 132.
3. What are the use cases for SCTP?
- Radio access network (RAN) security
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...