Before jumping into RestTemplateBuilder let’s have a quick overview of RestTemplate. RestTemplate is a synchronous REST client which performs HTTP requests using a simple template-style API. We can also state that RestTemplate class is a synchronous client and is designed to call REST services. RestTemplateBuilder is a Builder that can be used to configure and create a RestTemplate. RestTemplateBuilder provides convenient methods to register converters, error handlers, and UriTemplateHandlers. Let’s understand the concept with an example.
How to Use RestTemplate in Spring Boot Application?
If you want to use RestTemplate in Spring Boot Application then first we have to create a Bean of RestTemplate class inside our configuration class file like below.
Java
@Configuration
public class EmployeeConfig {
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplateBean() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
|
Then we can use this in our service class with the help of @Autowired annotation something like this
Java
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
@Autowired
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
employeeResponse.setAddressResponse(addressResponse);
}
|
Note: But it is highly recommended that we should always use the RestTemplateBuilder to create a RestTemplate instance.
So now let’s create a RestTemplate instance with the help of RestTemplateBuilder.
How to Use RestTemplateBuilder in Spring Boot Application?
If you are using RestTemplateBuilder there is no need to create a separate bean of RestTemplate in the configuration file. We can do it inside the service class only with help of the service class constructor; something like this.
Java
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
public EmployeeService(RestTemplateBuilder builder) {
this.restTemplate = builder.build();
}
public EmployeeResponse getEmployeeById(int id) {
employeeResponse.setAddressResponse(addressResponse);
return employeeResponse;
}
}
|
If you want to build a complete working Spring Boot project with the help of RestTemplateBuilder then you may follow the below example.
Example Spring Boot Project
In this project, we are going to develop two Spring Boot Microservices
- employee-service
- address-service
Developing Employee-Service Step by Step
Step 1: Create a New Spring Boot Project in Spring Initializr
To create a new Spring Boot project, please refer to How to Create a Spring Boot Project in Spring Initializr and Run it in IntelliJ IDEA. For this project choose the following things
- Project: Maven
- Language: Java
- Packaging: Jar
- Java: 17
Please choose the following dependencies while creating the project.
- Spring Boot DevTools
- Spring Data JPA
- MySQL Driver
- Spring Web
Generate the project and run it in IntelliJ IDEA by referring to the above article.
Note: We have used the MySQL database in this project.
Step 2: Create Schema in MySQL Workbench and Put Some Sample Data
Go to your MySQL Workbench and create a schema named gfgmicroservicesdemo and inside that create a table called employee and put some sample data as shown in the below image. Here we have created 4 columns and put some sample data.
- id
- name
- email
- age
.png)
Now we are going to fetch Employee Data from Employee Table in our Spring Boot project. To do it refer to the following steps. Before moving to IntelliJ IDEA let’s have a look at the complete project structure for our Microservices.
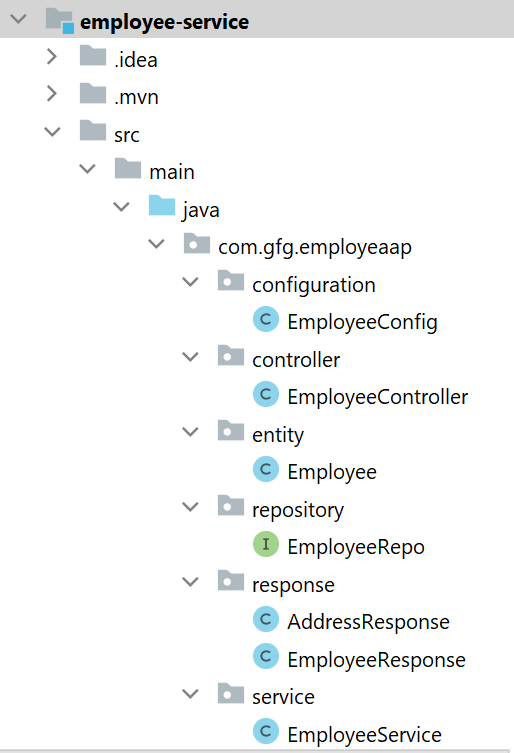
Step 3: Make Changes in Your application.properties File
Now make the following changes in your application.properties file.
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/gfgmicroservicesdemo
spring.datasource.username=put your username here
spring.datasource.password=put your password here
spring.application.name=employee-service
server.port=8080
# Set Your Context Path Here
server.servlet.context-path=/employee-service
addressservice.base.url=http://localhost:8081/address-service
Step 4: Create Your Entity/Model Class
Go to the src > main > java > entity and create a class Employee and put the below code. This is our model class.
Java
package com.gfg.employeaap.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "employee")
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "name")
private String name;
@Column(name = "email")
private String email;
@Column(name = "age")
private String age;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
|
Step 5: Create Your Repository Interface
Go to the src > main > java > repository and create an interface EmployeeRepo and put the below code. This is our repository where we write code for all the database-related stuff.
Java
package com.gfg.employeaap.repository;
import com.gfg.employeaap.entity.Employee;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
@Repository
public interface EmployeeRepo extends JpaRepository<Employee, Integer> {
}
|
Note: Please refer to this article to know more about JpaRepository.
Step 6: Create an AddressResponse and EmployeeResponse Class
Go to the src > main > java > response and create a class AddressResponse and put the below code.
Java
package com.gfg.employeaap.response;
public class AddressResponse {
private int id;
private String city;
private String state;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
}
|
Go to the src > main > java > response and create a class EmployeeResponse and put the below code.
Java
package com.gfg.employeaap.response;
public class EmployeeResponse {
private int id;
private String name;
private String email;
private String age;
private AddressResponse addressResponse;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
public AddressResponse getAddressResponse() {
return addressResponse;
}
public void setAddressResponse(AddressResponse addressResponse) {
this.addressResponse = addressResponse;
}
}
|
Step 7: Create Your Service Class
Go to the src > main > java > service and create a class EmployeeService and put the below code. This is our service class where we write our business logic. Here we are using the RestTemplateBuilder concept.
Java
package com.gfg.employeaap.service;
import com.gfg.employeaap.entity.Employee;
import com.gfg.employeaap.repository.EmployeeRepo;
import com.gfg.employeaap.response.AddressResponse;
import com.gfg.employeaap.response.EmployeeResponse;
import org.modelmapper.ModelMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.web.client.RestTemplateBuilder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.util.Optional;
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
@Autowired
private EmployeeRepo employeeRepo;
@Autowired
private ModelMapper mapper;
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
public EmployeeService(@Value("${addressservice.base.url}") String addressBaseUrl, RestTemplateBuilder builder) {
this.restTemplate = builder.rootUri(addressBaseUrl).build();
}
public EmployeeResponse getEmployeeById(int id) {
Optional<Employee> employee = employeeRepo.findById(id);
EmployeeResponse employeeResponse = mapper.map(employee, EmployeeResponse.class);
AddressResponse addressResponse = restTemplate.getForObject("/address/{id}", AddressResponse.class, id);
employeeResponse.setAddressResponse(addressResponse);
return employeeResponse;
}
}
|
Step 8: Create an Employee Controller
Go to the src > main > java > controller and create a class EmployeeController and put the below code. Here we are going to create an endpoint “/employees/{id}” to find an employee using id.
Java
package com.gfg.employeaap.controller;
import com.gfg.employeaap.response.EmployeeResponse;
import com.gfg.employeaap.service.EmployeeService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@GetMapping("/employees/{id}")
private ResponseEntity<EmployeeResponse> getEmployeeDetails(@PathVariable("id") int id) {
EmployeeResponse employee = employeeService.getEmployeeById(id);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(employee);
}
}
|
Step 9: Create a Configuration Class
Go to the src > main > java > configuration and create a class EmployeeConfig and put the below code.
Java
package com.gfg.employeaap.configuration;
import org.modelmapper.ModelMapper;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class EmployeeConfig {
@Bean
public ModelMapper modelMapperBean() {
return new ModelMapper();
}
}
|
Note: You may refer to these two articles
Before running the Microservice below is the complete pom.xml file. Please cross-verify if you have missed some dependencies
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>com.gfg.employeaap</groupId>
<artifactId>employee-service</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>employee-service</name>
<description>Employee Service</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.modelmapper</groupId>
<artifactId>modelmapper</artifactId>
<version>3.1.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
|
Developing Address-Service Step by Step
Step 1: Create a New Spring Boot Project in Spring Initializr
To create a new Spring Boot project, please refer to How to Create a Spring Boot Project in Spring Initializr and Run it in IntelliJ IDEA. For this project choose the following things
- Project: Maven
- Language: Java
- Packaging: Jar
- Java: 17
Please choose the following dependencies while creating the project.
- Spring Boot DevTools
- Spring Data JPA
- MySQL Driver
- Spring Web
Generate the project and run it in IntelliJ IDEA by referring to the above article.
Note: We have used the MySQL database in this project.
Step 2: Create Schema in MySQL Workbench and Put Some Sample Data
Go to your MySQL Workbench and create a schema named gfgmicroservicesdemo and inside that create a table called address and put some sample data as shown in the below image.
Address Table:
Here we have created 4 columns and put some sample data.
- id
- city
- state
- employee_id
Note: In the Address table, employee_id is a foreign key so create it accordingly. We are going to perform a SQL join operation in our native SQL query. So create tables carefully.
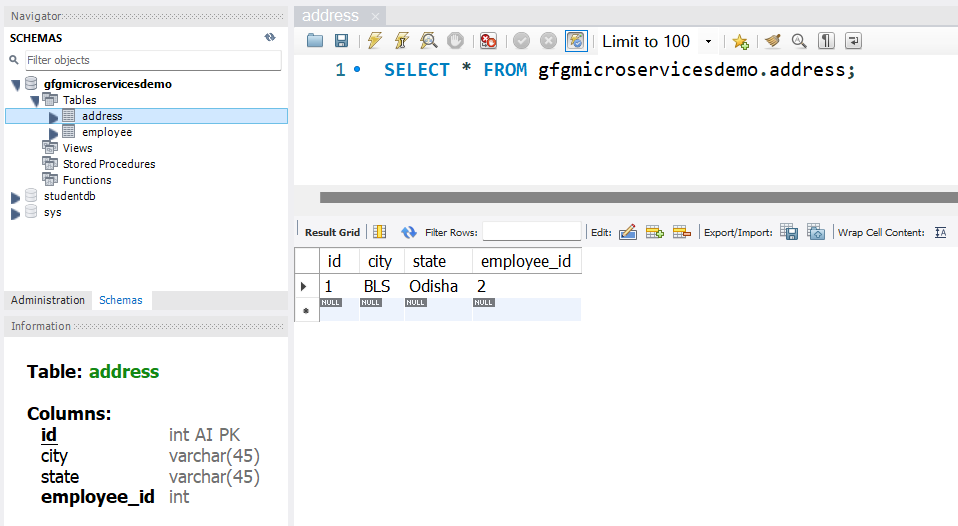
Before moving to IntelliJ IDEA let’s have a look at the complete project structure for our Microservices.
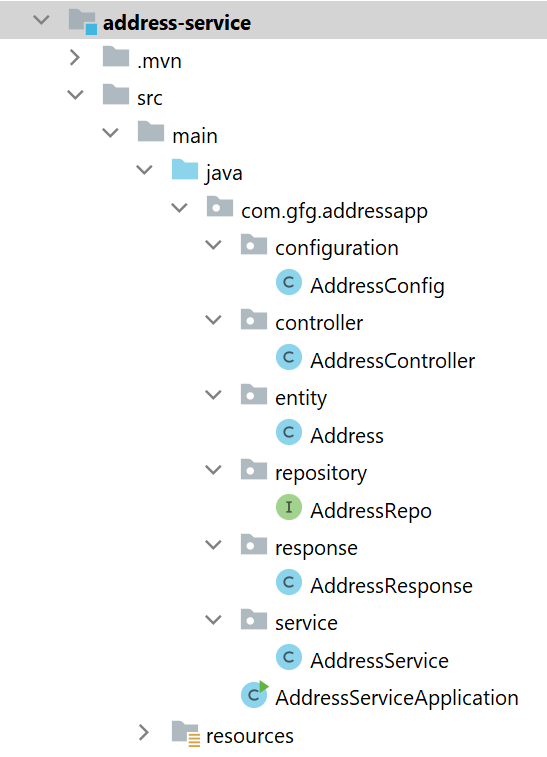
Step 3: Make Changes in Your application.properties File
Now make the following changes in your application.properties file.
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/gfgmicroservicesdemo
spring.datasource.username=put your username here
spring.datasource.password=put your password here
spring.application.name=address-service
server.port=8081
server.servlet.context-path=/address-service
Step 4: Create Your Entity/Model Class
Go to the src > main > java > entity and create a class Address and put the below code. This is our model class.
Java
package com.gfg.addressapp.entity;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
@Entity
@Table(name = "address")
public class Address {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name = "id")
private int id;
@Column(name = "city")
private String city;
@Column(name = "state")
private String state;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
}
|
Step 5: Create Your Repository Interface
Go to the src > main > java > repository and create an interface AddressRepo and put the below code. This is our repository where we write code for all the database-related stuff.
Java
package com.gfg.addressapp.repository;
import com.gfg.addressapp.entity.Address;
import java.util.Optional;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.data.repository.query.Param;
@Repository
public interface AddressRepo extends JpaRepository<Address, Integer> {
@Query(
nativeQuery = true,
value
= "SELECT ea.id, ea.city, ea.state FROM gfgmicroservicesdemo.address ea join gfgmicroservicesdemo.employee e on e.id = ea.employee_id where ea.employee_id=:employeeId")
Optional<Address> findAddressByEmployeeId(@Param("employeeId") int employeeId);
}
|
Note: Please refer to this article to know more about JpaRepository.
Step 6: Create an AddressResponse Class
Go to the src > main > java > response and create a class AddressResponse and put the below code.
Java
package com.gfg.addressapp.response;
public class AddressResponse {
private int id;
private String city;
private String state;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getCity() {
return city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getState() {
return state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
}
|
Step 7: Create Your Service Class
Go to the src > main > java > service and create a class AddressService and put the below code. This is our service class where we write our business logic.
Java
package com.gfg.addressapp.service;
import com.gfg.addressapp.entity.Address;
import com.gfg.addressapp.repository.AddressRepo;
import com.gfg.addressapp.response.AddressResponse;
import org.modelmapper.ModelMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.Optional;
@Service
public class AddressService {
@Autowired
private AddressRepo addressRepo;
@Autowired
private ModelMapper mapper;
public AddressResponse findAddressByEmployeeId(int employeeId) {
Optional<Address> addressByEmployeeId = addressRepo.findAddressByEmployeeId(employeeId);
AddressResponse addressResponse = mapper.map(addressByEmployeeId, AddressResponse.class);
return addressResponse;
}
}
|
Step 8: Create an Address Controller
Go to the src > main > java > controller and create a class AddressController and put the below code. Here we are going to create an endpoint “/address/{employeeId}” to find the address using employee_id. Thats why we have created a foreign key in the Address table and we have performed the SQL join operation in the native query to get our desired result.
Java
package com.gfg.addressapp.controller;
import com.gfg.addressapp.response.AddressResponse;
import com.gfg.addressapp.service.AddressService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class AddressController {
@Autowired
private AddressService addressService;
@GetMapping("/address/{employeeId}")
public ResponseEntity<AddressResponse> getAddressByEmployeeId(@PathVariable("employeeId") int employeeId) {
AddressResponse addressResponse = addressService.findAddressByEmployeeId(employeeId);
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.OK).body(addressResponse);
}
}
|
Step 9: Create a Configuration Class
Go to the src > main > java > configuration and create a class AddressConfig and put the below code.
Java
package com.gfg.addressapp.configuration;
import com.gfg.addressapp.service.AddressService;
import org.modelmapper.ModelMapper;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class AddressConfig {
@Bean
public ModelMapper modelMapperBean() {
return new ModelMapper();
}
}
|
Note: You may refer to these two articles
Before running the Microservice below is the complete pom.xml file. Please cross-verify if you have missed some dependencies
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>com.gfg.addressapp</groupId>
<artifactId>address-service</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>address-service</name>
<description>Address Service</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.modelmapper</groupId>
<artifactId>modelmapper</artifactId>
<version>3.1.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
|
Run Your Both Address and Employee Microservices
Now run your both Address and Employee Microservices. If everything goes well then you may see the following screen in your console. Please refer to the below image.
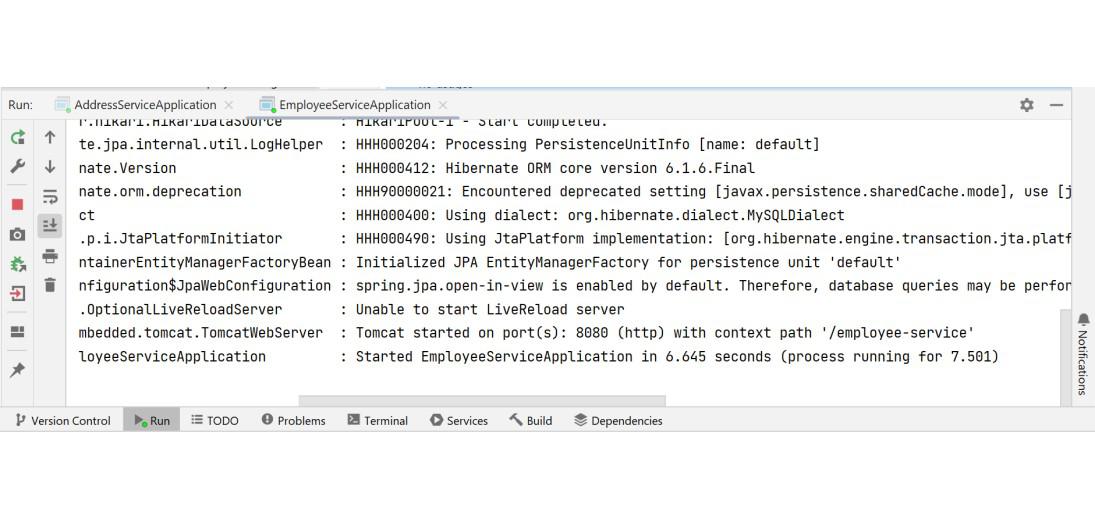
Test Your Endpoint in Postman:
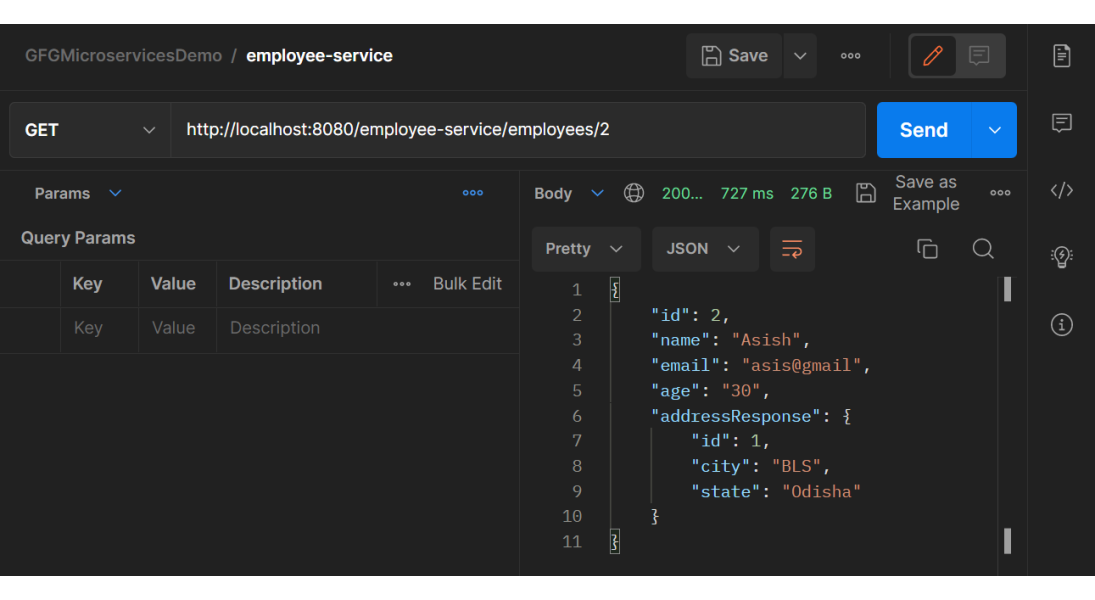
Now open Postman and hit the following URL
GET: http://localhost:8080/employee-service/employees/2
And you can see the following response
{
"id": 2,
"name": "Asish",
"email": "asis@gmail",
"age": "30",
"addressResponse": {
"id": 1,
"city": "BLS",
"state": "Odisha"
}
}
Please refer to the below image.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...