Solidity – Basics of Interface
Last Updated :
09 Mar, 2023
Interfaces are the same as abstract contracts created by using an interface keyword, also known as a pure abstract contract. Interfaces do not have any definition or any state variables, constructors, or any function with implementation, they only contain function declarations i.e. functions in interfaces do not have any statements. Functions of Interface can be only of type external. They can inherit from other interfaces, but they can’t inherit from other contracts. An interface can have enum, structs which can be accessed using interface name dot notation.
Example: In the below example, the contract MyContract implements an interface from the InterfaceExample.sol file and implements all the interface functions. Import the InterfaceExample.sol file into the MyContract.sol file before deploying it.
InterfaceExample.sol :
Solidity
pragma solidity >=0.8.6 <0.9.0;
interface InterfaceExample{
function getStr(
) external view returns(string memory);
function setValue(
uint _num1, uint _num2) external;
function add(
) external view returns(uint);
}
|
MyContract.sol:
Solidity
pragma solidity >=0.8.6 <0.9.0;
import "./InterfaceExample.sol";
contract MyContract is InterfaceExample{
uint private num1;
uint private num2;
function getStr() public view virtual override returns(string memory){
return "GeeksForGeeks";
}
function setValue(
uint _num1, uint _num2) public virtual override{
num1 = _num1;
num2 = _num2;
}
function add(
) public view virtual override returns(uint){
return num1 + num2;
}
}
contract call{
InterfaceExample obj;
constructor(){
obj = new MyContract();
}
function getValue(
) public returns(string memory,uint){
obj.setValue(10, 16);
return (obj.getStr(),obj.add());
}
}
|
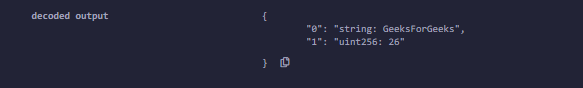
Output :
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...