SMTP Extensions: STARTTLS, and DANE
Last Updated :
08 Oct, 2023
SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol. SMTP is an application layer protocol. Whenever a client needs to send mail, opens a TCP connection to the SMTP server and then sends mail over the network. The connection is established by the SMTP server through port 25. The SMTP Protocol model is of two types namely the End-to-end method and the Store-and-forward method. STARTTLS and DANE are the further extensions of SMTP.
Need of STARTTLS and DANE
- Initially, when the Simple Mail Transport Protocol(SMTP) was adopted, all the messages were communicated as plain text. No encryption methods and algorithms were applied to the message data.
- Any unauthorized person trying to steal or check for the content was able to read the actual data that was transmitted between two servers.
- Later on, Extend SMTP (ESMTP) made it possible to transmit the encrypted data rather than sending simple plain text.
- Encryption was not mandatory for all the servers because all the servers were not able to handle transport encryption.
- In order to indicate the ability of encryption to the sending server, it was made mandatory that the receiving server needs to send the keyword STARTTLS at the beginning of an ESMTP transport session.
STARTTLS
STARTTLS is defined as a protocol that is an upgraded form of an existing protocol that provides an encrypted connection so that email messages can be protected over the network from unauthorized users. STARTTLS can encrypt the data that is being transmitted from one server to another. Once a secure connection is established between two servers, the sending server sends a signal to the receiving server that it is capable of encryption. This means that encryption can only be done if it has been negotiated between the sending and receiver servers.
STARTTLS is still prone to some attacks such as the Man in the Middle attack. In this attack, the attacker places himself between the sender and receiver server and pretends to be a legitimate user. As SMTP does not provide any other security methods, the SMTP server is not able to identify Man in the Middle. The sending server communicates with the wrong server.
Working of STARTTLS
Below figure describes the working of STARTTLS.

Working of STARTTLS
- SMTP protocol messages are unencrypted. in STARTTLS the messages are encrypted and maintains the security. Below are steps for working of STARTTLS according to the above figure.
- First in order to identify the email client and email sever, the process starts with the TCP(Transmission Control Protocol) handshake.
- The server then responds to the client with 220 Ready so that email client can proceed for the further communication.
- The client then sends a “EHLO” message to server to inform that the client wants to use the Extended SMTP for the further communication.
- The client then sends “250-STARTTLS” to the mail server. It asks whether the STARTTLS is accepted or not.
- Upon asking, if server sends back the message of “GO HEAD” the STARTTLS connection can be implemented.
- Once client receives message from server, client restarts the connection and the email message is in encrypted form.
DANE
DANE stands for DNS-Based Authentication of Named Entities. DANE is used as a secured DNS infrastructure that is used for storing generic verifiable information for multi-factor verification. DANE protocol makes use of DNS system for storing the fingerprint that certifies which CA the Domain makes use of for protecting from the security breeches. DANE can put the entire certificate or only the public key in a DNS record that specifies about the key or certificate that will be used for connecting the over TCP port 443. Today DANE is mostly used for TLSA (Transport Layer Security Authentication) record type which is used to verify the PKIX certificate that is received from the website by querying for its information in DNS.
Working of DANE
Below figure describes about the working of DANE protocol.
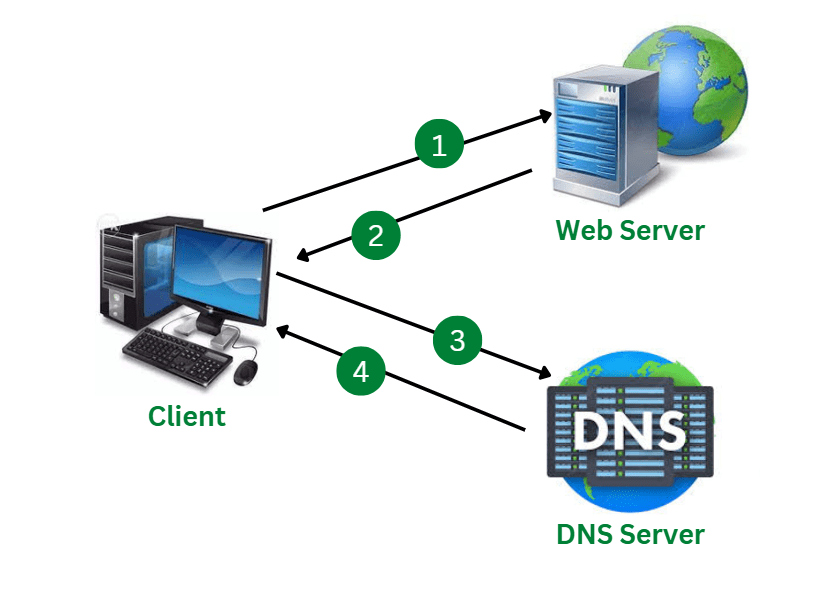
Working of DANE
The three main systems involved in the working of DANE are client, Web Server and DNS Server. The communication takes place according to the below steps:
- Step 1: The client browser initially connects to the web server. For example client connects to https://www.exampleabc.com
- Step 2: The web server then replies with the its certificate to the client.
- Step 3: The client asks for the TLSA (Transport Layer Security Authentication) record of www.exampleabc.com to its local DNS server.
- Step 4: The DNS server then performs a normal DNS lookup for www.exampleabc.com TLSA record and validates the response
Once the client receives validated TLSA record, the client browser then computes and performs comparison of value of the TLSA record from DNS with the certificate that is received from the web server. If these two does not match with each other, the web browser displays a warning message and does not loads the page.
FAQs on SMTP Extension
Q.1: What is STARTTLS command?
Answer:
STARTTLS is a command that is used by the email client to inform the email server that client wants to upgrade a insecure connection to a secure connection by using TLS or SSL.
Q.2: Which port is used for encrypting the SMTP messages using STARTTLS?
Answer:
Port 587 is used for encrypting the SMTP messages using STARTTLS that allows to establish a secure email connection between email client and email server.
Q.3: What are the limitations of STARTTLS?
Answer:
STARTTLS has a limitation that it is so-called opportunistic. The encryption can be used only if it is negotiated between the both sending and receiving servers over an unencrypted connection.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...