Domain Name System (DNS) in Application Layer
Last Updated :
06 Sep, 2023
Domain Name System (DNS) is a hostname for IP address translation service. DNS is a distributed database implemented in a hierarchy of name servers. It is an application layer protocol for message exchange between clients and servers. It is required for the functioning of the Internet.
What is the Need of DNS?
Every host is identified by the IP address but remembering numbers is very difficult for people also the IP addresses are not static therefore a mapping is required to change the domain name to the IP address. So DNS is used to convert the domain name of the websites to their numerical IP address.
Types of Domain
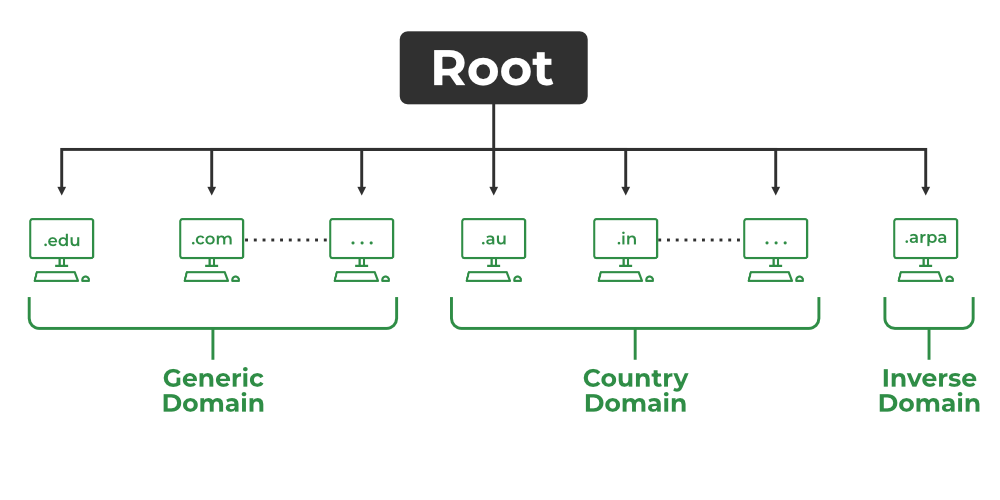
There are various kinds of domain:
- Generic domains: .com(commercial), .edu(educational), .mil(military), .org(nonprofit organization), .net(similar to commercial) all these are generic domains.
- Country domain: .in (India) .us .uk
- Inverse domain: if we want to know what is the domain name of the website. Ip to domain name mapping. So DNS can provide both the mapping for example to find the IP addresses of geeksforgeeks.org then we have to type
nslookup www.geeksforgeeks.org
Types of DNS
Organization of Domain
It is very difficult to find out the IP address associated with a website because there are millions of websites and with all those websites we should be able to generate the IP address immediately, there should not be a lot of delays for that to happen organization of the database is very important.

Root DNS Server
- DNS record: Domain name, IP address what is the validity? what is the time to live? and all the information related to that domain name. These records are stored in a tree-like structure.
- Namespace: Set of possible names, flat or hierarchical. The naming system maintains a collection of bindings of names to values – given a name, a resolution mechanism returns the corresponding value.
- Name server: It is an implementation of the resolution mechanism.
DNS = Name service in Internet – A zone is an administrative unit, and a domain is a subtree.
Name-to-Address Resolution
The host requests the DNS name server to resolve the domain name. And the name server returns the IP address corresponding to that domain name to the host so that the host can future connect to that IP address.

Name-to-Address Resolution
- Hierarchy of Name Servers Root name servers: It is contacted by name servers that can not resolve the name. It contacts the authoritative name server if name mapping is not known. It then gets the mapping and returns the IP address to the host.
- Top-level domain (TLD) server: It is responsible for com, org, edu, etc, and all top-level country domains like uk, fr, ca, in, etc. They have info about authoritative domain servers and know the names and IP addresses of each authoritative name server for the second-level domains.
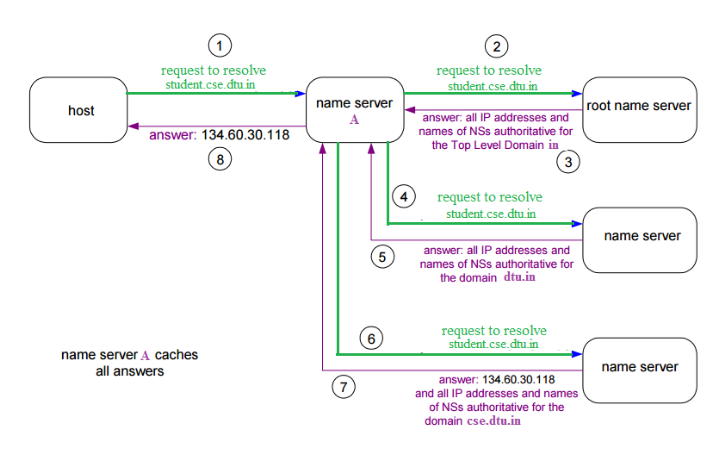
- Authoritative name servers are the organization’s DNS servers, providing authoritative hostnames to IP mapping for organization servers. It can be maintained by an organization or service provider. In order to reach cse.dtu.in we have to ask the root DNS server, then it will point out to the top-level domain server and then to the authoritative domain name server which actually contains the IP address. So the authoritative domain server will return the associative IP address.
Domain Name Server
The client machine sends a request to the local name server, which, if the root does not find the address in its database, sends a request to the root name server, which in turn, will route the query to a top-level domain (TLD) or authoritative name server. The root name server can also contain some hostName to IP address mappings. The Top-level domain (TLD) server always knows who the authoritative name server is. So finally the IP address is returned to the local name server which in turn returns the IP address to the host.
Domain Name Server
How Does DNS Work?
The working of DNS starts with converting a hostname into an IP Address. A domain name serves as a distinctive identification for a website. It is used in place of an IP address to make it simpler for consumers to visit websites. Domain Name System works by executing the database whose work is to store the name of hosts which are available on the Internet. The top-level domain server stores address information for top-level domains such as .com and .net, .org, and so on. If the Client sends the request, then the DNS resolver sends a request to DNS Server to fetch the IP Address. In case, when it does not contain that particular IP Address with a hostname, it forwards the request to another DNS Server. When IP Address has arrived at the resolver, it completes the request over Internet Protocol.
For more, you can refer to Working of DNS Server.
.gif)
How Does DNS Work?
Authoritative DNS Server Vs Recursive DNS Resolver
|
Function
|
Holds the official DNS records for a domain
|
Resolves DNS queries on behalf of clients |
| Role |
Provides answers to specific DNS queries |
Actively looks up information for clients |
| Query Handling |
Responds with authoritative DNS data |
Queries other DNS servers for DNS data |
| Client Interaction |
Doesn’t directly interact with end-users |
Serves end-users or client applications |
| Data Source |
Stores the DNS records for specific domains |
Looks up data from other DNS servers |
| Caching |
Generally, doesn’t perform caching |
Caches DNS responses for faster lookups |
| Hierarchical Resolution |
Does not participate in the recursive resolution |
Actively performs recursive name resolution |
| IP Address |
Has a fixed, known IP address |
IP address may vary depending on ISP |
| Zone Authority |
Manages a specific DNS zone (domain) |
Does not manage any specific DNS zone |
What is DNS Lookup?
DNS Lookup or DNS Resolution can be simply termed as the process that helps in allowing devices and applications that translate readable domain names to the corresponding IP Addresses used by the computers for communicating over the web.
DNS Servers Involved in Loading a Webpage
Upon loading the webpage, several DNS Servers are responsible for translating the domain name into the corresponding IP Address of the web server hosting the website. Here is the list of main DNS servers involved in loading a Webpage.
- Local DNS Resolver
- Root DNS Servers
- Top-Level Domain (TLD) DNS Servers
- Authoritative DNS Servers
- Web Server
This hierarchical system of DNS servers ensures that when you type a domain name into your web browser, it can be translated into the correct IP address, allowing you to access the desired webpage on the internet.
For more information you can refer DNS Look-Up article.
What is DNS Resolver?
DNS Resolver is simply called a DNS Client and has the functionality for initiating the process of DNS Lookup which is also called DNS Resolution. By using the DNS Resolver, applications can easily access different websites and services present on the Internet by using domain names that are very much friendly to the user and that also resolves the problem of remembering IP Address.
What Are the Types of DNS Queries?
There are basically three types of DNS Queries that occur in DNS Lookup. These are stated below.
- Recursive Query: In this query, if the resolver is unable to find the record, in that case, DNS client wants the DNS Server will respond to the client in any way like with the requested source record or an error message.
- Iterative Query: Iterative Query is the query in which DNS Client wants the best answer possible from the DNS Server.
- Non-Recursive Query: Non-Recursive Query is the query that occurs when a DNS Resolver queries a DNS Server for some record that has access to it because of the record that exists in its cache.
What is DNS Caching?
DNS Caching can be simply termed as the process used by DNS Resolvers for storing the previously resolved information of DNS that contains domain names, and IP Addresses for some time. The main principle of DNS Caching is to speed up the process of future DNS lookup and also help in reducing the overall time of DNS Resolution.
FAQs On Domain Name System (DNS)
Q.1: What do you mean by level 3 DNS Server?
Answer:
Level 3 can be termed as a third-party DNS Server that is completely free and open to the public.
Q.2: Is Domain Name System (DNS) a protocol?
Answer:
Domain Name System (DNS) is a protocol that is used to convert easily readable names for communicating over the network, instead of remembering IP Address.
Q.3: How can you categorize a DNS as a TCP or UDP?
Answer:
DNS is designed to be used in both the ways like as a TCP or as a UDP. It converts to TCP when it is not able to communicate on TCP.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...