Scrum for Agile, is a dynamic and collaborative framework, has emerged as a cornerstone for Agile product management teams seeking effective ways to navigate the complexities of modern software development. Designed to enhance flexibility and responsiveness, Scrum for Agile provides a structured approach to project management, emphasizing iterative progress, continuous improvement, and close collaboration among team members.

Scrum for Agile Product Management Teams
What is a Product Management Team?
The product management team is a multi-faceted team responsible for guiding a product throughout its lifecycle. Made up of professionals from various backgrounds such as product managers, designers, manufacturers and market researchers, the team works at the intersection of business strategy, user experience and technical implementation. Their role focuses on the creation and implementation of comprehensive production systems. Product managers on the team are tasked with defining a product vision, aligning it with organizational objectives, and developing a roadmap that outlines sequential improvement steps
Continuity is a key attribute of the product management team, as effective communication with cross-functional teams is required to ensure that the final product is aligned with market needs and business objectives Throughout the development process in the team overcomes various challenges from concept and design to implementation and design . Essentially, the product management team acts as the coordinator of the entire production process, ensuring that the final product not only meets customer expectations but also makes a meaningful contribution to the overall execution of the business well. Their responsibilities include market research, competitor analysis, product prioritization, and constant adaptation to market trends, making them key contributors to any organization’s innovation and growth.
What is Scrum for Agile Product Management Teams?
Scrum is an agile project management framework designed to enhance collaboration, transparency, and adaptability in complex and dynamic development environments. Originating in software development, Scrum has found widespread application in various industries. At its core, Scrum for Agile provides a structured yet flexible framework for teams to iteratively and incrementally develop high-quality products. The framework operates on the principles of transparency, inspection, and adaptation.
A Scrum team, typically small and cross-functional, consists of three primary roles: the Product Owner, responsible for prioritizing and representing stakeholder interests; the Scrum Master, facilitating the Scrum process and ensuring adherence to principles; and the Development Team, self-organizing professionals responsible for delivering a potentially shippable product increment.
Scrum for Agile organizes work into fixed-length iterations called sprints, usually lasting two to four weeks. Key events include Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-up, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective. These events, combined with artifacts like the product backlog and burndown charts, create a framework that fosters collaboration, continuous improvement, and the ability to respond quickly to changing requirements. Scrum’s simplicity and focus on delivering incremental value make it a powerful tool for teams aiming to navigate complexity and deliver products that meet evolving customer needs.
What is the Structure of a Scrum for Agile Team?
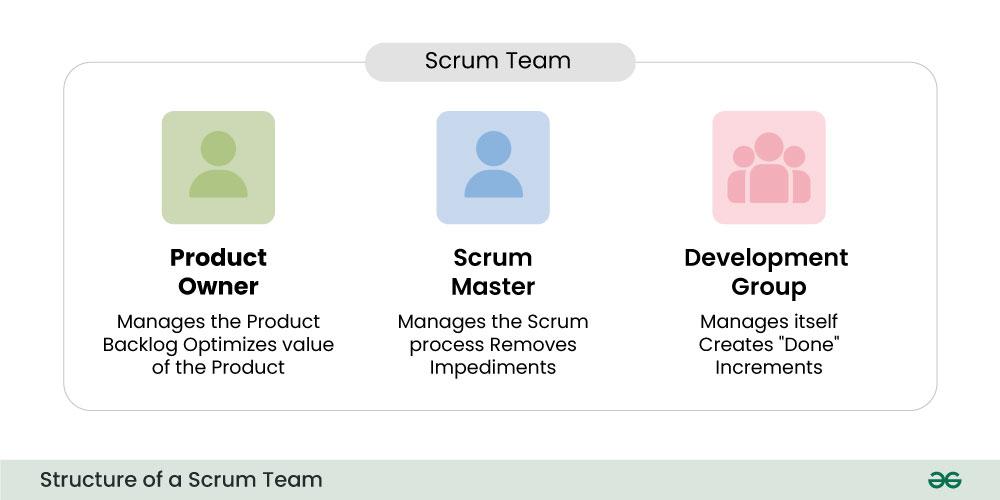
Structure of a scrum team
A Scrum for Agile Team is typically small, cross-functional, and self-organizing. It consists of three primary roles:
- Product Owner: Acts as a bridge between the product owner and the development team and stakeholders. They represent the interests and needs of the project or end users. More importantly, it is the product owner’s responsibility to define and prioritize the active list of backlogs, inventories, improvements, and repairs Appropriate decisions are made on which resources to drive each run to make it more valuable.
- Scrum Master: The Scrum Master has a key role to play in ensuring the successful implementation of the Scrum process. They act as a facilitator, guiding the team through the Scrum process and helping them understand and adhere to the Scrum principles. The Scrum Master is also a servant-leader, focusing on removing obstacles that hinder the team’s progress. Continuous improvement is an important part of their role, as they facilitate feedback to identify areas for improvement in the team’s processes.
- Development Group: The development team consists of professionals with the necessary skills to convert backlogs into exportable products. The team is self-organized, which means they have the autonomy to determine how to achieve their goals. Cross-functional means that there are a variety of different skill sets that are needed for end-to-end production within the team. This can include skills in design, regulation, testing, and related knowledge among others.
How does Scrum Work?
Scrum for agile framework is designed to manage and enhance the process of developing complex products. At its core, Scrum operates on the principles of transparency, inspection, and adaptation, providing a structured approach to deliver incremental value. Here’s a simple breakdown of how Scrum works:
- Sprints: The Scrum process is organized into fixed-length iterations called sprints, typically lasting two to four weeks. This time-boxed approach allows teams to focus on a specific set of tasks, fostering efficiency and adaptability. Each sprint begins with a Sprint Planning meeting and ends with a Sprint Review and a Sprint Retrospective.
- Sprint Planning: At the start of each sprint, the Scrum Team, consisting of the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team, collaborates to plan the work to be done. The Product Owner presents the prioritized items from the product backlog, a dynamic list of features and tasks. The team discusses and decides which items to include in the upcoming sprint, creating a sprint backlog—a list of tasks to be completed during the sprint.
- Daily Stand-up: Throughout the sprint, the team engages in a short, daily meeting known as the Daily Stand-up or Daily Scrum. Each team member provides a brief update on their progress, sharing what they’ve accomplished since the last meeting, what they plan to work on next, and any impediments they are facing. This quick, focused interaction ensures everyone is aligned, impediments are addressed promptly, and the team stays on track.
- Sprint Review: At the end of the sprint, the team conducts a Sprint Review, showcasing the completed work to stakeholders. This provides an opportunity for stakeholders to provide feedback and ensures that the product is evolving in alignment with expectations. The Product Owner evaluates the increment against the acceptance criteria, and the team discusses what was achieved during the sprint.
- Sprint backward-looking: This reflective session allows team members to discuss what went well during the sprint and what could be improved. It is a crucial component of continuous improvement, fostering a culture of learning and adaptability. The insights gained from the retrospective contribute to refining and optimizing the team’s processes in the next sprint.
Various tools support Scrum implementation, including project management tools like Jira, Trello, or Asana. These tools assist in managing the product backlog, tracking sprint progress, and visualizing team workflows.
Scrum Tools
- Jira: Jira is a versatile project management tool that is widely used in the software development industry. It provides a centralized platform for Scrum teams to manage their product backlog, which is a prioritized list of features and tasks. Teams can easily create, prioritize, and update backlog items in Jira, ensuring everyone is aligned on what needs to be done.
- Trello: Trello is a visual collaboration tool that is particularly effective for managing tasks and workflows in a Scrum environment. It uses boards, lists, and cards to help teams organize and prioritize their work. Trello’s intuitive interface allows teams to quickly grasp the status of tasks, making it easier to track sprint progress and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Asana: Asana is another project management tool that supports Scrum practices. It offers features for creating and managing tasks, tracking work progress, and collaborating on projects. Asana’s flexibility allows Scrum teams to adapt their workflows to fit the specific needs of their projects, making it a versatile choice for product management teams.
These tools assist in managing the product backlog, a crucial aspect of Scrum. The product backlog is a dynamic list of features, enhancements, and bug fixes that need attention. Project management tools make it easy to create, prioritize, and update backlog items, ensuring that the team is working on the most valuable tasks first.
Mistakes to be Avoided by Scrum for Agile Teams:
1. Lack of Clear Product Vision:
A fundamental mistake that Scrum teams should avoid is the absence of a clear product vision. Without a well-defined goal or direction, the team may find it challenging to prioritize tasks effectively and deliver value to the customer. A robust product vision aligns the team towards a common objective, guiding decision-making and ensuring that the product meets both business and user needs.
2. Ignoring the Scrum Values:
The Scrum framework is built on a set of values—commitment, courage, focus, openness, and respect. Ignoring or neglecting these values can undermine the effectiveness of the Scrum process. Teams must actively incorporate these principles into their daily work, fostering a collaborative and positive environment. Commitment to goals, the courage to address challenges, focus on delivering value, openness to feedback, and respect for team members are essential for a successful Scrum implementation.
3. Overcommitting in Sprints:
Setting unrealistic goals or commitments within a sprint can have detrimental effects on the team. Overcommitting often leads to burnout as team members struggle to meet unattainable targets. Additionally, compromised product quality may result from rushed development. Scrum teams should carefully plan and prioritize during sprint planning, ensuring that commitments are realistic and achievable within the defined timeframe.
4. Poor Communication:
Effective communication is the lifeblood of Scrum. Poor communication can result in misunderstandings, delays, and a breakdown of collaboration. Transparency is a key principle in Scrum, and teams must communicate openly about progress, challenges, and changes. Regular communication through daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives helps maintain a shared understanding of the project’s status, prevents surprises, and enables timely adjustments to the plan.
Implementing Scrum in product management teams offers a structured yet flexible approach to product development. By embracing the iterative and collaborative nature of Scrum, teams can respond effectively to changing requirements and deliver high-quality products. However, success requires adherence to Scrum principles, effective communication, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Avoiding common mistakes and leveraging appropriate tools further enhances the likelihood of achieving successful outcomes in product management with Scrum.
Conclusion
Scrum for Agile is like a guiding light product management teams. It’s a smart way of working together that helps teams adapt quickly to changes, improve their work continuously, and deliver valuable products step by step. With its clear roles and routines, Scrum keeps everyone on the same page and makes the development process dynamic and responsive.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...