Replacing elements of a collection in Julia – replace() and replace!() Methods
Last Updated :
01 Apr, 2020
The replace() is an inbuilt function in julia which is used to return a copy of the specified array with different types of replacement. These all operations are illustrated with below examples.
Syntax:
replace(A, old_new::Pair…; count::Integer)
or
replace(new::Function, A; count::Integer)
Parameters:
- A: Specified array.
- old_new::Pair: Specified values to get updated.
- count::Integer: This optional count value is used to replace at most count occurrences in total.
- new::Function: Specified set of instruction.
Returns: It returns a copy of the specified array with different types of replacement.
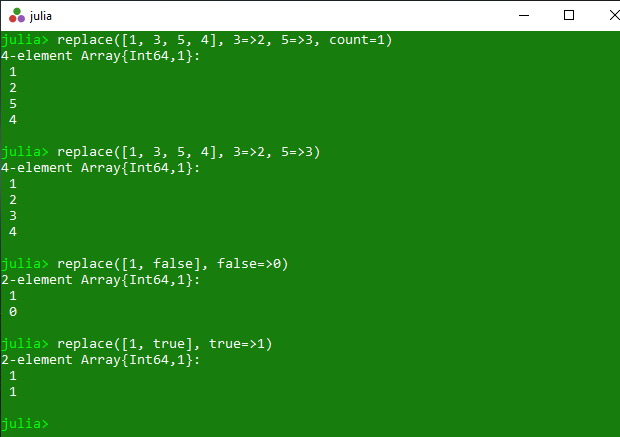
Example 1: This example returns a copy of the specified collection. In this collection old value get replaced with new value and if count is specified, then replace at most count occurrences in total.
println(replace([1, 3, 5, 4], 3 =>2, 5 =>3, count = 1))
println(replace([1, 3, 5, 4], 3 =>2, 5 =>3))
println(replace([1, false], false =>0))
println(replace([1, true], true =>1))
|
Output:
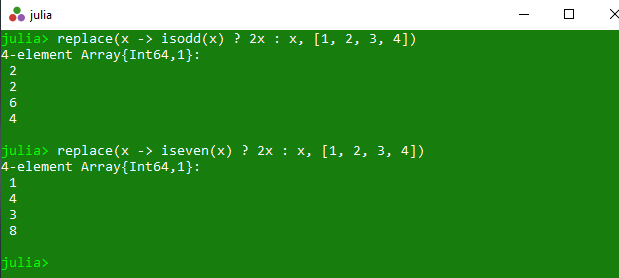
Example 2: This example returns a copy of a specified array where each value x in the array is replaced by new(x).
println(replace(x -> isodd(x) ? 2x : x, [1, 2, 3, 4]))
println(replace(x -> iseven(x) ? 2x : x, [1, 2, 3, 4]))
|
Output:
replace!()
The replace!() is an inbuilt function in julia which is used to return the replaced specified array with different types of replacement. These all operations are illustrated with below examples.
Syntax:
replace!(A, old_new::Pair…; count::Integer)
or
replace!(new::Function, A; count::Integer)
Parameters:
- A: Specified array.
- old_new::Pair: Specified values to get updated.
- count::Integer: This optional count value is used to replace at most count occurrences in total.
- new::Function: Specified set of instruction.
Returns: It returns the replaced array with different types of replacement method.
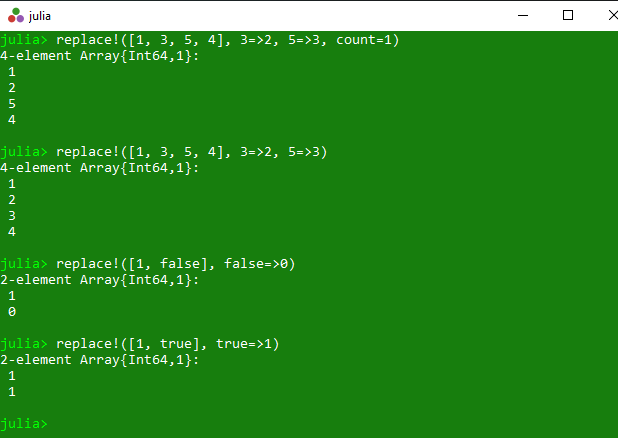
Example 1: This example returns the replaced collection. In this collection old value get replaced with new value and if count is specified, then replace at most count occurrences in total.
println(replace !([1, 3, 5, 4], 3 =>2, 5 =>3, count = 1))
println(replace !([1, 3, 5, 4], 3 =>2, 5 =>3))
println(replace !([1, false], false =>0))
println(replace !([1, true], true =>1))
|
Output:
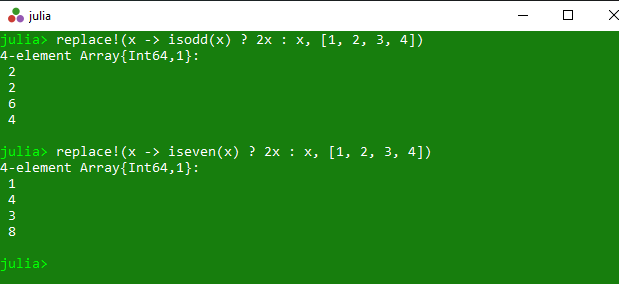
Example 2: This example returns the replaced specified array where each value x in the array is replaced by new(x).
println(replace !(x -> isodd(x) ? 2x : x, [1, 2, 3, 4]))
println(replace !(x -> iseven(x) ? 2x : x, [1, 2, 3, 4]))
|
Output:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...