Python | Pandas Series.rolling()
Last Updated :
07 Feb, 2019
Pandas series is a One-dimensional ndarray with axis labels. The labels need not be unique but must be a hashable type. The object supports both integer and label-based indexing and provides a host of methods for performing operations involving the index.
Pandas Series.rolling() function is a very useful function. It Provides rolling window calculations over the underlying data in the given Series object.
Syntax: Series.rolling(window, min_periods=None, center=False, win_type=None, on=None, axis=0, closed=None)
Parameter :
window : Size of the moving window
min_periods : Minimum number of observations in window required to have a value
center : Set the labels at the center of the window.
win_type : Provide a window type.
on : str, optional
axis : int or str, default 0
closed : Make the interval closed on the ‘right’, ‘left’, ‘both’ or ‘neither’ endpoints.
Returns : a Window or Rolling sub-classed for the particular operation
Example #1: Use Series.rolling() function to find the rolling window sum of the underlying data for the given Series object. The size of the rolling window should be 2 and the weightage of each element should be same.
import pandas as pd
sr = pd.Series([10, 25, 3, 11, 24, 6])
index_ = ['Coca Cola', 'Sprite', 'Coke', 'Fanta', 'Dew', 'ThumbsUp']
sr.index = index_
print(sr)
|
Output :
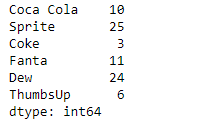
Now we will use Series.rolling() function to find the sum of the underlying data having a window size of 2.
result = sr.rolling(2).sum()
print(result)
|
Output :
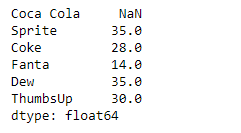
As we can see in the output, the Series.rolling() function has successfully returned a series object having found the sum of the underlying data over a window size of 2. Notice the first value is a missing value as there was no element previous to it so the sum could not be performed.
Example #2: Use Series.rolling() function to find the rolling window sum of the underlying data for the given Series object. The size of the rolling window should be 2 and the rolling window type should be ‘triang’.
import pandas as pd
sr = pd.Series([10, 25, 3, 11, 24, 6])
index_ = ['Coca Cola', 'Sprite', 'Coke', 'Fanta', 'Dew', 'ThumbsUp']
sr.index = index_
print(sr)
|
Output :
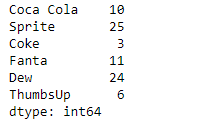
Now we will use Series.rolling() function to find the sum of the underlying data having a window size of 2.
result = sr.rolling(2, win_type ='triang').sum()
print(result)
|
Output :
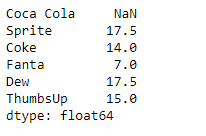
As we can see in the output, the Series.rolling() function has successfully returned a series object having found the sum of the underlying data over a window size of 2. Notice the first value is a missing value as there was no element previous to it so the sum could not be performed.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...