Push Relabel Algorithm | Set 2 (Implementation)
Last Updated :
28 Mar, 2024
We strongly recommend to refer below article before moving on to this article.
Push Relabel Algorithm | Set 1 (Introduction and Illustration)
Problem Statement:
Given a graph that represents a flow network where every edge has a capacity. Also given two vertices source ‘s’ and sink ‘t’ in the graph, find the maximum possible flow from s to t with following constraints:
- Flow on an edge doesn’t exceed the given capacity of the edge.
- Incoming flow is equal to outgoing flow for every vertex except s and t.
For example, consider the following graph from CLRS book.
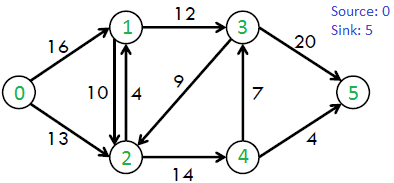
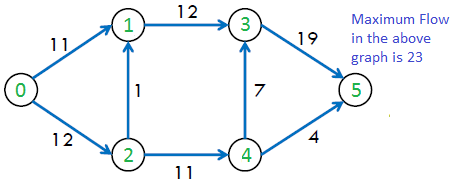
The maximum possible flow in the above graph is 23.
Push-Relabel Algorithm
1) Initialize PreFlow : Initialize Flows and Heights
2) While it is possible to perform a Push() or Relabel() on a vertex
// Or while there is a vertex that has excess flow
Do Push() or Relabel()
// At this point all vertices have Excess Flow as 0 (Except source
// and sink)
3) Return flow.
Below are main operations performed in Push Relabel algorithm.
There are three main operations in Push-Relabel Algorithm
1. Initialize PreFlow() It initializes heights and flows of all vertices.
Preflow()
1) Initialize height and flow of every vertex as 0.
2) Initialize height of source vertex equal to total
number of vertices in graph.
3) Initialize flow of every edge as 0.
4) For all vertices adjacent to source s, flow and
excess flow is equal to capacity initially.
2. Push() is used to make the flow from a node that has excess flow. If a vertex has excess flow and there is an adjacent with a smaller height (in the residual graph), we push the flow from the vertex to the adjacent with a lower height. The amount of pushed flow through the pipe (edge) is equal to the minimum of excess flow and capacity of the edge.
3. Relabel() operation is used when a vertex has excess flow and none of its adjacents is at the lower height. We basically increase the height of the vertex so that we can perform push(). To increase height, we pick the minimum height adjacent (in residual graph, i.e., an adjacent to whom we can add flow) and add 1 to it.
Implementation:
The following implementation uses the below structure for representing a flow network.
struct Vertex
{
int h; // Height of node
int e_flow; // Excess Flow
}
struct Edge
{
int u, v; // Edge is from u to v
int flow; // Current flow
int capacity;
}
class Graph
{
Edge edge[]; // Array of edges
Vertex ver[]; // Array of vertices
}
The below code uses the given graph itself as a flow network and residual graph. We have not created a separate graph for the residual graph and have used the same graph for simplicity.
Implementation:
C++
// C++ program to implement push-relabel algorithm for
// getting maximum flow of graph
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Edge
{
// To store current flow and capacity of edge
int flow, capacity;
// An edge u--->v has start vertex as u and end
// vertex as v.
int u, v;
Edge(int flow, int capacity, int u, int v)
{
this->flow = flow;
this->capacity = capacity;
this->u = u;
this->v = v;
}
};
// Represent a Vertex
struct Vertex
{
int h, e_flow;
Vertex(int h, int e_flow)
{
this->h = h;
this->e_flow = e_flow;
}
};
// To represent a flow network
class Graph
{
int V; // No. of vertices
vector<Vertex> ver;
vector<Edge> edge;
// Function to push excess flow from u
bool push(int u);
// Function to relabel a vertex u
void relabel(int u);
// This function is called to initialize
// preflow
void preflow(int s);
// Function to reverse edge
void updateReverseEdgeFlow(int i, int flow);
public:
Graph(int V); // Constructor
// function to add an edge to graph
void addEdge(int u, int v, int w);
// returns maximum flow from s to t
int getMaxFlow(int s, int t);
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
// all vertices are initialized with 0 height
// and 0 excess flow
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
ver.push_back(Vertex(0, 0));
}
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v, int capacity)
{
// flow is initialized with 0 for all edge
edge.push_back(Edge(0, capacity, u, v));
}
void Graph::preflow(int s)
{
// Making h of source Vertex equal to no. of vertices
// Height of other vertices is 0.
ver[s].h = ver.size();
//
for (int i = 0; i < edge.size(); i++)
{
// If current edge goes from source
if (edge[i].u == s)
{
// Flow is equal to capacity
edge[i].flow = edge[i].capacity;
// Initialize excess flow for adjacent v
ver[edge[i].v].e_flow += edge[i].flow;
// Add an edge from v to s in residual graph with
// capacity equal to 0
edge.push_back(Edge(-edge[i].flow, 0, edge[i].v, s));
}
}
}
// returns index of overflowing Vertex
int overFlowVertex(vector<Vertex>& ver)
{
for (int i = 1; i < ver.size() - 1; i++)
if (ver[i].e_flow > 0)
return i;
// -1 if no overflowing Vertex
return -1;
}
// Update reverse flow for flow added on ith Edge
void Graph::updateReverseEdgeFlow(int i, int flow)
{
int u = edge[i].v, v = edge[i].u;
for (int j = 0; j < edge.size(); j++)
{
if (edge[j].v == v && edge[j].u == u)
{
edge[j].flow -= flow;
return;
}
}
// adding reverse Edge in residual graph
Edge e = Edge(0, flow, u, v);
edge.push_back(e);
}
// To push flow from overflowing vertex u
bool Graph::push(int u)
{
// Traverse through all edges to find an adjacent (of u)
// to which flow can be pushed
for (int i = 0; i < edge.size(); i++)
{
// Checks u of current edge is same as given
// overflowing vertex
if (edge[i].u == u)
{
// if flow is equal to capacity then no push
// is possible
if (edge[i].flow == edge[i].capacity)
continue;
// Push is only possible if height of adjacent
// is smaller than height of overflowing vertex
if (ver[u].h > ver[edge[i].v].h)
{
// Flow to be pushed is equal to minimum of
// remaining flow on edge and excess flow.
int flow = min(edge[i].capacity - edge[i].flow,
ver[u].e_flow);
// Reduce excess flow for overflowing vertex
ver[u].e_flow -= flow;
// Increase excess flow for adjacent
ver[edge[i].v].e_flow += flow;
// Add residual flow (With capacity 0 and negative
// flow)
edge[i].flow += flow;
updateReverseEdgeFlow(i, flow);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// function to relabel vertex u
void Graph::relabel(int u)
{
// Initialize minimum height of an adjacent
int mh = INT_MAX;
// Find the adjacent with minimum height
for (int i = 0; i < edge.size(); i++)
{
if (edge[i].u == u)
{
// if flow is equal to capacity then no
// relabeling
if (edge[i].flow == edge[i].capacity)
continue;
// Update minimum height
if (ver[edge[i].v].h < mh)
{
mh = ver[edge[i].v].h;
// updating height of u
ver[u].h = mh + 1;
}
}
}
}
// main function for printing maximum flow of graph
int Graph::getMaxFlow(int s, int t)
{
preflow(s);
// loop until none of the Vertex is in overflow
while (overFlowVertex(ver) != -1)
{
int u = overFlowVertex(ver);
if (!push(u))
relabel(u);
}
// ver.back() returns last Vertex, whose
// e_flow will be final maximum flow
return ver.back().e_flow;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
int V = 6;
Graph g(V);
// Creating above shown flow network
g.addEdge(0, 1, 16);
g.addEdge(0, 2, 13);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 10);
g.addEdge(2, 1, 4);
g.addEdge(1, 3, 12);
g.addEdge(2, 4, 14);
g.addEdge(3, 2, 9);
g.addEdge(3, 5, 20);
g.addEdge(4, 3, 7);
g.addEdge(4, 5, 4);
// Initialize source and sink
int s = 0, t = 5;
cout << "Maximum flow is " << g.getMaxFlow(s, t);
return 0;
}
import java.util.*;
// Class to represent an edge in the graph
class Edge {
int flow, capacity, u, v;
// Constructor for Edge class
public Edge(int flow, int capacity, int u, int v) {
this.flow = flow;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.u = u;
this.v = v;
}
}
// Class to represent a vertex in the graph
class Vertex {
int h, e_flow;
// Constructor for Vertex class
public Vertex(int h, int e_flow) {
this.h = h;
this.e_flow = e_flow;
}
}
// Class to represent a graph
class Graph {
int V; // Number of vertices
List<Vertex> ver; // List of vertices
List<Edge> edge; // List of edges
// Constructor for Graph class
public Graph(int V) {
this.V = V;
ver = new ArrayList<>();
edge = new ArrayList<>();
// Initialize all vertices with 0 height and 0 excess flow
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
ver.add(new Vertex(0, 0));
}
// Method to add an edge to the graph
public void addEdge(int u, int v, int capacity) {
// Add an edge with 0 flow
edge.add(new Edge(0, capacity, u, v));
}
// Method to initialize preflow
public void preflow(int s) {
// Set height of source equal to total number of vertices
ver.get(s).h = ver.size();
// Initialize flow of edges going from source
for (int i = 0; i < edge.size(); i++) {
if (edge.get(i).u == s) {
// Flow is equal to capacity
edge.get(i).flow = edge.get(i).capacity;
// Initialize excess flow for adjacent vertex
ver.get(edge.get(i).v).e_flow += edge.get(i).flow;
// Add reverse edge in residual graph
edge.add(new Edge(-edge.get(i).flow, 0, edge.get(i).v, s));
}
}
}
// Method to return index of overflowing vertex
public int overFlowVertex() {
for (int i = 1; i < ver.size() - 1; i++)
if (ver.get(i).e_flow > 0)
return i;
// Return -1 if no overflowing vertex
return -1;
}
// Method to update reverse flow for flow added on ith edge
public void updateReverseEdgeFlow(int i, int flow) {
int u = edge.get(i).v, v = edge.get(i).u;
// Find edge
for (int j = 0; j < edge.size(); j++) {
if (edge.get(j).v == v && edge.get(j).u == u) {
edge.get(j).flow -= flow;
return;
}
}
// Add reverse edge in residual graph
Edge e = new Edge(0, flow, u, v);
edge.add(e);
}
// Method to push flow from vertex u
public boolean push(int u) {
// Traverse through all edges to find an adjacent vertex
for (int i = 0; i < edge.size(); i++) {
// Check if u of current edge is same as given overflowing vertex
if (edge.get(i).u == u) {
// If flow is equal to capacity then no push is possible
if (edge.get(i).flow == edge.get(i).capacity)
continue;
// Push is only possible if height of adjacent vertex is smaller than height of overflowing vertex
if (ver.get(u).h > ver.get(edge.get(i).v).h) {
// Flow to be pushed is equal to minimum of remaining flow on edge and excess flow
int flow = Math.min(edge.get(i).capacity - edge.get(i).flow,
ver.get(u).e_flow);
// Reduce excess flow for overflowing vertex
ver.get(u).e_flow -= flow;
// Increase excess flow for adjacent vertex
ver.get(edge.get(i).v).e_flow += flow;
// Increase flow along the edge
edge.get(i).flow += flow;
// Update reverse edge
updateReverseEdgeFlow(i, flow);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// Method to relabel vertex u
public void relabel(int u) {
int mh = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// Find adjacent vertex with minimum height
for (int i = 0; i < edge.size(); i++) {
if (edge.get(i).u == u) {
// If flow is equal to capacity then no relabeling
if (edge.get(i).flow == edge.get(i).capacity)
continue;
// Update minimum height
if (ver.get(edge.get(i).v).h < mh) {
mh = ver.get(edge.get(i).v).h;
// Update height of u
ver.get(u).h = mh + 1;
}
}
}
}
// Method to get maximum flow from source s to sink t
public int getMaxFlow(int s, int t) {
preflow(s);
// Loop until none of the vertices is in overflow
while (overFlowVertex() != -1) {
int u = overFlowVertex();
if (!push(u))
relabel(u);
}
// Return excess flow of sink
return ver.get(ver.size() - 1).e_flow;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int V = 6;
Graph g = new Graph(V);
// Creating the graph
g.addEdge(0, 1, 16);
g.addEdge(0, 2, 13);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 10);
g.addEdge(2, 1, 4);
g.addEdge(1, 3, 12);
g.addEdge(2, 4, 14);
g.addEdge(3, 2, 9);
g.addEdge(3, 5, 20);
g.addEdge(4, 3, 7);
g.addEdge(4, 5, 4);
int s = 0, t = 5;
// Print the maximum flow from source to sink
System.out.println("Maximum flow is " + g.getMaxFlow(s, t));
}
}
// C# program to implement push-relabel algorithm for
// getting maximum flow of graph
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Collections;
using System.Linq;
class Edge
{
public int flow;
public int capacity;
public int u;
public int v;
public Edge(int flow,int capacity,int u,int v)
{
this.flow = flow;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.u = u;
this.v = v;
}
}
// Represent a Vertex
class Vertex
{
public int h;
public int e_flow;
public Vertex(int h,int e_flow)
{
this.h = h;
this.e_flow = e_flow;
}
}
// To represent a flow network
class Graph
{
public int V; // No. of vertices
public List<Vertex> ver;
public List<Edge> edge;
public Graph(int V)
{
this.V = V;
ver = new List<Vertex>();
edge = new List<Edge>();
// all vertices are initialized with 0 height
// and 0 excess flow
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
ver.Add(new Vertex(0, 0));
}
public void addEdge(int u,int v,int capacity)
{
// flow is initialized with 0 for all edge
edge.Add(new Edge(0, capacity, u, v));
}
public void preflow(int s)
{
// Making h of source Vertex equal to no. of vertices
// Height of other vertices is 0.
ver[s].h = ver.Count;
//
for (int i = 0; i < edge.Count; i++)
{
// If current edge goes from source
if (edge[i].u == s)
{
// Flow is equal to capacity
edge[i].flow = edge[i].capacity;
// Initialize excess flow for adjacent v
ver[edge[i].v].e_flow += edge[i].flow;
// Add an edge from v to s in residual graph with
// capacity equal to 0
edge.Add(new Edge(-edge[i].flow, 0, edge[i].v, s));
}
}
}
// returns index of overflowing Vertex
public int overFlowVertex()
{
for (int i = 1; i < ver.Count - 1; i++)
if (ver[i].e_flow > 0)
return i;
// -1 if no overflowing Vertex
return -1;
}
// Update reverse flow for flow added on ith Edge
public void updateReverseEdgeFlow(int i,int flow)
{
int u = edge[i].v;
int v = edge[i].u;
for (int j = 0; j < edge.Count; j++)
{
if (edge[j].v == v && edge[j].u == u)
{
edge[j].flow -= flow;
return;
}
}
// adding reverse Edge in residual graph
Edge e = new Edge(0, flow, u, v);
edge.Add(e);
}
// To push flow from overflowing vertex u
public bool push(int u)
{
// Traverse through all edges to find an adjacent (of u)
// to which flow can be pushed
for (int i = 0; i < edge.Count; i++)
{
// Checks u of current edge is same as given
// overflowing vertex
if (edge[i].u == u)
{
// if flow is equal to capacity then no push
// is possible
if (edge[i].flow == edge[i].capacity)
continue;
// Push is only possible if height of adjacent
// is smaller than height of overflowing vertex
if (ver[u].h > ver[edge[i].v].h)
{
// Flow to be pushed is equal to minimum of
// remaining flow on edge and excess flow.
int flow = Math.Min(edge[i].capacity - edge[i].flow,
ver[u].e_flow);
// Reduce excess flow for overflowing vertex
ver[u].e_flow -= flow;
// Increase excess flow for adjacent
ver[edge[i].v].e_flow += flow;
// Add residual flow (With capacity 0 and negative
// flow)
edge[i].flow += flow;
updateReverseEdgeFlow(i, flow);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// function to relabel vertex u
public void relabel(int u)
{
// Initialize minimum height of an adjacent
int mh = 2100000;
// Find the adjacent with minimum height
for (int i = 0; i < edge.Count; i++)
{
if (edge[i].u == u)
{
// if flow is equal to capacity then no
// relabeling
if (edge[i].flow == edge[i].capacity)
continue;
// Update minimum height
if (ver[edge[i].v].h < mh)
{
mh = ver[edge[i].v].h;
// updating height of u
ver[u].h = mh + 1;
}
}
}
}
// main function for printing maximum flow of graph
public int getMaxFlow(int s,int t)
{
preflow(s);
// loop until none of the Vertex is in overflow
while (overFlowVertex() != -1)
{
int u = overFlowVertex();
if (!push(u))
relabel(u);
}
// ver.back() returns last Vertex, whose
// e_flow will be final maximum flow
return ver[ver.Count-1].e_flow;
}
}
class HelloWorld {
static void Main() {
// Driver program to test above functions
int V = 6;
Graph g = new Graph(V);
// Creating above shown flow network
g.addEdge(0, 1, 16);
g.addEdge(0, 2, 13);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 10);
g.addEdge(2, 1, 4);
g.addEdge(1, 3, 12);
g.addEdge(2, 4, 14);
g.addEdge(3, 2, 9);
g.addEdge(3, 5, 20);
g.addEdge(4, 3, 7);
g.addEdge(4, 5, 4);
// Initialize source and sink
int s = 0, t = 5;
Console.WriteLine("Maximum flow is " + g.getMaxFlow(s, t));
}
}
// The code is contributed by Arushi jindal.
// javascript program to implement push-relabel algorithm for
// getting maximum flow of graph
class Edge
{
constructor(flow, capacity, u, v)
{
this.flow = flow;
this.capacity = capacity;
this.u = u;
this.v = v;
}
}
// Represent a Vertex
class Vertex
{
constructor(h, e_flow)
{
this.h = h;
this.e_flow = e_flow;
}
}
// To represent a flow network
class Graph
{
// int V; // No. of vertices
// vector<Vertex> ver;
// vector<Edge> edge;
constructor(V)
{
this.V = V;
this.edge = new Array();
this.ver = new Array();
// all vertices are initialized with 0 height
// and 0 excess flow
for (let i = 0; i < V; i++)
this.ver.push(new Vertex(0, 0));
}
addEdge(u, v, capacity)
{
// flow is initialized with 0 for all edge
this.edge.push(new Edge(0, capacity, u, v));
}
preflow(s)
{
// Making h of source Vertex equal to no. of vertices
// Height of other vertices is 0.
this.ver[s].h = this.ver.length;
//
for (let i = 0; i < this.edge.length; i++)
{
// If current edge goes from source
if (this.edge[i].u == s)
{
// Flow is equal to capacity
this.edge[i].flow = this.edge[i].capacity;
// Initialize excess flow for adjacent v
this.ver[this.edge[i].v].e_flow += this.edge[i].flow;
// Add an edge from v to s in residual graph with
// capacity equal to 0
this.edge.push(new Edge(-this.edge[i].flow, 0, this.edge[i].v, s));
}
}
}
// returns index of overflowing Vertex
overFlowVertex()
{
for (let i = 1; i < this.ver.length - 1; i++)
if (this.ver[i].e_flow > 0)
return i;
// -1 if no overflowing Vertex
return -1;
}
// Update reverse flow for flow added on ith Edge
updateReverseEdgeFlow(i, flow)
{
let u = this.edge[i].v;
let v = this.edge[i].u;
for (let j = 0; j < this.edge.length; j++)
{
if (this.edge[j].v == v && this.edge[j].u == u)
{
this.edge[j].flow -= flow;
return;
}
}
// adding reverse Edge in residual graph
let e = new Edge(0, flow, u, v);
this.edge.push(e);
}
// To push flow from overflowing vertex u
push(u)
{
// Traverse through all edges to find an adjacent (of u)
// to which flow can be pushed
for (let i = 0; i < this.edge.length; i++)
{
// Checks u of current edge is same as given
// overflowing vertex
if (this.edge[i].u == u)
{
// if flow is equal to capacity then no push
// is possible
if (this.edge[i].flow == this.edge[i].capacity)
continue;
// Push is only possible if height of adjacent
// is smaller than height of overflowing vertex
if (this.ver[u].h > this.ver[this.edge[i].v].h)
{
// Flow to be pushed is equal to minimum of
// remaining flow on edge and excess flow.
let flow = Math.min(this.edge[i].capacity - this.edge[i].flow,
this.ver[u].e_flow);
// Reduce excess flow for overflowing vertex
this.ver[u].e_flow -= flow;
// Increase excess flow for adjacent
this.ver[this.edge[i].v].e_flow += flow;
// Add residual flow (With capacity 0 and negative
// flow)
this.edge[i].flow += flow;
this.updateReverseEdgeFlow(i, flow);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
// function to relabel vertex u
relabel(u)
{
// Initialize minimum height of an adjacent
let mh = 2100000;
// Find the adjacent with minimum height
for (let i = 0; i < this.edge.length; i++)
{
if (this.edge[i].u == u)
{
// if flow is equal to capacity then no
// relabeling
if (this.edge[i].flow == this.edge[i].capacity)
continue;
// Update minimum height
if (this.ver[this.edge[i].v].h < mh)
{
mh = this.ver[this.edge[i].v].h;
// updating height of u
this.ver[u].h = mh + 1;
}
}
}
}
// main function for printing maximum flow of graph
getMaxFlow(s, t)
{
this.preflow(s);
// loop until none of the Vertex is in overflow
while (this.overFlowVertex() != -1)
{
let u = this.overFlowVertex();
if (!this.push(u))
this.relabel(u);
}
// ver.back() returns last Vertex, whose
// e_flow will be final maximum flow
return this.ver[this.ver.length-1].e_flow;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
let V = 6;
let g = new Graph(V);
// Creating above shown flow network
g.addEdge(0, 1, 16);
g.addEdge(0, 2, 13);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 10);
g.addEdge(2, 1, 4);
g.addEdge(1, 3, 12);
g.addEdge(2, 4, 14);
g.addEdge(3, 2, 9);
g.addEdge(3, 5, 20);
g.addEdge(4, 3, 7);
g.addEdge(4, 5, 4);
// Initialize source and sink
let s = 0, t = 5;
console.log("Maximum flow is " + g.getMaxFlow(s, t));
// The code is contributed by Nidhi goel.
# python program to implement push-relabel algorithm for
# getting maximum flow of graph
class Edge:
def __init__(self, flow, capacity, u, v):
self.flow = flow
self.capacity = capacity
self.u = u
self.v = v
# Represent a Vertex
class Vertex:
def __init__(self, h, e_flow):
self.h = h
self.e_flow = e_flow
# To represent a flow network
class Graph:
# int V; # No. of vertices
# vector<Vertex> ver;
# vector<Edge> edge;
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V;
self.edge = []
self.ver = []
# all vertices are initialized with 0 height
# and 0 excess flow
for i in range(V):
self.ver.append(Vertex(0, 0))
def addEdge(self, u, v, capacity):
# flow is initialized with 0 for all edge
self.edge.append(Edge(0, capacity, u, v))
def preflow(self, s):
# Making h of source Vertex equal to no. of vertices
# Height of other vertices is 0.
self.ver[s].h = len(self.ver);
for i in range(len(self.edge)):
# If current edge goes from source
if (self.edge[i].u == s):
# Flow is equal to capacity
self.edge[i].flow = self.edge[i].capacity
# Initialize excess flow for adjacent v
self.ver[self.edge[i].v].e_flow += self.edge[i].flow
# Add an edge from v to s in residual graph with
# capacity equal to 0
self.edge.append(Edge(-self.edge[i].flow, 0, self.edge[i].v, s))
# returns index of overflowing Vertex
def overFlowVertex(self):
for i in range(1, len(self.ver)-1):
if(self.ver[i].e_flow > 0):
return i
# -1 if no overflowing Vertex
return -1
# Update reverse flow for flow added on ith Edge
def updateReverseEdgeFlow(self, i, flow):
u = self.edge[i].v
v = self.edge[i].u
for j in range(0, len(self.edge)):
if (self.edge[j].v == v and self.edge[j].u == u):
self.edge[j].flow -= flow
return
# adding reverse Edge in residual graph
e = Edge(0, flow, u, v)
self.edge.append(e)
# To push flow from overflowing vertex u
def push(self, u):
# Traverse through all edges to find an adjacent (of u)
# to which flow can be pushed
for i in range(0, len(self.edge)):
# Checks u of current edge is same as given
# overflowing vertex
if (self.edge[i].u == u):
# if flow is equal to capacity then no push
# is possible
if (self.edge[i].flow == self.edge[i].capacity):
continue;
# Push is only possible if height of adjacent
# is smaller than height of overflowing vertex
if (self.ver[u].h > self.ver[self.edge[i].v].h):
# Flow to be pushed is equal to minimum of
# remaining flow on edge and excess flow.
flow = min(self.edge[i].capacity - self.edge[i].flow, self.ver[u].e_flow)
# Reduce excess flow for overflowing vertex
self.ver[u].e_flow -= flow;
# Increase excess flow for adjacent
self.ver[self.edge[i].v].e_flow += flow;
# Add residual flow (With capacity 0 and negative
# flow)
self.edge[i].flow += flow;
self.updateReverseEdgeFlow(i, flow);
return True;
return False;
# function to relabel vertex u
def relabel(self, u):
# Initialize minimum height of an adjacent
mh = 2100000
# Find the adjacent with minimum height
for i in range(len(self.edge)):
if (self.edge[i].u == u):
# if flow is equal to capacity then no
# relabeling
if (self.edge[i].flow == self.edge[i].capacity):
continue;
# Update minimum height
if (self.ver[self.edge[i].v].h < mh):
mh = self.ver[self.edge[i].v].h;
# updating height of u
self.ver[u].h = mh + 1;
# main function for printing maximum flow of graph
def getMaxFlow(self, s, t):
self.preflow(s);
# loop until none of the Vertex is in overflow
while (self.overFlowVertex() != -1):
u = self.overFlowVertex();
if (self.push(u) == False):
self.relabel(u);
# ver.back() returns last Vertex, whose
# e_flow will be final maximum flow
return self.ver[len(self.ver)-1].e_flow
# Driver program to test above functions
V = 6;
g = Graph(V);
# Creating above shown flow network
g.addEdge(0, 1, 16);
g.addEdge(0, 2, 13);
g.addEdge(1, 2, 10);
g.addEdge(2, 1, 4);
g.addEdge(1, 3, 12);
g.addEdge(2, 4, 14);
g.addEdge(3, 2, 9);
g.addEdge(3, 5, 20);
g.addEdge(4, 3, 7);
g.addEdge(4, 5, 4);
# Initialize source and sink
s = 0
t = 5;
print("Maximum flow is ", g.getMaxFlow(s, t));
# The code is contributed by Arushi goel.
The code in this article is contributed by Siddharth Lalwani and Utkarsh Trivedi.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...