PriorityQueue in Java
Last Updated :
10 Apr, 2023
A PriorityQueue is used when the objects are supposed to be processed based on the priority. It is known that a Queue follows the First-In-First-Out algorithm, but sometimes the elements of the queue are needed to be processed according to the priority, that’s when the PriorityQueue comes into play.
The PriorityQueue is based on the priority heap. The elements of the priority queue are ordered according to the natural ordering, or by a Comparator provided at queue construction time, depending on which constructor is used.

In the below priority queue, an element with a maximum ASCII value will have the highest priority.
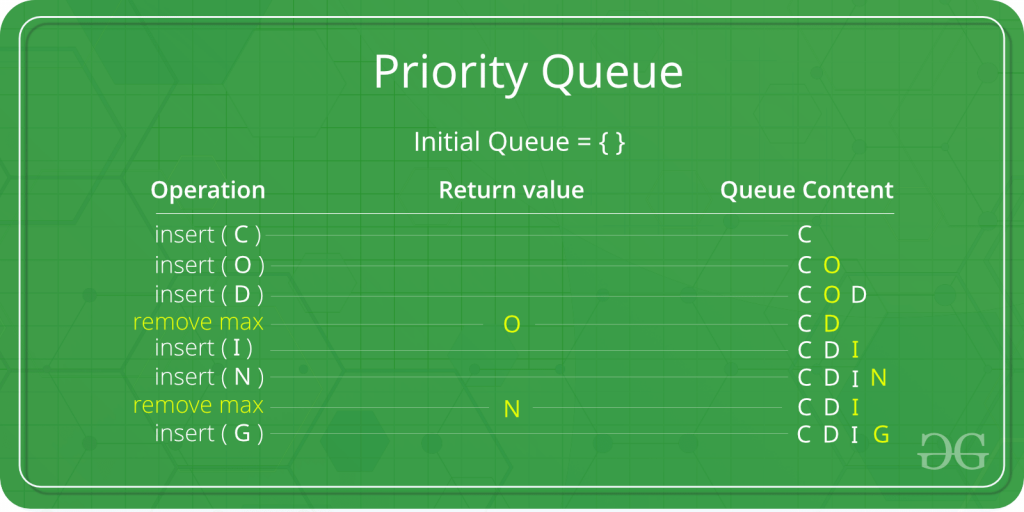
Declaration:
public class PriorityQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E> implements Serializable
where E is the type of elements held in this queue
The class implements Serializable, Iterable<E>, Collection<E>, Queue<E> interfaces.
A few important points on Priority Queue are as follows:
- PriorityQueue doesn’t permit null.
- We can’t create a PriorityQueue of Objects that are non-comparable
- PriorityQueue are unbound queues.
- The head of this queue is the least element with respect to the specified ordering. If multiple elements are tied for the least value, the head is one of those elements — ties are broken arbitrarily.
- Since PriorityQueue is not thread-safe, java provides PriorityBlockingQueue class that implements the BlockingQueue interface to use in a java multithreading environment.
- The queue retrieval operations poll, remove, peek, and element access the element at the head of the queue.
- It provides O(log(n)) time for add and poll methods.
- It inherits methods from AbstractQueue, AbstractCollection, Collection, and Object class.
Constructors:
1. PriorityQueue(): Creates a PriorityQueue with the default initial capacity (11) that orders its elements according to their natural ordering.
PriorityQueue<E> pq = new PriorityQueue<E>();
2. PriorityQueue(Collection<E> c): Creates a PriorityQueue containing the elements in the specified collection.
PriorityQueue<E> pq = new PriorityQueue<E>(Collection<E> c);
3. PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity): Creates a PriorityQueue with the specified initial capacity that orders its elements according to their natural ordering.
PriorityQueue<E> pq = new PriorityQueue<E>(int initialCapacity);
4. PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity, Comparator<E> comparator): Creates a PriorityQueue with the specified initial capacity that orders its elements according to the specified comparator.
PriorityQueue<E> pq = new PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity, Comparator<E> comparator);
5. PriorityQueue(PriorityQueue<E> c): Creates a PriorityQueue containing the elements in the specified priority queue.
PriorityQueue<E> pq = new PriorityQueue(PriorityQueue<E> c);
6. PriorityQueue(SortedSet<E> c): Creates a PriorityQueue containing the elements in the specified sorted set.
PriorityQueue<E> pq = new PriorityQueue<E>(SortedSet<E> c);
7. PriorityQueue(Comparator<E> comparator): Creates a PriorityQueue with the default initial capacity and whose elements are ordered according to the specified comparator.
PriorityQueue<E> pq = new PriorityQueue<E>(Comparator<E> c);
Example:
The example below explains the following basic operations of the priority queue.
- boolean add(E element): This method inserts the specified element into this priority queue.
- public peek(): This method retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty.
- public poll(): This method retrieves and removes the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty.
Java
import java.util.*;
class PriorityQueueDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
PriorityQueue<Integer> pQueue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>();
pQueue.add(10);
pQueue.add(20);
pQueue.add(15);
System.out.println(pQueue.peek());
System.out.println(pQueue.poll());
System.out.println(pQueue.peek());
}
}
|
Operations on PriorityQueue
Let’s see how to perform a few frequently used operations on the Priority Queue class.
1. Adding Elements: In order to add an element in a priority queue, we can use the add() method. The insertion order is not retained in the PriorityQueue. The elements are stored based on the priority order which is ascending by default.
Java
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
pq.add(i);
pq.add(1);
}
System.out.println(pq);
}
}
|
Output
[0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1]
We will not get sorted elements by printing PriorityQueue.
Java
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
PriorityQueue<String> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add("Geeks");
pq.add("For");
pq.add("Geeks");
System.out.println(pq);
}
}
|
Output
[For, Geeks, Geeks]
2. Removing Elements: In order to remove an element from a priority queue, we can use the remove() method. If there are multiple such objects, then the first occurrence of the object is removed. Apart from that, the poll() method is also used to remove the head and return it.
Java
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
PriorityQueue<String> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add("Geeks");
pq.add("For");
pq.add("Geeks");
System.out.println("Initial PriorityQueue " + pq);
pq.remove("Geeks");
System.out.println("After Remove - " + pq);
System.out.println("Poll Method - " + pq.poll());
System.out.println("Final PriorityQueue - " + pq);
}
}
|
Output
Initial PriorityQueue [For, Geeks, Geeks]
After Remove - [For, Geeks]
Poll Method - For
Final PriorityQueue - [Geeks]
3. Accessing the elements: Since Queue follows the First In First Out principle, we can access only the head of the queue. To access elements from a priority queue, we can use the peek() method.
Java
import java.util.*;
class PriorityQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
PriorityQueue<String> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add("Geeks");
pq.add("For");
pq.add("Geeks");
System.out.println("PriorityQueue: " + pq);
String element = pq.peek();
System.out.println("Accessed Element: " + element);
}
}
|
Output
PriorityQueue: [For, Geeks, Geeks]
Accessed Element: For
4. Iterating the PriorityQueue: There are multiple ways to iterate through the PriorityQueue. The most famous way is converting the queue to the array and traversing using the for loop. However, the queue also has an inbuilt iterator which can be used to iterate through the queue.
Java
import java.util.*;
public class PriorityQueueDemo {
public static void main(String args[])
{
PriorityQueue<String> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
pq.add("Geeks");
pq.add("For");
pq.add("Geeks");
Iterator iterator = pq.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.print(iterator.next() + " ");
}
}
}
|
Example:
Java
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class PriorityQueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(10);
pq.add(3);
pq.add(1);
pq.add(2);
pq.add(5);
pq.add(4);
System.out.println("Priority queue: " + pq);
System.out.println("Peek: " + pq.peek());
pq.poll();
System.out.println("Priority queue after removing top element: " + pq);
System.out.println("Does the queue contain 3? " + pq.contains(3));
System.out.println("Size of queue: " + pq.size());
pq.clear();
System.out.println("Is the queue empty? " + pq.isEmpty());
}
}
|
Output
Priority queue: [1, 3, 2, 5, 4]
Peek: 1
Priority queue after removing top element: [2, 3, 4, 5]
Does the queue contain 3? true
Size of queue: 4
Is the queue empty? true
Real Time Examples:
Priority Queue is a data structure in which elements are ordered by priority, with the highest-priority elements appearing at the front of the queue. Here are some real-world examples of where priority queues can be used:
- Task Scheduling: In operating systems, priority queues are used to schedule tasks based on their priority levels. For example, a high-priority task like a critical system update may be scheduled ahead of a lower-priority task like a background backup process.
- Emergency Room: In a hospital emergency room, patients are triaged based on the severity of their condition, with those in critical condition being treated first. A priority queue can be used to manage the order in which patients are seen by doctors and nurses.
- Network Routing: In computer networks, priority queues are used to manage the flow of data packets. High-priority packets like voice and video data may be given priority over lower-priority data like email and file transfers.
- Transportation: In traffic management systems, priority queues can be used to manage traffic flow. For example, emergency vehicles like ambulances may be given priority over other vehicles to ensure that they can reach their destination quickly.
- Job Scheduling: In job scheduling systems, priority queues can be used to manage the order in which jobs are executed. High-priority jobs like critical system updates may be scheduled ahead of lower-priority jobs like data backups.
- Online Marketplaces: In online marketplaces, priority queues can be used to manage the delivery of products to customers. High-priority orders like express shipping may be given priority over standard shipping orders.
Overall, priority queues are a useful data structure for managing tasks and resources based on their priority levels in various real-world scenarios.
Methods in PriorityQueue class
| METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
| add(E e) |
Inserts the specified element into this priority queue. |
| clear() |
Removes all of the elements from this priority queue. |
| comparator() |
Returns the comparator used to order the elements in this queue, or null if this queue is sorted according to the natural ordering of its elements. |
| contains?(Object o) |
Returns true if this queue contains the specified element. |
| forEach?(Consumer<? super E> action) |
Performs the given action for each element of the Iterable until all elements have been processed or the action throws an exception. |
| iterator() |
Returns an iterator over the elements in this queue. |
| offer?(E e) |
Inserts the specified element into this priority queue. |
| remove?(Object o) |
Removes a single instance of the specified element from this queue, if it is present. |
| removeAll?(Collection<?> c) |
Removes all of this collection’s elements that are also contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| removeIf?(Predicate<? super E> filter) |
Removes all of the elements of this collection that satisfy the given predicate. |
| retainAll?(Collection<?> c) |
Retains only the elements in this collection that are contained in the specified collection (optional operation). |
| spliterator() |
Creates a late-binding and fail-fast Spliterator over the elements in this queue. |
| toArray() |
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue. |
| toArray?(T[] a) |
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this queue; the runtime type of the returned array is that of the specified array. |
Methods Declared in class java.util.AbstractQueue
Methods Declared in class java.util.AbstractCollection
| METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
| containsAll(Collection<?> c) |
Returns true if this collection contains all of the elements in the specified collection. |
| isEmpty() |
Returns true if this collection contains no elements. |
| toString() |
Returns a string representation of this collection. |
Methods Declared in interface java.util.Collection
| METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
| containsAll(Collection<?> c) |
Returns true if this collection contains all of the elements in the specified collection. |
| equals(Object o) |
Compares the specified object with this collection for equality. |
| hashCode() |
Returns the hash code value for this collection. |
| isEmpty() |
Returns true if this collection contains no elements. |
| parallelStream() |
Returns a possibly parallel Stream with this collection as its source. |
| size() |
Returns the number of elements in this collection. |
| stream() |
Returns a sequential Stream with this collection as its source. |
| toArray(IntFunction<T[]> generator) |
Returns an array containing all of the elements in this collection, using the provided generator function to allocate the returned array. |
Methods Declared in interface java.util.Queue
| METHOD |
DESCRIPTION |
| peek() |
Retrieves, but does not remove, the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty. |
| poll() |
Retrieves and removes the head of this queue, or returns null if this queue is empty. |
Applications:
Related Articles:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...