Print all ways to break a string in bracket form
Last Updated :
12 Mar, 2023
Given a string, find all ways to break the given string in bracket form. Enclose each substring within a parenthesis.
Examples:
Input : abc
Output: (a)(b)(c)
(a)(bc)
(ab)(c)
(abc)
Input : abcd
Output : (a)(b)(c)(d)
(a)(b)(cd)
(a)(bc)(d)
(a)(bcd)
(ab)(c)(d)
(ab)(cd)
(abc)(d)
(abcd)
We strongly recommend you to minimize your browser and try this yourself first.
The idea is to use recursion. We maintain two parameters – index of the next character to be processed and the output string so far. We start from index of next character to be processed, append substring formed by unprocessed string to the output string and recurse on remaining string until we process the whole string. We use std::substr to form the output string. substr(pos, n) returns a substring of length n that starts at position pos of current string.
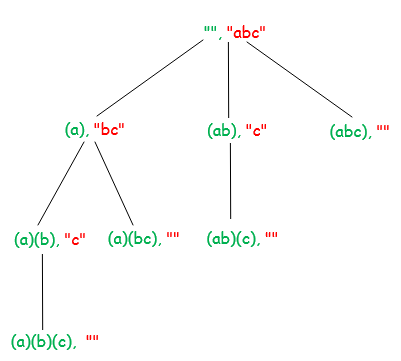
Below diagram shows recursion tree for input string “abc”. Each node on the diagram shows processed string (marked by green) and unprocessed string (marked by red).
Below is the implementation of the above idea
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void findCombinations(string str, int index, string out)
{
if (index == str.length())
cout << out << endl;
for (int i = index; i < str.length(); i++)
{
findCombinations(
str,
i + 1,
out + "(" + str.substr(index, i + 1 - index)
+ ")");
}
}
int main()
{
string str = "abcd";
findCombinations(str, 0, "");
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
static void findCombinations(String str, int index,
String out)
{
if (index == str.length())
System.out.println(out);
for (int i = index; i < str.length(); i++)
findCombinations(str, i + 1, out +
"(" + str.substring(index, i+1) + ")" );
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
String str = "abcd";
findCombinations(str, 0, "");
}
}
|
Python3
def findCombinations(string, index, out):
if index == len(string):
print(out)
for i in range(index, len(string), 1):
findCombinations(string, i + 1, out + "(" +
string[index:i + 1] + ")")
if __name__ == "__main__":
string = "abcd"
findCombinations(string, 0, "")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
public static void
findCombinations(string str, int index, string @out)
{
if (index == str.Length) {
Console.WriteLine(@out);
}
for (int i = index; i < str.Length; i++) {
findCombinations(
str, i + 1,
@out + "("
+ str.Substring(index, (i + 1) - index)
+ ")");
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
string str = "abcd";
findCombinations(str, 0, "");
}
}
|
Javascript
function findCombinations(string, index, out) {
if (index == string.length) {
console.log(out);
}
for (let i = index; i < string.length; i++) {
findCombinations(string, i + 1, out + "(" + string.substring(index, i + 1) + ")");
}
}
const string = "abcd";
findCombinations(string, 0, "");
|
Output
(a)(b)(c)(d)
(a)(b)(cd)
(a)(bc)(d)
(a)(bcd)
(ab)(c)(d)
(ab)(cd)
(abc)(d)
(abcd)
Time Complexity: O(N2)
Auxiliary Space: O(N2)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...