Print all nodes that are at distance k from a leaf node
Last Updated :
16 Oct, 2023
Given a Binary Tree and a positive integer K, print all nodes that are distance K from a leaf node. Here K distance from a leaf means K levels higher than a leaf node. For example, if K is more than the height of the Binary Tree, then nothing should be printed.
Examples:
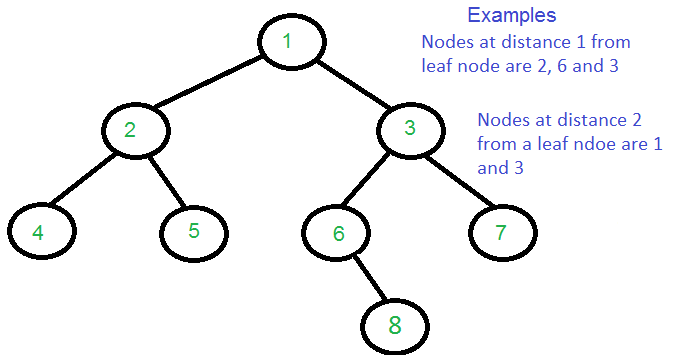
Approach: To solve the problem follow the below idea:
We can store the nodes in the path of our recursion and whenever we reach a leaf node, then print the Kth node in the saved path
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Traverse the tree and keep storing all ancestors till we hit a leaf node.
- When we reach a leaf node, we print the ancestor at distance K using the values stored in the array.
- We also need to keep track of nodes that are already printed as output. For that, we use a boolean array visited[]
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_HEIGHT 10000
struct Node {
int key;
Node *left, *right;
};
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* node = new Node;
node->key = key;
node->left = node->right = NULL;
return (node);
}
void kDistantFromLeafUtil(Node* node, int path[],
bool visited[], int pathLen,
int k)
{
if (node == NULL)
return;
path[pathLen] = node->key;
visited[pathLen] = false;
pathLen++;
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL
&& pathLen - k - 1 >= 0
&& visited[pathLen - k - 1] == false) {
cout << path[pathLen - k - 1] << " ";
visited[pathLen - k - 1] = true;
return;
}
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node->left, path, visited, pathLen,
k);
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node->right, path, visited,
pathLen, k);
}
void printKDistantfromLeaf(Node* node, int k)
{
int path[MAX_HEIGHT];
bool visited[MAX_HEIGHT] = { false };
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node, path, visited, 0, k);
}
int main()
{
Node* root = newNode(1);
root->left = newNode(2);
root->right = newNode(3);
root->left->left = newNode(4);
root->left->right = newNode(5);
root->right->left = newNode(6);
root->right->right = newNode(7);
root->right->left->right = newNode(8);
cout << "Nodes at distance 2 are: ";
printKDistantfromLeaf(root, 2);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class Node {
int data;
Node left, right;
Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
class BinaryTree {
Node root;
void kDistantFromLeafUtil(Node node, int path[],
boolean visited[],
int pathLen, int k)
{
if (node == null)
return;
path[pathLen] = node.data;
visited[pathLen] = false;
pathLen++;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null
&& pathLen - k - 1 >= 0
&& visited[pathLen - k - 1] == false) {
System.out.print(path[pathLen - k - 1] + " ");
visited[pathLen - k - 1] = true;
return;
}
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node.left, path, visited,
pathLen, k);
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node.right, path, visited,
pathLen, k);
}
void printKDistantfromLeaf(Node node, int k)
{
int path[] = new int[1000];
boolean visited[] = new boolean[1000];
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node, path, visited, 0, k);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(7);
tree.root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
System.out.print(" Nodes at distance 2 are : ");
tree.printKDistantfromLeaf(tree.root, 2);
}
}
|
Python3
class newNode:
def __init__(self, key):
self.key = key
self.left = self.right = None
def kDistantFromLeafUtil(node, path, visited,
pathLen, k):
if (node == None):
return
path[pathLen] = node.key
visited[pathLen] = False
pathLen += 1
if (node.left == None and node.right == None and
pathLen - k - 1 >= 0 and
visited[pathLen - k - 1] == False):
print(path[pathLen - k - 1], end=" ")
visited[pathLen - k - 1] = True
return
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node.left, path,
visited, pathLen, k)
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node.right, path,
visited, pathLen, k)
def printKDistantfromLeaf(node, k):
global MAX_HEIGHT
path = [None] * MAX_HEIGHT
visited = [False] * MAX_HEIGHT
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node, path, visited, 0, k)
MAX_HEIGHT = 10000
root = newNode(1)
root.left = newNode(2)
root.right = newNode(3)
root.left.left = newNode(4)
root.left.right = newNode(5)
root.right.left = newNode(6)
root.right.right = newNode(7)
root.right.left.right = newNode(8)
print("Nodes at distance 2 are:", end=" ")
printKDistantfromLeaf(root, 2)
|
C#
using System;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node left, right;
public Node(int item)
{
data = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinaryTree {
public Node root;
public virtual void
kDistantFromLeafUtil(Node node, int[] path,
bool[] visited, int pathLen, int k)
{
if (node == null) {
return;
}
path[pathLen] = node.data;
visited[pathLen] = false;
pathLen++;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null
&& pathLen - k - 1 >= 0
&& visited[pathLen - k - 1] == false) {
Console.Write(path[pathLen - k - 1] + " ");
visited[pathLen - k - 1] = true;
return;
}
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node.left, path, visited,
pathLen, k);
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node.right, path, visited,
pathLen, k);
}
public virtual void printKDistantfromLeaf(Node node,
int k)
{
int[] path = new int[1000];
bool[] visited = new bool[1000];
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node, path, visited, 0, k);
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
tree.root = new Node(1);
tree.root.left = new Node(2);
tree.root.right = new Node(3);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(4);
tree.root.left.right = new Node(5);
tree.root.right.left = new Node(6);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(7);
tree.root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
Console.Write(" Nodes at distance 2 are : ");
tree.printKDistantfromLeaf(tree.root, 2);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node
{
constructor(item) {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.data = item;
}
}
let root;
function kDistantFromLeafUtil(node, path, visited, pathLen, k)
{
if (node == null)
return;
path[pathLen] = node.data;
visited[pathLen] = false;
pathLen++;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null
&& (pathLen - k - 1) >= 0 &&
visited[pathLen - k - 1] == false) {
document.write(path[pathLen - k - 1] + " ");
visited[pathLen - k - 1] = true;
return;
}
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node.left, path, visited, pathLen, k);
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node.right, path, visited, pathLen, k);
}
function printKDistantfromLeaf(node, k)
{
let path = new Array(1000);
path.fill(0);
let visited = new Array(1000);
visited.fill(false);
kDistantFromLeafUtil(node, path, visited, 0, k);
}
root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
document.write(" Nodes at distance 2 are : ");
printKDistantfromLeaf(root, 2);
</script>
|
Output
Nodes at distance 2 are: 1 3
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N)
Approach 2: Iterative Solution
In this approach, we use an iterative method to traverse the binary tree using a stack. We maintain a stack of pairs, where each pair consists of a node and its depth. We start by pushing the root node and its depth onto the stack. Then, we repeatedly pop a node from the stack and push its left and right children, along with their depths, onto the stack. When we encounter a leaf node, we check its depth and see if it is at a distance k from the current node. If it is, we print the current node.
- Initialize an empty stack st, an empty vector path, and an empty vector visited.
- Push a pair (root, 0) onto the stack, where root is the root of the binary tree and 0 is the depth of root.
- While st is not empty, do the following:
- Pop the top pair (curr, depth) from st.
- If curr is nullptr, continue to the next iteration of the loop.
- Append curr->val to path and false to visited.
- If curr is a leaf node, check if its depth is k less than the current depth of curr. If so, check if the node at that depth has already been visited. If not, print the value of the node at that depth and mark it as visited.
- Push the pairs (curr->left, depth + 1) and (curr->right, depth + 1) onto st.
- If depth + 1 is less than the size of path, resize path and visited to remove the nodes beyond depth + 1.
Here’s the codes for this approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left, *right;
Node(int v) : val(v), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
};
void printKDist(Node* root, int k) {
stack<pair<Node*, int>> st;
vector<int> path;
vector<bool> visited;
st.push(make_pair(root, 0));
while (!st.empty()) {
pair<Node*, int> curr = st.top();
st.pop();
if (curr.first == nullptr) {
continue;
}
path.push_back(curr.first->val);
visited.push_back(false);
if (curr.first->left == nullptr && curr.first->right == nullptr) {
int depth = path.size() - 1 - k;
if (depth >= 0 && !visited[depth]) {
cout << path[depth] << " ";
visited[depth] = true;
}
}
st.push(make_pair(curr.first->left, curr.second + 1));
st.push(make_pair(curr.first->right, curr.second + 1));
if (curr.second + 1 < path.size()) {
path.resize(curr.second + 1);
visited.resize(curr.second + 1);
}
}
}
int main() {
Node* root = new Node(1);
root->left = new Node(2);
root->right = new Node(3);
root->left->left = new Node(4);
root->left->right = new Node(5);
root->right->left = new Node(6);
root->right->right = new Node(7);
root->right->left->right = new Node(8);
printKDist(root, 2);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Stack;
class Node {
int val;
Node left, right;
Node(int v)
{
val = v;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
public class GFG {
public static void printKDist(Node root, int k)
{
Stack<Pair> stack = new Stack<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<Boolean> visited = new ArrayList<>();
stack.push(new Pair(root, 0));
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
Pair curr = stack.pop();
if (curr.node == null) {
continue;
}
path.add(curr.node.val);
visited.add(false);
if (curr.node.left == null
&& curr.node.right == null) {
int depth = path.size() - 1 - k;
if (depth >= 0 && !visited.get(depth)) {
System.out.print(
path.get(depth)
+ " ");
visited.set(depth, true);
}
}
stack.push(
new Pair(curr.node.left, curr.depth + 1));
stack.push(
new Pair(curr.node.right, curr.depth + 1));
if (curr.depth + 1 < path.size()) {
int newSize = curr.depth + 1;
path.subList(newSize, path.size()).clear();
visited.subList(newSize, visited.size())
.clear();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
printKDist(root, 2);
}
}
class Pair {
Node node;
int depth;
Pair(Node n, int d)
{
node = n;
depth = d;
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
def printKDist(root, k):
stack = []
path = []
visited = []
stack.append([root, 0])
while stack:
curr, depth = stack.pop()
if curr is None:
continue
path.append(curr.val)
visited.append(False)
if curr.left is None and curr.right is None:
dist = len(path) - 1 - k
if dist >= 0 and not visited[dist]:
print(path[dist])
visited[dist] = True
stack.append([curr.left, depth + 1])
stack.append([curr.right, depth + 1])
if depth + 1 < len(path):
path = path[:depth + 1]
visited = visited[:depth + 1]
root = Node(1)
root.left = Node(2)
root.right = Node(3)
root.left.left = Node(4)
root.left.right = Node(5)
root.right.left = Node(6)
root.right.right = Node(7)
root.right.left.right = Node(8)
printKDist(root, 2)
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
printKDist(root, 2);
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void printKDist(Node root, int k)
{
Stack<Tuple<Node, int>> st = new Stack<Tuple<Node, int>>();
List<int> path = new List<int>();
List<bool> visited = new List<bool>();
st.Push(new Tuple<Node, int>(root, 0));
while (st.Count > 0)
{
Tuple<Node, int> curr = st.Pop();
if (curr.Item1 == null)
{
continue;
}
path.Add(curr.Item1.val);
visited.Add(false);
if (curr.Item1.left == null && curr.Item1.right == null)
{
int depth = path.Count - 1 - k;
if (depth >= 0 && !visited[depth])
{
Console.Write(path[depth] + " ");
visited[depth] = true;
}
}
st.Push(new Tuple<Node, int>(curr.Item1.left, curr.Item2 + 1));
st.Push(new Tuple<Node, int>(curr.Item1.right, curr.Item2 + 1));
if (curr.Item2 + 1 < path.Count)
{
path.RemoveRange(curr.Item2 + 1, path.Count - curr.Item2 - 1);
visited.RemoveRange(curr.Item2 + 1, visited.Count - curr.Item2 - 1);
}
}
}
}
class Node
{
public int val;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node(int v)
{
val = v;
left = null;
right = null;
}
}
}
|
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function printKDist(root, k) {
const stack = [];
const path = [];
const visited = [];
stack.push([root, 0]);
while (stack.length > 0) {
const [curr, depth] = stack.pop();
if (curr === null) {
continue;
}
path.push(curr.val);
visited.push(false);
if (curr.left === null && curr.right === null) {
const dist = path.length - 1 - k;
if (dist >= 0 && !visited[dist]) {
console.log(path[dist]);
visited[dist] = true;
}
}
stack.push([curr.left, depth + 1]);
stack.push([curr.right, depth + 1]);
if (depth + 1 < path.length) {
path.length = depth + 1;
visited.length = depth + 1;
}
}
}
const root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right = new Node(7);
root.right.left.right = new Node(8);
printKDist(root, 2);
|
Time Complexity:
In the worst case, we visit every node in the binary tree once. For each node, we append its value to path and false to visited, which takes O(1) time. If the node is a leaf node, we check its depth and mark the corresponding node in visited if necessary, which also takes O(1) time. Finally, we push its left and right children onto st, which takes O(1) time each. Thus, the time complexity of the algorithm is O(n), where n is the number of nodes in the binary tree.
Space Complexity:
The space used by the algorithm is proportional to the maximum depth of the binary tree. In the worst case, the binary tree is a skewed tree, in which case the maximum depth is n. In this case, the size of path and visited is O(n), and the size of the stack st is also O(n). Thus, the space complexity of the algorithm is O(n). However, in the best case, the binary tree is a balanced tree, in which case the maximum depth is log(n). In this case, the space complexity is O(log(n)).
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...