PRINCE2 Project Management Methodology
Last Updated :
24 Apr, 2024
PRINCE2 focuses on dividing projects into manageable stages, each with its own set of processes and deliverables. These stages include starting up a project, initiating a project, directing a project, controlling a stage, managing product delivery, managing stage boundaries, and closing a project. This staged approach helps ensure that projects are well-planned, controlled, and monitored throughout their lifecycle.
What is PRINCE2?
PRINCE2, which stands for Projects IN Controlled Environments, is a structured project management methodology that provides a systematic approach to managing projects. It originated in the UK government sector in the late 1980s as a response to the need for a standardized project management framework to improve the success rate of government projects. Since then, it has evolved into a widely recognized and adopted methodology used across industries and sectors globally.
The History of PRINCE2
- PRINCE2 Roots: The origins of PRINCE2 can be traced back to the UK government’s imperative for consistent and standardized project management practices. Facing challenges in overseeing diverse projects efficiently, the government sought a structured approach to enhance project success rates and accountability.
- Initial Development- PROMPT: PROMPT (Project Resource Organization Management Planning Technique) marked the initial step towards structured project management within the UK government. It laid the foundation for systematic project planning and control, aiming to streamline project execution and resource allocation.
- Evolution: From PROMPT emerged PRINCE (Projects IN Controlled Environments) in 1989, signifying a significant evolution in project management methodologies. PRINCE introduced a more structured and controlled approach to project management, emphasizing defined processes and clear responsibilities.
- Official Establishment- PRINCE2: In 1996, PRINCE2 was formally established as the successor to PRINCE, consolidating years of refinement and feedback from project management practitioners. This official recognition solidified PRINCE2’s status as a leading project management methodology, both within the UK government and across industries worldwide.
- Purpose: PRINCE2 serves the purpose of providing a comprehensive and adaptable framework for managing projects of varying sizes and complexities. Its structured approach, coupled with flexibility for customization, equips project managers with the tools needed to navigate through project lifecycles effectively, ensuring timely delivery, budget control, and quality assurance.
Benefits of PRINCE2 Project Management
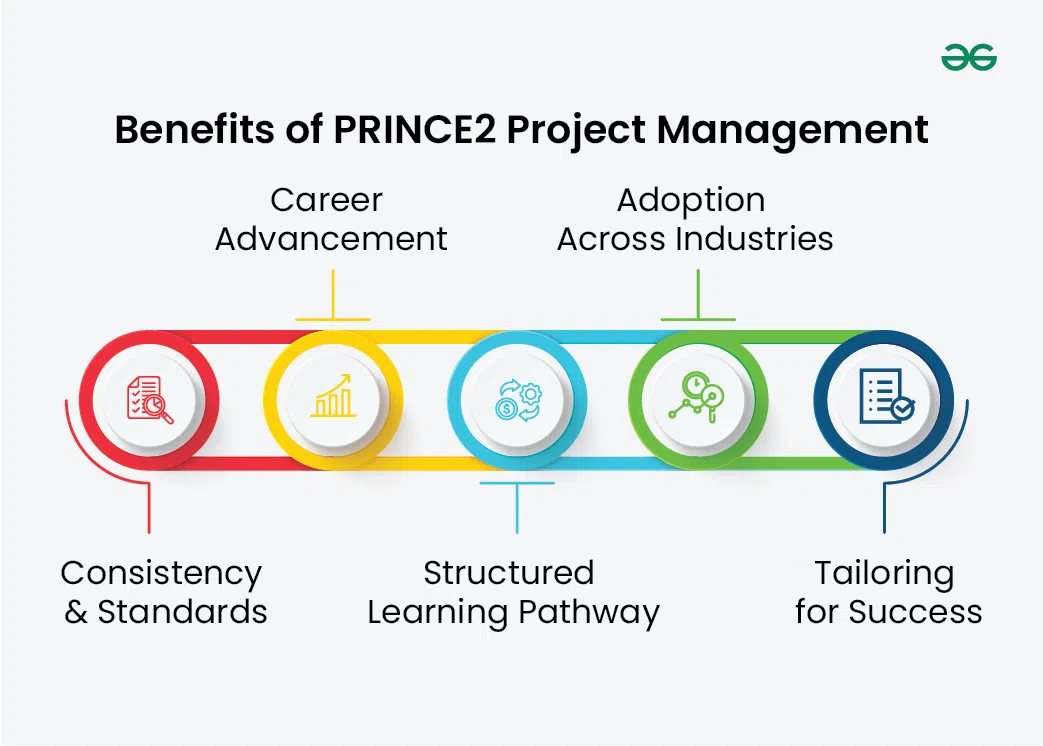
Benefits of PRINCE2 Project Management
- Consistency and Standards: PRINCE2’s global recognition stems from its ability to establish consistent standards in project management practices. Its widespread adoption across industries and sectors ensures that project managers trained in PRINCE2 possess a common understanding of project management principles and terminology, fostering collaboration and coherence in project teams.
- Career Advancement: For project managers, certification in PRINCE2 serves as a badge of proficiency and competence. Employers often prioritize candidates with PRINCE2 certification, recognizing it as evidence of a solid understanding of project management best practices.
- Structured Learning Pathway: Training courses and study materials are readily available, catering to individuals with varying levels of experience in project management. This accessibility enables beginners to embark on their journey of mastering PRINCE2 with confidence, supported by comprehensive guidance and support.
- Adoption Across Industries: From IT and construction to healthcare and finance, PRINCE2 has been successfully applied across diverse sectors, demonstrating its adaptability and relevance in addressing a wide range of project management challenges.
- Tailoring for Success: Project managers can adapt PRINCE2 principles and processes to accommodate unique project constraints, such as budgetary constraints, regulatory compliance, or stakeholder preferences. This tailoring ensures that PRINCE2 remains applicable and effective in addressing the distinct needs of each project, maximizing the chances of success.
PRINCE2 Project Roles

PRINCE2 Project Roles
In a PRINCE2 project, roles are clearly defined to ensure accountability and effective communication. Some key roles include:
- Project Manager: Leads project delivery, including planning, execution, and monitoring, while serving as the primary liaison with stakeholders.
- Team Manager: Oversees daily team activities, ensuring tasks are completed efficiently and to the required standard.
- Project Board: Provides strategic direction, approves major decisions, and resolves escalated issues to ensure project alignment with organizational objectives.
- Project Assurance: Ensures adherence to standards, methodologies, and quality criteria throughout the project lifecycle.
- Change Authority: Responsible for evaluating and approving changes to project scope, objectives, or requirements based on their impact and alignment with project goals.
6 Key Aspects of a PRINCE2 Project

Key Aspects of a PRINCE2 Project
1. Business Case
The business case serves as the foundation for the project, providing a comprehensive rationale for its initiation and investment. It outlines the project’s objectives, anticipated benefits, estimated costs, and associated risks. By establishing clear goals and expected outcomes, the business case guides decision-making and ensures alignment with organizational priorities.
2. Organization
Effective project governance relies on a well-defined organizational structure that delineates roles, responsibilities, and reporting lines. This clarity ensures accountability and facilitates communication within the project team. By assigning specific responsibilities to individuals or teams, the organization structure streamlines decision-making processes and promotes efficient project execution.
3. Plans
Detailed planning is essential for guiding project activities and managing resources effectively. Project plans encompass various aspects such as time, cost, quality, risk, and benefits. They provide a roadmap for project execution, outlining tasks, milestones, and dependencies. By anticipating potential challenges and defining mitigation strategies, plans enable project managers to proactively manage project constraints and uncertainties.
4. Controls
Project controls are mechanisms for monitoring and regulating the project’s progress against predefined objectives and performance criteria. This includes establishing regular checkpoints and reviews to assess project status, identify deviations from the plan, and take corrective actions as necessary. By implementing robust control mechanisms, project managers can maintain visibility into project activities and ensure alignment with project goals.
5. Management of Risk
Effective risk management involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential threats to project success. This proactive approach helps minimize the impact of risks on project outcomes by implementing strategies to avoid, transfer, or mitigate them. By systematically addressing risks throughout the project lifecycle, project managers can enhance resilience and increase the likelihood of achieving project objectives.
6. Quality Management
Quality management processes are essential for ensuring that project deliverables meet specified standards and satisfy customer requirements. This includes establishing quality criteria, conducting inspections and reviews, and implementing corrective actions to address any deviations from the expected quality levels. By prioritizing quality assurance and continuous improvement, project teams can enhance customer satisfaction and deliver value-added outcomes.
The 7 Phases of a PRINCE2 Project

7 Phases of a PRINCE2 Project
A PRINCE2 project is typically divided into seven sequential phases:
- Starting Up a Project (SU): The initial phase where the project’s feasibility is assessed, and key stakeholders are identified.
- Initiating a Project (IP): Detailed planning takes place, including the creation of a comprehensive Project Initiation Document (PID).
- Directing a Project (DP): The Project Board provides ongoing direction and guidance, ensuring that the project remains on track.
- Controlling a Stage (CS): Each stage of the project is managed and controlled, with regular checkpoints to assess progress and address any issues.
- Managing Product Delivery (MP): The focus shifts to delivering the project’s products or outputs according to the agreed specifications.
- Managing a Stage Boundary (SB): Occurs at the end of each stage, where the Project Board reviews progress and decides whether to proceed to the next stage.
- Closing a Project (CP): The final phase involves formally closing the project, evaluating its success, and capturing lessons learned for future reference.
PRINCE2 Practitioner Certifications
For those looking to enhance their project management credentials, PRINCE2 offers a range of certifications:
- PRINCE2 Foundation: An entry-level certification that provides a basic understanding of PRINCE2 principles and terminology.
- PRINCE2 Practitioner: Builds upon the Foundation level, focusing on the practical application of PRINCE2 principles in real-world scenarios.
- PRINCE2 Agile: Combines PRINCE2 with agile methodologies, catering to projects that require flexibility and adaptability.
Related Posts:
Conclusion: PRINCE2 Project Management Methodology
In the dynamic world of project management, having a reliable methodology can mean the difference between success and failure. PRINCE2 offers a structured yet adaptable approach that empowers project managers to navigate even the most complex challenges with confidence. By understanding its principles, embracing its flexibility, and leveraging its proven practices, you can unlock the full potential of PRINCE2 and propel your projects towards greater success.
FAQs: PRINCE2 Project Management Methodology
Is PRINCE2 suitable for all types of projects?
While PRINCE2 is versatile, it may not be the best fit for every project. Its structured approach is particularly well-suited to projects with defined objectives and deliverables.
How can I learn more about PRINCE2?
There are numerous training providers offering PRINCE2 certification courses, both online and in-person. Additionally, there are plenty of books, articles, and resources available to help you deepen your understanding of PRINCE2 principles and practices.
Can PRINCE2 be combined with other methodologies?
Absolutely! PRINCE2 is compatible with various project management methodologies, including agile, waterfall, and hybrid approaches. This flexibility allows organizations to tailor their project management approach to suit their unique requirements.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...