Prime Factorization is a way of writing numbers as the product of prime numbers. Prime numbers are natural numbers that have only two divisors, 1 and themselves. Composite numbers, on the other hand, have more than two divisors.

Let’s learn how to perform the prime factorization of numbers step by step.
Prime Factorization Definition
Prime factorization is the method of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors.
For instance, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, and so forth are all prime numbers. The process of prime factorization involves representing a given number as a product of its prime factors.
Prime Factors
Prime factors are the prime numbers that divide a given number exactly without leaving a remainder. In other words, they are the building blocks of a number.
When a number is expressed as a product of its prime factors, it is said to be in its prime factorization form.
Some examples of prime factors are:
- 2 and 3 are the prime factors of 12, as 12 = 22 × 3,
- 3 and 5 are the prime factors of 15, as 15 = 3 × 5,
- 2 and 7 are the prime factors of 14, as 15 = 3 × 5.
List of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers are those that have only two factors: 1 and the number itself. The prime factors from 1 to 100 are
2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 53, 59, 61, 67, 71, 73, 79, 83, 89, and 97.
Prime Factorization of Numbers
Some examples of prime factorization are listed below:
| Number |
Prime Factorization |
| 72 |
2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 |
| 36 |
2 × 2 × 3 × 3 |
| 48 |
2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 |
| 12 |
2 × 2 × 3 |
| 100 |
2 × 2 × 5 × 5 |
| 84 |
2 × 2 × 3 × 7 |
| 8 |
2 × 2 × 2 |
| 32 |
2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 |
| 24 |
2 × 2 × 2 × 3 |
| 91 |
7 × 13 |
| 15 |
3 × 5 |
Prime Factorization Methods
Two common methods of Prime Factorization are:
- Division Method
- Factor Tree Method
Prime Factorization by Division Method
In this method, the number is successively divided by prime numbers until the quotient becomes 1, with each division identifying a prime factor.
Steps to identify the prime factors of a number by Division Method :
Step 1: Divide the number by the smallest prime number (i.e. 2) until we are able to divide the given number without leaving any remainder.
Step 2: Move on to the next prime number and repeat the division until the quotient becomes 1.
Step 3: The prime factors are the divisors used in the division process.
Let’s consider some examples for better understanding.
Example 1: Find the Prime Factorization of 60 using Division Method.
Prime factorization of 60 using the division method can be given as follows:
 Prime Factorization by Division Method
Prime Factorization by Division Method
Example 2: Find the Prime Factorization of 210 using Division Method.
Prime factorization of 210 using the division method can be given as follows:
 Prime Factorization by Division Method
Prime Factorization by Division Method
Example 3: Express 56 as the product of its Prime Factors.
To express 56 as the product of its prime factors, we need to find the prime factors of 56 first. Prime factorization of 56 can be evaluated as follows:
 Prime Factorization by Division Method
Prime Factorization by Division Method
Prime Factorization by Factor Tree Method
The Factor Tree Method involves breaking down a number into its prime factors by constructing a tree-like structure called a factor tree.
Steps to identify the prime factors of a number by Factor Tree Method:
Step 1: Identify two factors of the number that are not prime.
Step 2: Write these two factors as branches of the factor tree.
Step 3: Repeat steps 1 and 2 for each non-prime factor until all branches end with prime numbers.
Step 4: The prime factors are the numbers at the end of the branches.
Let’s consider some examples for better understanding as follows:
Example 1: Find the factorization of 60 by the Factor Tree Method.
Solution:
Factor tree of 60 is given as follows:

Example 2: Make the Factor Tree of 210.
Solution:
Factor tree of 210 is given as follows:
 Prime Factorization of 210 by Factor Tree
Prime Factorization of 210 by Factor Tree
Related Articles:
Prime Factorization Solved Examples
Let’s solve some questions on Prime Factorisation.
Problem 1: What is the Prime Factorisation of 80?
Solution:
To find the prime factorization of 80, we can start by dividing it by the smallest prime number, which is 2.
- 80 divided by 2 equals 40.
- 40 divided by 2 equals 20.
- 20 divided by 2 equals 10.
- 10 divided by 2 equals 5.
Now, since 5 is a prime number, we can stop dividing. Therefore, the prime factorization of 80 is: 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 5.
Problem 2: Prime factorization of 120.
Solution:
Starting with the smallest prime number, which is 2.
- 120 divided by 2 equals 60.
- 60 divided by 2 equals 30.
- 30 divided by 2 equals 15.
- Now, since 15 is not divisible by 2, we move on to the next prime number (i.e, 3)
- 15 divided by 3 equals 5.
Now, since 5 is a prime number, we can stop dividing. Therefore, the prime factorization of 120 is: 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5
Problem 3: What is the Factor Tree of 56?
Solution:
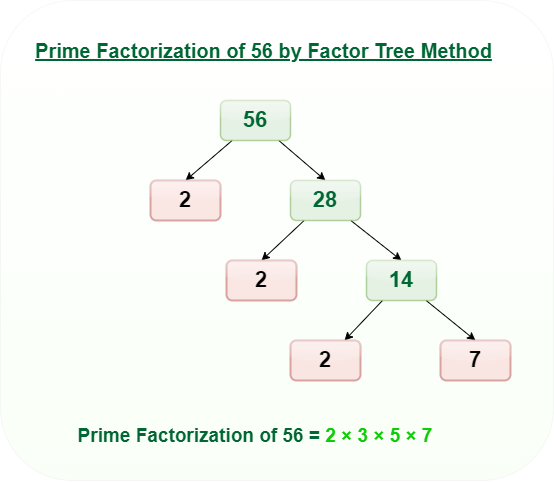
Prime Factorization Questions
1. Find the prime factorization of 36.
2. Determine the prime factorization of 90.
3. What is the prime factorization of 48?
4. Find the prime factorization of 105.
FAQs on Prime Factorization
What is Prime factorization in Math?
A method to decompose any given number into its constituent prime number is called prime factorization.
Define Prime Factors of a Number.
In Prime Factorization, the prime consitituents of the number are called prime factors of that given number. For example, 2 and 3 are the prime factors of 24 as 24 = 23 × 3.
How To Find Prime Factors of a Number?
To find the prime factors of a number, you can use the method of trial division. Start dividing the number by the smallest prime number i.e., 2 and continue dividing by prime numbers until the quotient becomes 1. The divisors you used are the prime factors.
Can a Number have More than One Prime Factorization?
No, a number has a unique prime factorization. This is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic. Regardless of the order in which the factors are written, the prime factors of a number remain the same.
What is Difference between Prime and Composite Factors?
Prime factors are the prime numbers that divide a given number without leaving a remainder, while composite factors are the composite numbers (non-prime numbers) that divide a given number without leaving a remainder.
How To Find LCM using Prime Factorization?
To find the least common multiple (LCM), you consider all the prime factors and take the highest exponent for each prime factor.
How To Find HCF by Prime Factorization Method?
To find the HCF of two or more numbers, you identify the common prime factors and take the smallest exponent for each prime factor.
What are Prime Factors of 32?
The prime factors of 32 are 2 raised to the power of 5 (25).
What are Prime Factors of 45?
The prime factors of 45 are 3 and 5, since 45 = 32 × 5.
What are Prime Factors of 75?
The prime factors of 75 are 3 and 5.
How To Find Prime Factors of a Large Number?
To find the prime factors of a large number:
- Start with the smallest prime number, 2. Divide the large number by 2. If it’s divisible, 2 is a prime factor; divide as many times as possible until it’s no longer divisible by 2.
- Move to the next prime numbers (3, 5, 7, 11, …) and repeat the process for each: divide the number by the prime number, and if it’s divisible, that prime is a factor. Continue dividing by that prime until it’s no longer divisible.
- Continue the process with increasing prime numbers until the number you’re dividing by is greater than the square root of the original number. At that point, if the number you’re left with is greater than 1, it’s also a prime factor.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...