PostgreSQL – DROP TABLESPACE
Last Updated :
08 Feb, 2021
In PostgreSQL, the DROP TABLESPACE statement is used to remove a tablespace.
Syntax: DROP TABLESPACE [IF EXISTS] tablespace_name;
Let’s analyze the above syntax:
- First, specify the name of the tablespace that is to be deleted after the DROP TABLESPACE keywords.
- Second, use the IF EXISTS option to handle errors in case the tablespace doesn’t exists.
Note: It is important to note that only tablespace owners or superusers can execute the DROP TABLESPACE statement.
Example:
First, we create a new tablespace named gfg and map it to the C:\data\gfg directory:
CREATE TABLESPACE gfg
LOCATION 'C:\data\gfg';
Now create a database named db_gfg and set its tablespace to gfg:
CREATE DATABASE db_gfg
TABLESPACE = gfg;
Now create a new table named test in the db_gfg and set it tablespace to gfg:
CREATE TABLE test (
ID serial PRIMARY KEY,
title VARCHAR (255) NOT NULL
) TABLESPACE gfg;
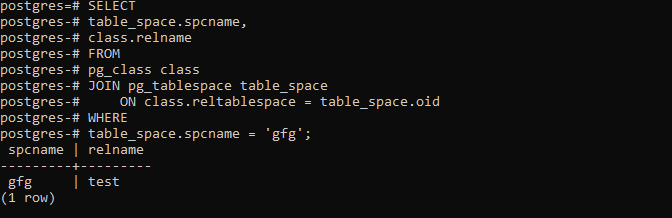
The following statement returns all objects in the gfg tablespace:
SELECT
table_space.spcname,
class.relname
FROM
pg_class class
JOIN pg_tablespace table_space
ON class.reltablespace = table_space.oid
WHERE
table_space.spcname = 'gfg';
This will lead to the following:
Now if you try to drop the gfgtablespace:
DROP TABLESPACE gfg;
This will raise the following error:

As the gfg tablespace is not empty,it is not possible to drop the tablespace. Now, login to the Postgres database and drop the db_gfg database:
DROP DATABASE db_gfg;
Now delete the gfg tablespace again:
DROP TABLESPACE gfg;
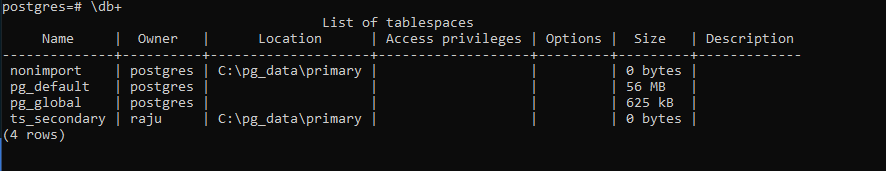
Now check for the tablespace using the below command to verify:
\db+
Output:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...