Permutation Coefficient
Last Updated :
25 Feb, 2023
Permutation refers to the process of arranging all the members of a given set to form a sequence. The number of permutations on a set of n elements is given by n! , where “!” represents factorial.
The Permutation Coefficient represented by P(n, k) is used to represent the number of ways to obtain an ordered subset having k elements from a set of n elements.
Mathematically it’s given as:
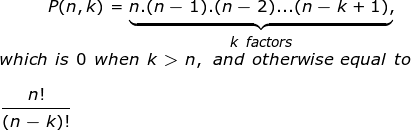
Image Source : Wiki
Examples :
P(10, 2) = 90
P(10, 3) = 720
P(10, 0) = 1
P(10, 1) = 10
The coefficient can also be computed recursively using the below recursive formula:
P(n, k) = P(n-1, k) + k* P(n-1, k-1)
The recursive formula for permutation-coefficient is :
P(n, k) = P(n-1, k) + k* P(n-1, k-1)
But how ??
here is the proof,
We already know,
The binomial coefficient is nCk = n!
k! (n-k)!
and, permutation-coefficient nPr = n!
(n-k)!
So, I can write
nCk = nPk
k!
=> k! * nCk = nPk ———————- eq.1
The recursive formula for the Binomial coefficient nCk can be written as,
nCk(n,k) = nCk(n-1,k-1) + nCk(n-1,k) you can refer to the following article for more details
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/binomial-coefficient-dp-9/
Basically, it makes use of Pascal’s triangle which states that in order to fill the value at nCk[n][k] you need the summation of nCk[n-1][k-1] and nCk[n-1][k] along with some base cases. i.e,
nCk[n][k] = nCk[n-1][k-1]+nCk[n-1][k].
nCk[n][0] = nCk[n][n] = 1 (Base Case)
Anyways, let’s proceed with our eq.1
=> k! * nCk = nPk
=> k! * ( nCk(n-1,k-1) + nCk(n-1,k) ) = nPk [ as, nCk = nCk(n-1,k-1)+nCk(n-1,k) ]
=> k! * ( (n-1)! + (n-1)! ) = nPk
((n-1)-(k-1))! * (k-1)! (n-1-k)! * k!
=> k! * (n-1)! + k! * (n-1)! = nPk
((n-1)-(k-1))! * (k-1)! (n-1-k)! * k!
=> k * (k-1)! * (n-1)! + k! * (n-1)! = nPk [ as, k! = k*(k-1)! ]
((n-1)-(k-1))! * (k-1)! (n-1-k)! * k!
=> k * (n-1)! + (n-1)! = nPk
((n-1)-(k-1))! (n-1-k)!
(n-1)! can be replaced by nPk(n-1,k-1) as per the permutation-coefficient
((n-1) – (k-1))!
Similarly, (n-1)! can be replaced by nPk(n-1,k).
(n-1-k)!
Therefore,
=> k * nPk(n-1, k-1) + nPk(n-1, k) = nPk
Finally, that is where our recursive formula came from.
P(n, k) = P(n-1, k) + k* P(n-1, k-1)
If we observe closely, we can analyze that the problem has an overlapping substructure, hence we can apply dynamic programming here. Below is a program implementing the same idea.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
int permutationCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int P[n + 1][k + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= std::min(i, k); j++)
{
if (j == 0)
P[i][j] = 1;
else
P[i][j] = P[i - 1][j] +
(j * P[i - 1][j - 1]);
P[i][j + 1] = 0;
}
}
return P[n][k];
}
int main()
{
int n = 10, k = 2;
cout << "Value of P(" << n <<" " << k<< ") is " << permutationCoeff(n, k);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
int permutationCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int P[n + 1][k + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j <= std::min(i, k); j++)
{
if (j == 0)
P[i][j] = 1;
else
P[i][j] = P[i - 1][j] +
(j * P[i - 1][j - 1]);
P[i][j + 1] = 0;
}
}
return P[n][k];
}
int main()
{
int n = 10, k = 2;
printf("Value of P(%d, %d) is %d ",
n, k, permutationCoeff(n, k));
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
class GFG
{
static int permutationCoeff(int n,
int k)
{
int P[][] = new int[n + 2][k + 2];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0;
j <= Math.min(i, k);
j++)
{
if (j == 0)
P[i][j] = 1;
else
P[i][j] = P[i - 1][j] +
(j * P[i - 1][j - 1]);
P[i][j + 1] = 0;
}
}
return P[n][k];
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n = 10, k = 2;
System.out.println("Value of P( " + n + ","+ k +")" +
" is " + permutationCoeff(n, k) );
}
}
|
Python3
def permutationCoeff(n, k):
P = [[0 for i in range(k + 1)]
for j in range(n + 1)]
for i in range(n + 1):
for j in range(min(i, k) + 1):
if (j == 0):
P[i][j] = 1
else:
P[i][j] = P[i - 1][j] + (
j * P[i - 1][j - 1])
if (j < k):
P[i][j + 1] = 0
return P[n][k]
n = 10
k = 2
print("Value of P(", n, ", ", k, ") is ",
permutationCoeff(n, k), sep = "")
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
static int permutationCoeff(int n,
int k)
{
int [,]P = new int[n + 2,k + 2];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0;
j <= Math.Min(i, k);
j++)
{
if (j == 0)
P[i,j] = 1;
else
P[i,j] = P[i - 1,j] +
(j * P[i - 1,j - 1]);
P[i,j + 1] = 0;
}
}
return P[n,k];
}
public static void Main()
{
int n = 10, k = 2;
Console.WriteLine("Value of P( " + n +
","+ k +")" + " is " +
permutationCoeff(n, k) );
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function permutationCoeff( $n, $k)
{
$P = array(array());
for($i = 0; $i <= $n; $i++)
{
for($j = 0; $j <= min($i, $k); $j++)
{
if ($j == 0)
$P[$i][$j] = 1;
else
$P[$i][$j] = $P[$i - 1][$j] +
($j * $P[$i - 1][$j - 1]);
$P[$i][$j + 1] = 0;
}
}
return $P[$n][$k];
}
$n = 10; $k = 2;
echo "Value of P(",$n," ,",$k,") is ",
permutationCoeff($n, $k);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function permutationCoeff(n, k)
{
let P = new Array(n + 2);
for(let i = 0; i < n + 2; i++)
{
P[i] = new Array(k + 2);
}
for (let i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{
for (let j = 0; j <= Math.min(i, k); j++)
{
if (j == 0)
P[i][j] = 1;
else
P[i][j] = P[i - 1][j] + (j * P[i - 1][j - 1]);
P[i][j + 1] = 0;
}
}
return P[n][k];
}
let n = 10, k = 2;
document.write("Value of P(" + n + ","+ k +")" + " is " + permutationCoeff(n, k) );
</script>
|
Output :
Value of P(10, 2) is 90
Here as we can see the time complexity is O(n*k) and space complexity is O(n*k) as the program uses an auxiliary matrix to store the result.
Can we do it in O(n) time ?
Let us suppose we maintain a single 1D array to compute the factorials up to n. We can use computed factorial value and apply the formula P(n, k) = n! / (n-k)!. Below is a program illustrating the same concept.
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int permutationCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int fact[n + 1];
fact[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
fact[i] = i * fact[i - 1];
return fact[n] / fact[n - k];
}
int main()
{
int n = 10, k = 2;
cout << "Value of P(" << n << ", "
<< k << ") is "
<< permutationCoeff(n, k);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
int permutationCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int fact[n + 1];
fact[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
fact[i] = i * fact[i - 1];
return fact[n] / fact[n - k];
}
int main()
{
int n = 10, k = 2;
printf ("Value of P(%d, %d) is %d ",
n, k, permutationCoeff(n, k) );
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java .io.*;
public class GFG {
static int permutationCoeff(int n,
int k)
{
int []fact = new int[n+1];
fact[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
fact[i] = i * fact[i - 1];
return fact[n] / fact[n - k];
}
static public void main (String[] args)
{
int n = 10, k = 2;
System.out.println("Value of"
+ " P( " + n + ", " + k + ") is "
+ permutationCoeff(n, k) );
}
}
|
Python3
def permutationCoeff(n, k):
fact = [0 for i in range(n + 1)]
fact[0] = 1
for i in range(1, n + 1):
fact[i] = i * fact[i - 1]
return int(fact[n] / fact[n - k])
n = 10
k = 2
print("Value of P(", n, ", ", k, ") is ",
permutationCoeff(n, k), sep = "")
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
static int permutationCoeff(int n,
int k)
{
int []fact = new int[n+1];
fact[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
fact[i] = i * fact[i - 1];
return fact[n] / fact[n - k];
}
static public void Main ()
{
int n = 10, k = 2;
Console.WriteLine("Value of"
+ " P( " + n + ", " + k + ") is "
+ permutationCoeff(n, k) );
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function permutationCoeff($n, $k)
{
$fact = array();
$fact[0] = 1;
for ($i = 1; $i <= $n; $i++)
$fact[$i] = $i * $fact[$i - 1];
return $fact[$n] / $fact[$n - $k];
}
$n = 10;
$k = 2;
echo"Value of P(",$n," ", $k,") is ",
permutationCoeff($n, $k) ;
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function permutationCoeff(n, k)
{
let fact = new Array(n+1);
fact[0] = 1;
for (let i = 1; i <= n; i++)
fact[i] = i * fact[i - 1];
return parseInt(fact[n] / fact[n - k], 10);
}
let n = 10, k = 2;
document.write("Value of"
+ " P(" + n + ", " + k + ") is "
+ permutationCoeff(n, k) );
</script>
|
Output :
Value of P(10, 2) is 90
A O(n) time and O(1) Extra Space Solution
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int PermutationCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int P = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++)
P *= (n-i) ;
return P;
}
int main()
{
int n = 10, k = 2;
cout << "Value of P(" << n << ", " << k
<< ") is " << PermutationCoeff(n, k);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG
{
static int PermutationCoeff(int n,
int k)
{
int Fn = 1, Fk = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
Fn *= i;
if (i == n - k)
Fk = Fn;
}
int coeff = Fn / Fk;
return coeff;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n = 10, k = 2;
System.out.println("Value of P( " + n + "," +
k +") is " +
PermutationCoeff(n, k) );
}
}
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int PermutationCoeff(int n,
int k)
{
int Fn = 1, Fk = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
Fn *= i;
if (i == n - k)
Fk = Fn;
}
int coeff = Fn / Fk;
return coeff;
}
public static void Main()
{
int n = 10, k = 2;
Console.WriteLine("Value of P( "
+ n + "," + k +") is "
+ PermutationCoeff(n, k) );
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function PermutationCoeff( $n, $k)
{
$Fn = 1; $Fk;
for ( $i = 1; $i <= $n; $i++)
{
$Fn *= $i;
if ($i == $n - $k)
$Fk = $Fn;
}
$coeff = $Fn / $Fk;
return $coeff;
}
$n = 10; $k = 2;
echo "Value of P(" , $n , ", " , $k , ")
is " , PermutationCoeff($n, $k);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function PermutationCoeff(n, k)
{
let P = 1;
for(let i = 0; i < k; i++)
P *= (n - i);
return P;
}
let n = 10, k = 2;
document.write("Value of P(" + n +
", " + k + ") is " +
PermutationCoeff(n, k));
</script>
|
Python3
def permutationCoeff(n, k):
f=1
for i in range(k):
f*=(n-i)
return f
n = 10
k = 2
print("Value of P(", n, ", ", k, ") is ",
permutationCoeff(n, k))
|
Output :
Value of P(10, 2) is 90
Thanks to Shiva Kumar for suggesting this solution.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...