Levels in Data Flow Diagrams (DFD)
Last Updated :
16 May, 2024
In Software engineering DFD(data flow diagram) can be drawn to represent the system of different levels of abstraction. Higher-level DFDs are partitioned into low levels-hacking more information and functional elements. Levels in DFD are numbered 0, 1, 2 or beyond. Here, we will see mainly 3 levels in the data flow diagram, which are: 0-level DFD, 1-level DFD, and 2-level DFD.
What is Data Flow Diagram (DFD) ?
Data Flow Diagram (DFD) is a graphical representation of data flow in any system. It is capable of illustrating incoming data flow, outgoing data flow and store data. Data flow diagram describes anything about how data flows through the system.
Levels in Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
DFDs can be divided into different levels, which provide varying degrees of detail about the system. The following are the four levels of DFDs:
- Level 0 DFD
- Level 1 DFD
- Level 2 DFD
- Level 3 DFD
The choice of DFD level depends on the complexity of the system and the level of detail required to understand the system. Higher levels of DFD provide a broad overview of the system, while lower levels provide more detail about the system’s processes, data flows, and data stores. A combination of different levels of DFD can provide a complete understanding of the system.
Level 0 Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
Level 0 is the highest-level Data Flow Diagram (DFD), which provides an overview of the entire system. It shows the major processes, data flows, and data stores in the system, without providing any details about the internal workings of these processes.
It is also known as a context diagram. It’s designed to be an abstraction view, showing the system as a single process with its relationship to external entities. It represents the entire system as a single bubble with input and output data indicated by incoming/outgoing arrows.
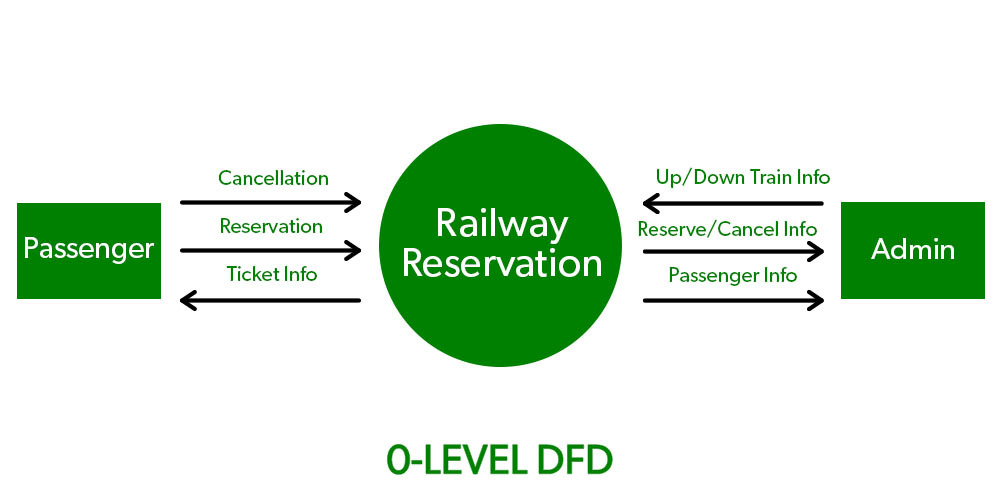
1-Level Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
1-Level provides a more detailed view of the system by breaking down the major processes identified in the level 0 Data Flow Diagram (DFD) into sub-processes. Each sub-process is depicted as a separate process on the level 1 Data Flow Diagram (DFD). The data flows and data stores associated with each sub-process are also shown.
In 1-level Data Flow Diagram (DFD), the context diagram is decomposed into multiple bubbles/processes. In this level, we highlight the main functions of the system and breakdown the high-level process of 0-level Data Flow Diagram (DFD) into subprocesses.
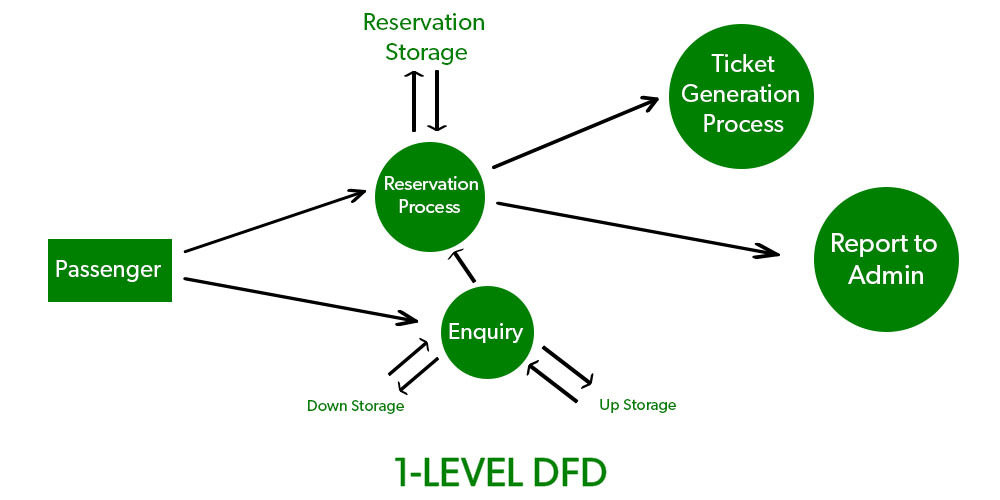
2-Level Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
2-Level provides an even more detailed view of the system by breaking down the sub-processes identified in the level 1 Data Flow Diagram (DFD) into further sub-processes. Each sub-process is depicted as a separate process on the level 2 DFD. The data flows and data stores associated with each sub-process are also shown.
2-Level Data Flow Diagram (DFD) goes one step deeper into parts of 1-level DFD. It can be used to plan or record the specific/necessary detail about the system’s functioning.
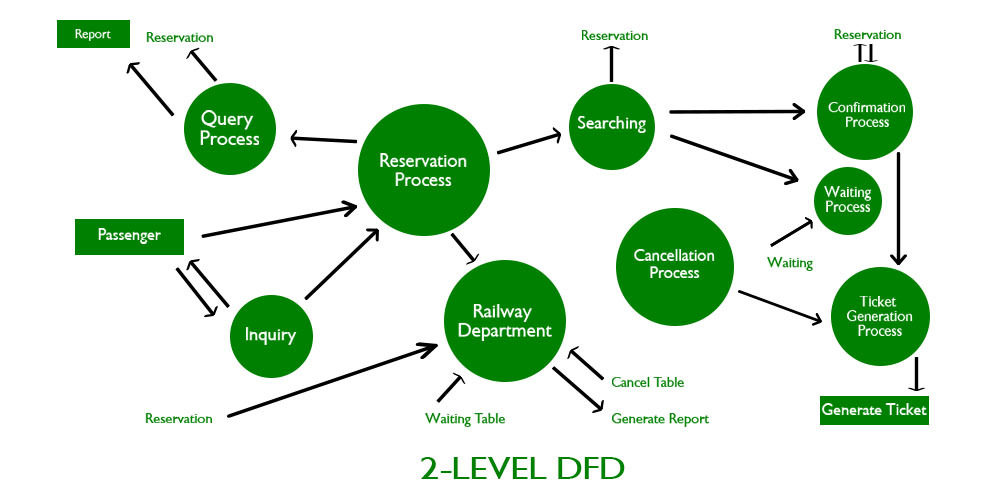
3-Level Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
3-Level is the most detailed level of Data Flow Diagram (DFDs), which provides a detailed view of the processes, data flows, and data stores in the system. This level is typically used for complex systems, where a high level of detail is required to understand the system. Each process on the level 3 DFD is depicted with a detailed description of its input, processing, and output. The data flows and data stores associated with each process are also shown.
Advantages of using Data Flow Diagrams (DFD)
Following are the Advantage of Data Flow Diagram (DFD) :
- Easy to understand: DFDs are graphical representations that are easy to understand and communicate, making them useful for non-technical stakeholders and team members.
- Improves system analysis: DFDs are useful for analyzing a system’s processes and data flow, which can help identify inefficiencies, redundancies, and other problems that may exist in the system.
- Supports system design: DFDs can be used to design a system’s architecture and structure, which can help ensure that the system is designed to meet the requirements of the stakeholders.
- Enables testing and verification: DFDs can be used to identify the inputs and outputs of a system, which can help in the testing and verification of the system’s functionality.
- Facilitates documentation: DFDs provide a visual representation of a system, making it easier to document and maintain the system over time.
Disadvantages of using Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
Following are the Disadvantage of Data Flow Diagram (DFD) :
- Can be time-consuming: Creating DFDs can be a time-consuming process, especially for complex systems.
- Limited focus: DFDs focus primarily on the flow of data in a system, and may not capture other important aspects of the system, such as user interface design, system security, or system performance.
- Can be difficult to keep up-to-date: DFDs may become out-of-date over time as the system evolves and changes.
- Requires technical expertise: While DFDs are easy to understand, creating them requires a certain level of technical expertise and familiarity with the system being analyzed.
Overall, the benefits of using DFDs outweigh the disadvantages. However, it is important to recognize the limitations of DFDs and use them in conjunction with other tools and techniques to analyze and design complex software systems.
Conclusion
Levels of Data Flow Diagrams (DFDs) offer a hierarchical view of system processes. Higher levels provide a broad overview, while lower levels detail specific processes and data flows. Analyzing these levels reveals system scope, data transformations, and potential inefficiencies, helping in understanding and improving system architecture. Effective communication and optimization opportunities are key takeaways from DFD level analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions on Levels of Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
What are the levels of DFD?
Levels in DFD are numbered 0, 1, 2 or beyond.
What is top level of DFD?
Level 0 DFD is the top level of DFD. Level 0 DFD are also known as Context Diagram, which provides an overview of the entire system.
DFD stands for Data Flow Diagram that is a graphical representation of data flow in any system.
What is the Difference between DFD and Flow Chart?
There is a major difference between data flow diagram and flowchart. The flowchart illustrates flow of control in program modules. Data flow diagrams illustrate flow of data in the system at various levels. Data flow diagram does not have any control or branch elements.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...