JavaScript Program to Find Maximum Width of Binary Tree
Last Updated :
27 Feb, 2024
The maximum width of a given binary tree can be calculated by finding the maximum of all the level widths. The maximum width of a Binary tree is the maximum number of nodes present at any level. The maximum width of the Binary tree will include only the present node and not include null nodes.
The maximum width of a Binary Tree
In this example, we are going to see what is the maximum width of a binary tree. The maximum width of a binary tree is the maximum number of nodes present at any level. The maximum number of nodes present is returned as the maximum width of a binary tree.
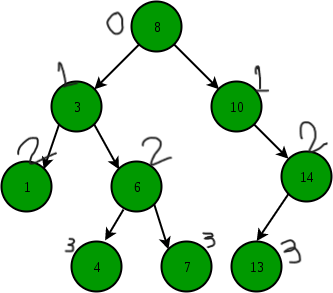
Maximum Width
- The maximum width at level 0 is 1.
- The maximum width at level 1 is 2.
- The maximum width at level 2 is 3.
- The maximum width at level 3 is 3.
As the maximum width of the binary tree is 3 at level 2 and level 3. So the maximum width of a binary tree is 3.
There are several ways to find the maximum width of a Binary tree in JavaScript which are as follows:
Level order Traversal using a queue
The level order traversal of the binary tree can be used to find the maximum width of the binary tree using the level order traversal of a binary tree. Perform the level order traversal using a queue. We calculate the maximum width of a binary tree. Keep the count of nodes at each level stored in the queue which will return the maximum width of a binary tree. Return the maximum width of a binary tree.
Example: In this queue is used to traverse each level of the binary tree using the queue data structure. At each level, we update the maximum width of a binary tree. Lastly, we return the maximum width of the binary tree stored in the variable after completing the whole traversal of a binary tree.
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(key) {
this.data = key;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function maxWidth(root) {
if (root === null) {
return 0;
}
let maxWidth = 0;
let queue = [];
queue.push(root);
while (queue.length > 0) {
let count = queue.length;
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, count);
while (count > 0) {
let node = queue.shift();
if (node.left) {
queue.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right) {
queue.push(node.right);
}
count--;
}
}
return maxWidth;
}
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.right = new Node(8);
root.right.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right.right = new Node(7);
console.log("Maximum width of the binary tree:", maxWidth(root));
|
Output
Maximum width of the binary tree: 3
Using Breadth-First Search
This is a simple approach to calculate the maximum width of a binary tree. We traverse the tree using the breadth-first search technique. We store the maximum width at each level and update it if a greater width is found than previously stored. This way the maximum width of the binary tree is returned. Declare a maximum variable that will store the maximum width of the binary tree and update the value of a maximum variable as traversing each level of the binary tree is done using the BFS technique and in the last return the maximum width of the Binary tree is stored in a maximum variable.
Example: In the given below example BFS at each level is performed and the maximum width of the binary tree is updated at each level. After the traversal of the binary tree is completed the maximum width of the binary tree is returned.
Javascript
class Node {
constructor(key) {
this.data = key;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function maxWidth(root) {
if (root === null) return 0;
let max = 0;
let levelNodes = [root];
while (levelNodes.length) {
let count = levelNodes.length;
max = Math.max(max, count);
let nextLevelNodes = [];
for (let i = 0; i < count; i++) {
let node = levelNodes[i];
if (node.left) {
nextLevelNodes.push(node.left);
}
if (node.right) {
nextLevelNodes.push(node.right);
}
}
levelNodes = nextLevelNodes;
}
return max;
}
let root = new Node(1);
root.left = new Node(2);
root.right = new Node(3);
root.left.left = new Node(4);
root.left.right = new Node(5);
root.right.right = new Node(8);
root.right.right.left = new Node(6);
root.right.right.right = new Node(7);
console.log("Maximum width of the binary tree:", maxWidth(root));
|
Output
Maximum width of the binary tree: 3
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...