Introduction to R-tree
Last Updated :
05 Sep, 2022
R-tree is a tree data structure used for storing spatial data indexes in an efficient manner. R-trees are highly useful for spatial data queries and storage. Some of the real-life applications are mentioned below:
- Indexing multi-dimensional information.
- Handling geospatial coordinates.
- Implementation of virtual maps.
- Handling game data.
Example:
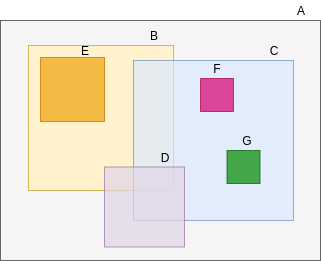
R-Tree Representation:

R Tree Representation
Properties of R-tree:
- Consists of a single root, internals nodes, and leaf nodes.
- The root contains the pointer to the largest region in the spatial domain.
- Parent nodes contains pointers to their child nodes where the region of child nodes completely overlaps the regions of parent nodes.
- Leaf nodes contains data about the MBR to the current objects.
- MBR-Minimum bounding region refers to the minimal bounding box parameter surrounding the region/object under consideration.
Comparison with Quad-trees:
- Tiling level optimization is required in Quad-trees whereas an R-tree doesn’t require any such optimization.
- Quad-tree can be implemented on top of existing B-tree whereas R-tree follow a different structure from a B-tree.
- Spatial index creation in Quad-trees is faster as compared to R-trees.
- R-trees are faster than Quad-trees for Nearest Neighbour queries while for window queries, Quad-trees are faster than R-trees.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...