In SQLite databases, string concatenation is crucial for various tasks, from generating reports to organizing data. One particularly useful function for this purpose is GROUP_CONCAT. SQLite is a lightweight and versatile relational database management system that offers a powerful solution with its GROUP_CONCAT function. In this article, we’ll explore how to use GROUP_CONCAT to concatenate strings effortlessly within SQLite queries.
How to Concatenate Strings Using GROUP_CONCAT?
The GROUP_CONCAT is an aggregation function that is used to concat values from various records into one single value. Since it is an aggregating function it is used with GROUP BY clause.
Syntax:
SELECT col1, col2, ..., coln
GROUP_CONCAT ( col_name, str_val )
FROM table GROUP BY col1, col2, ..., coln;
Explanation:
- col1, col2, coln: The columns which will be used to group the records.
- col_name: The name of the column whose value needs to be concatenated.
- str_val: The optional separator value.
- table: The table from which to aggregate the results.
let’s Setting Up Environment for Concatenate Strings
We will create a table called test and insert some sample values in the table. The following code creates the test table and inserts some entries into it.
CREATE TABLE test (
id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
val1 VARCHAR(20),
val2 VARCHAR(20)
);
INSERT INTO test VALUES (21, 'val1', '32');
INSERT INTO test VALUES (11, 'val2', '90');
INSERT INTO test VALUES (90, 'val1', '18');
INSERT INTO test VALUES (77, 'val1', '65');
INSERT INTO test VALUES (43, 'val3', '20');
INSERT INTO test VALUES (81, 'val3', '88');
INSERT INTO test VALUES (29, 'val2', '72');
INSERT INTO test VALUES (55, 'val2', '47');
INSERT INTO test VALUES (72, 'val3', '11');
Output:
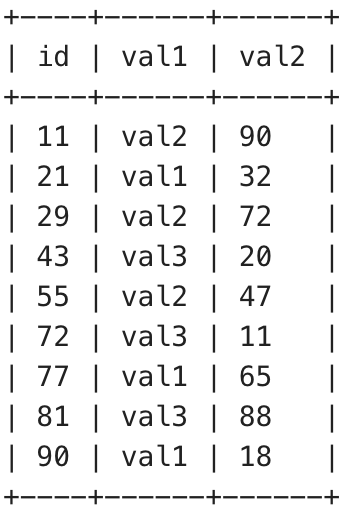
Output
Explanation: Now that we have the table in place, lets go through the GROUP_CONCAT() function.
Examples of GROUP_CONCAT Function to Concatenate Strings
Example 1: Group According to Values
The following query groups the table according to the values in the field ‘val1‘ and then uses GROUP_CONCAT() to concat the values of ‘val2‘:
SELECT val1, GROUP_CONCAT(val2) as val2
FROM test
GROUP BY val1;
Output:

Output
Explanation: In the above query we retrieves data from a table named test, grouping it by the val1 column. It concatenates the values from the val2 column for each group of val1 using the GROUP_CONCAT function.
Example 2: Group the Data and Concatenates Values
Like the query presented in example 1, The following query groups the data by ‘val1’ and concatenates values of ‘val2’. The only difference it is that it uses ‘/’ as the separator.
SELECT val1, GROUP_CONCAT(val2, '/') as val2
FROM test
GROUP BY val1;
Output:

Explanation: In the above query, we retrieves data from the test table, grouping it by the val1 column. It concatenates the values from the val2 column for each group of val1 using the GROUP_CONCAT function, with a ‘/’ delimiter between each concatenated value.
Example 3: Group According to Values in Ascending Order
The following query is similar to the query performed in the above examples. The only difference is that it orders the values in ‘val2’ in ascending Order By making use a subquery and then using that in GROUP_CONCAT function for concatenating:
SELECT val1, GROUP_CONCAT(val2) as val2
FROM (
SELECT val1, val2
FROM test
ORDER BY val2
) t
GROUP BY val1;
Output:

Output
Explanation: In the above query, first we sorts the data by the val2 column from the test table and then uses the sorted result set to group the data by the val1 column. It concatenates the values from the val2 column for each group of val1 using the GROUP_CONCAT function and providing a sorted and concatenated output for each val1 group.
Advanced Example of GROUP_CONCAT Function
Let’s understand through the technical example. Let’s create the table and insert some data inside it.
CREATE TABLE language (
state VARCHAR(50),
name VARCHAR(50)
);
INSERT INTO language VALUES ('Bihar', 'Hindi');
INSERT INTO language VALUES ('Punjab', 'Punjabi');
INSERT INTO language VALUES ('Assam', 'Assamese');
INSERT INTO language VALUES ('Punjab', 'Urdu');
INSERT INTO language VALUES ('Bihar', 'English');
INSERT INTO language VALUES ('Bihar', 'Maithili');
INSERT INTO language VALUES ('Punjab', 'Hindi');
INSERT INTO language VALUES ('Assam', 'Bengali');
INSERT INTO language VALUES ('Maharashtra', 'Marathi');
INSERT INTO language VALUES ('Gujarat', 'Gujarati');
INSERT INTO language VALUES ('Maharashtra', 'Hindi');
INSERT INTO language VALUES ('Maharashtra', 'English');
INSERT INTO language VALUES ('Assam', 'Bodo');
Output:
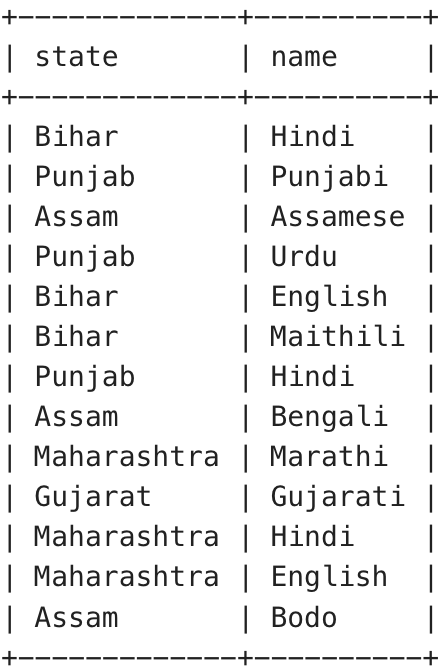
Output
Explanation: As we can see in the image, the above table contains the various languages spoken in various states of India.
Let’s use GROUP_CONCAT() function to concat the different languages spoken in a particular state. First we will start by the vanilla version of the query to use GROUP_CONCAT. We will group using the state column and concat the values in the name column.
SELECT state, GROUP_CONCAT(name) different_languages FROM language
GROUP BY state;
Output:
.png)
Output
Explanation: We get the desired output from the above query.
Now we will provide a custom separator in the second argument to concatenate the languages.
SELECT state, GROUP_CONCAT(name, ';') different_languages FROM language
GROUP BY state;
Output:

Output
Explanation: In the above query, we retrieves data from the language table and groups it by the state column. For each group of states it concatenates the name column values using the GROUP_CONCAT function through storing the result in a column named different_languages.
We can even make use of subquery and ORDER BY clause to order the different languages in ascending order before concatenation.
SELECT state, GROUP_CONCAT(name) as different_languages
FROM (
SELECT state, name
FROM language
ORDER BY name
)
GROUP BY state;
Output:

Output
Explanation: In the above query, we first selects the state and name columns from the language table, orders the results by the name column, and then groups the data by the state column. For each group of states, it concatenates the name values into a single string using the GROUP_CONCAT function and the result is stored in a column named different_languages.
Conclusion
In this article, we covered how we can make use of GROUP_CONCAT function to concatenate strings in SQLite. We started by looking at what GROUP_CONCAT is, and then we looked at several examples. In the examples, we made use of the vanilla version, ORDER BY clause and even provided custom separator for concatenation. Finally, we also saw how we can use the concepts we learned in this article to a real-life situation through the technical example.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...