How to Qualify Methods as Static in Scala?
Last Updated :
08 Apr, 2024
In this article, we will learn how to qualify methods as static in Scala. you declare a method as static using the object keyword instead of the class keyword. By defining a method within an object, you create a singleton object that can hold static methods.
Syntax:
object MyClass {
def myStaticMethod(): Unit = {
// Your static method implementation here
println(“This is a static method”)
}
}
Here, myStaticMethod is a static method because it is defined within the MyClass object. You can access it without creating an instance of MyClass.
Using Object Approach
Below is the Scala program to qualify methods as static:
Scala
// Define an object with static methods
object MathUtils {
def add(x: Int, y: Int): Int = {
x + y
}
def subtract(x: Int, y: Int): Int = {
x - y
}
}
// Main program
object Main {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
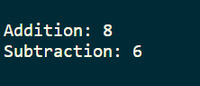
println("Addition: " + MathUtils.add(5, 3))
println("Subtraction: " + MathUtils.subtract(10, 4))
}
}
Output:
Explanation:
In this example, MathUtils object contains two static methods add and subtract, which can be called directly without creating an instance of MathUtils. The Main object demonstrates how to use these static methods.
Using Companion Object Approach
Below is the Scala program to qualify method as static:
Scala
// Define a class
class StringUtil {
// Instance method
def capitalize(s: String): String = {
s.toUpperCase
}
}
// Define a companion object for the class StringUtil
object StringUtil {
// Static method
def reverse(s: String): String = {
s.reverse
}
}
// Main program
object Main {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val inputString = "hello world"
// Using instance method
val capitalizedString = new StringUtil().capitalize(inputString)
println("Capitalized String: " + capitalizedString)
// Using static method
val reversedString = StringUtil.reverse(inputString)
println("Reversed String: " + reversedString)
}
}
Output:

Explanation:
In this example, StringUtil class has an instance method capitalize, and its companion object contains a static method reverse. The Main object demonstrates how to use both instance and static methods of the StringUtil class.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...