How to make a box with the help of nested loops using Python arcade?
Last Updated :
11 Oct, 2020
Arcade library is modern framework currently used in making 2D games. Nested loop discussed here are analogous to nested loops in any other programming language.
The following tutorial will step by step explain how to draw a box with the help of nested loops using Python’s arcade module.
- Import arcade library.
- Here we will be using circles to form a box. Thus, declare parameters, that will be used later in the program to specify spacing and margin between two circles.
- Use arcade.open_window() to specify the width, height and title of the output screen.
- Set the background color of the output screen.(optional)
- Tell arcade module that you will now be sending drawing commands.
- Define the functionality using nested loop i.e one loop inside the other. We have defined a for loop for each row and inside that another for loop for column.
- Finally, we need to inform arcade module that which object we want the box should be made up of. Here, a circle is employed but you can define any other geometrical shape of your choice.
- Tell arcade that you have finished drawing and ask it to stop the output at the output window until the user doesn’t press exit.
Below is the implementation.
Python3
import arcade
col_spacing = 20
row_spacing = 20
lmargin = 110
bmargin = 110
arcade.open_window(500, 500, "BOX")
arcade.set_background_color(arcade.color.BABY_PINK)
arcade.start_render()
for row in range(10):
for col in range(10):
x = col * col_spacing + lmargin
y = row * row_spacing + bmargin
arcade.draw_circle_filled(x+1, y+2, 10, arcade.color.BLUE)
arcade.finish_render()
arcade.run()
|
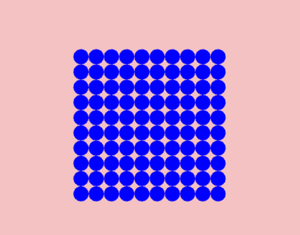
Output:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...