How to Display all Threads Status in Java?
Last Updated :
24 Feb, 2022
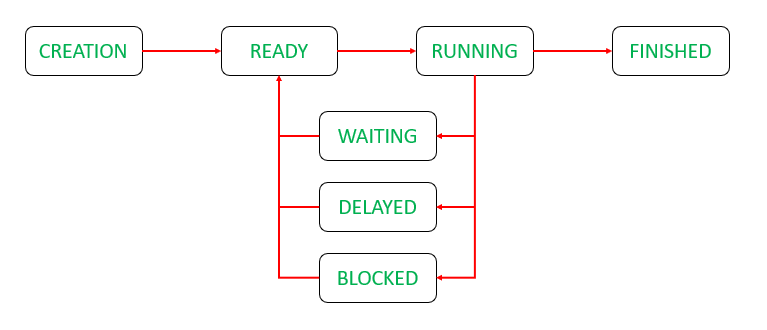
Threads are light-weight processes within a process.. Multithreading in java is a feature that allows concurrent execution of two or more parts of a program to maximize the utilization of CPU. here the approach to retrieve the state of the thread is via getState() method of the Thread class. A java thread can exist in any one of the following states, the status of a thread is the state in which it exists at a given instance. The life cycle of a thread as shown above is the best way out to learn more about the states where the states are as follows:
- New
- Runnable
- Blocked
- Waiting
- Timed Waiting
- Terminated
Note: When a thread is getting executed all other threads are in blocking state and not in waiting state.
Procedure: Displaying thread status
- Threads are created by implementing the runnable interface.
- The status of a thread can be retrieved by getState() method of the Thread class object.
Example:
Java
import java.util.Set;
class MyThread implements Runnable {
public void run()
{
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
catch (Exception err) {
System.out.println(err);
}
}
}
public class GFG {
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
for (int thread_num = 0; thread_num < 5;
thread_num++) {
Thread t = new Thread(new MyThread());
t.setName("MyThread:" + thread_num);
t.start();
}
Set<Thread> threadSet
= Thread.getAllStackTraces().keySet();
for (Thread t : threadSet) {
System.out.println("Thread :" + t + ":"
+ "Thread status : "
+ t.getState());
}
}
}
|
Output:

Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...