Difference Between Java Threads and OS Threads
Last Updated :
26 Apr, 2023
Multithreading is a Java feature that allows concurrent execution of two or more parts of a program for maximum utilization of CPU. Each part of such a program is called a thread. So, threads are lightweight processes within a process.
The primary difference is that threads within the same process run in shared memory space, while processes run in separate memory spaces. A thread is a path of execution within a process. A process can contain multiple threads. Now let us discuss the differences between java threads and OS threads. Here first we will be defining both of them alongside providing with the help of a program wherever we can fit in to dwell better understanding and lastly we will be tabulating the differences between them in a tabular manner.
Java threads vs OS threads
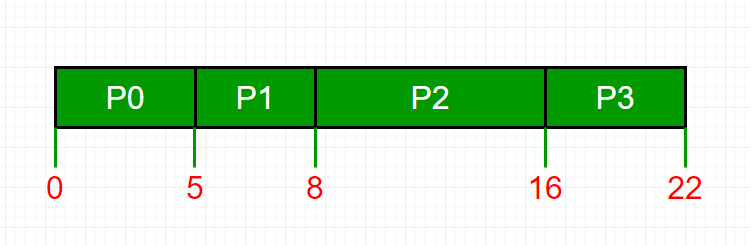
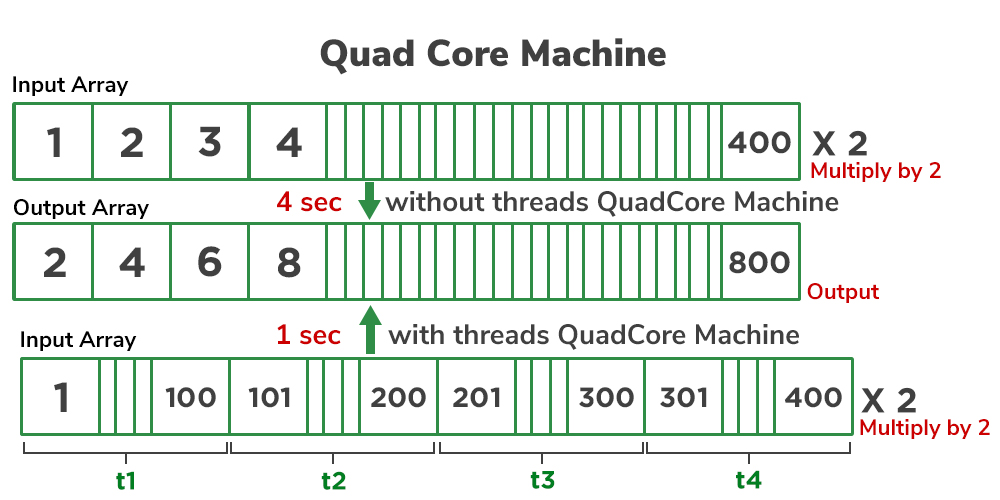
| Key Point |
OS Threads |
Java Threads |
| Definition |
A thread is the smallest unit of processing that can be performed in an OS |
A thread, in the context of Java, is the path followed when executing a program |
| Minimum threads |
A process can contain multiple threads. |
Java programs have at least one thread, known as the main thread |
| Types |
User-level threads & Kernel-level threads |
User threads & Daemon threads. |
| Created/Managed by |
Operating System |
Java Virtual Machine (JVM) at the program’s start, when the main() method is invoked with the main thread. |
| Communication |
Threads can share common data & communication is easier. |
wait(), notify(), notifyAll() are methods used for threads to communicate. |
| Thread Scheduling |
1) Scheduling of user-level threads (ULT) to kernel-level threads (KLT) via Light-Weight Process (LWP) by the application developer.
2) Scheduling of kernel-level threads by the system scheduler to perform different unique os functions.
|
The thread scheduler in java is the part of the JVM that decides which thread should run. Types: 1) Pre-emptive Scheduling, 2) Time Slicing. |
| Synchronization |
The most popular way of achieving thread synchronization is by using Mutexes. |
Implemented using monitors, synchronizing using synchronized blocks. |
| Implementation using models |
Many-to-One, One-to-One, Many-to-Many |
Green Thread model (many-to-one model), Native Thread Model (many-to-many model) |
| Deadlock detection |
1) If resources have a single instance
2) If there are multiple instances of resources
|
1) nested synchronized block or trying to get a lock on a different object or calling a synchronized method from another synchronized method
2) to use the io portal. It allows us to upload a thread dump and analyze it.
3) can also use jConsole or VisualVM to detect deadlock
|
| Deadlock avoidance |
Can be done with Banker’s Algorithm. |
1) Avoid Unnecessary Locks
2) Avoid Nested Locks
3) Using Thread.join() Method
4) Use Lock Ordering
5) Lock Time-out
|
Also, have a look at the different thread states:
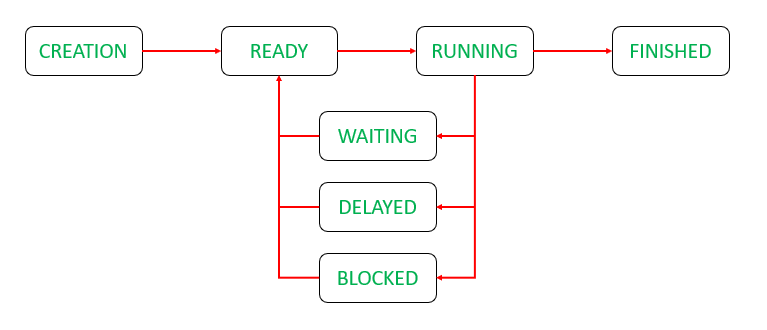
State of Thread in Operating System

Various states of a thread at any instant of time
Note: Green threads were abandoned in the Sun JVM for Linux as of the release of version 1.3 and native threads which are managed by OS are used. Refer to this for more details.
Java threads and operating system (OS) threads are both used for concurrent programming and to achieve multitasking in an application. However, there are some differences between them.
- Implementation: Java threads are implemented entirely in the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) while OS threads are implemented by the operating system kernel.
- Scheduling: Java threads are scheduled by the JVM using its own scheduling algorithm, while OS threads are scheduled by the operating system using its scheduling algorithm.
- Context switching: Switching between Java threads is done entirely in user space by the JVM, while switching between OS threads requires a system call to the kernel, which involves switching to kernel mode.
- Overhead: Java threads have less overhead than OS threads, as the JVM can manage them more efficiently than the operating system. Context switching between Java threads is less expensive than switching between OS threads.
- Portability: Java threads are more portable than OS threads, as they are implemented entirely in Java and do not depend on the operating system.
- Synchronization: Java provides built-in synchronization mechanisms such as synchronized blocks and methods, while OS threads require the use of OS-specific synchronization mechanisms such as semaphores and mutexes.
Overall, Java threads are easier to use and more portable than OS threads. They have less overhead and do not require system calls to switch between threads. However, OS threads may provide better performance in certain situations, especially when dealing with low-level system resources or when working with other system-specific features. It is important to choose the appropriate threading model based on the requirements of the application.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...