How to Crack System Design Interview Round
Last Updated :
05 Apr, 2024
In the System Design Interview round, You will have to give a clear explanation about designing large scalable distributed systems (like Twitter, Messenger, Netflix, Uber, etc..) to the interviewer. This round may be a challenging and complex round for you because you are supposed to cover all the topics and tradeoffs within this limited time frame which seems to be impossible. But this article will work as a guide to solve all these doubts and problems and make you excel in the System Design Interview Round

Steps to Crack System Design Interview Round
Steps to Crack System Design Round in Interviews
We know that it might be an overwhelming round for you so let’s start discussing step by step approach and try to make this round easier for you.
Apart from that, if you want to crack the interview rounds smoothly then enroll now with GeeksforGeeks Mastering System Design Course, mentored by experts.
1. Understand the Goal and Gather All the Requirements
System design interview questions, by nature, are vague or abstract. Asking questions about the exact scope of the problem, and clarifying functional requirements early in the interview is essential. Usually, requirements are divided into three parts:
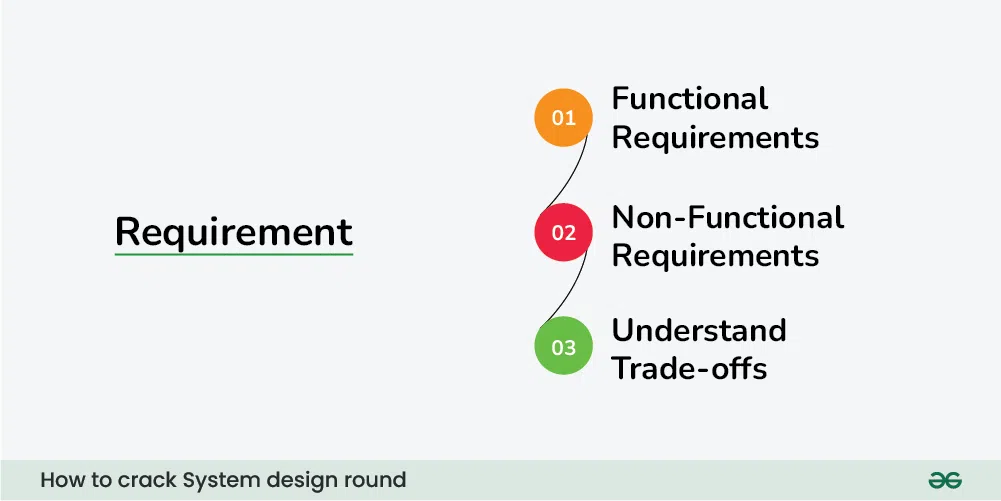
These are the requirements that the end user specifically demands as basic functionalities that the system should offer. All these functionalities need to be necessarily incorporated into the system as part of the contract.
For example:
- “What are the features that we need to design for this system?”
- “What are the edge cases we need to consider, if any, in our design?”
These are the quality constraints that the system must satisfy according to the project contract. The priority or extent to which these factors are implemented varies from one project to another. They are also called non-behavioral requirements. For example, portability, maintainability, reliability, scalability, security, etc.
For example:
- “Each request should be processed with the minimum latency”
- “System should be highly available”
1.3 Extended requirements
These are basically “nice to have” requirements that might be out of the scope of the system.
For example:
- “Our system should record metrics and analytics”
- “Service health and performance monitoring?”
2. Understand the Estimation and Constraints
Estimate the scale of the system we’re going to design. It is important to ask questions such as:
- “What is the desired scale that this system will need to handle?”
- “What is the read/write ratio of our system?”
- “How many requests per second?”
- “How much storage will be needed?”
These questions will help us scale our design later.
3. Define the Data model design
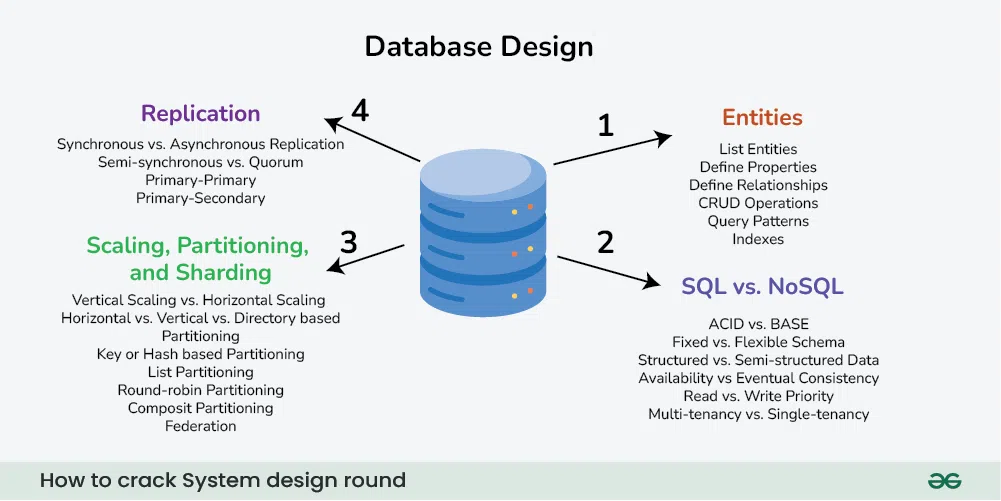
Once we have the estimations, we can start with defining the database schema. Doing so in the early stages of the interview would help us to understand the data flow which is the core of every system. In this step, we basically define all the entities and relationships between them.
- “What are the different entities in the system?”
- “What are the relationships between these entities?”
- “How many tables do we need?”
- “Is NoSQL a better choice here?”
4. API design
Next, we can start designing APIs for the system. These APIs will help us define the expectations from the system explicitly. We don’t have to write any code, just a simple interface defining the API requirements such as parameters, functions, classes, types, entities, etc.
For example:
API
createUser(name: string, email: string): User
It is advised to keep the interface as simple as possible and come back to it later when covering extended requirements.
Now we have established our data model and API design, it’s time to identify system components (such as Load Balancers, API Gateway, etc.) that are needed to solve our problem and draft the first design of our system.
- “Is it best to design a monolithic or a microservices architecture?”
- “What type of database should we use?”
Once we have a basic diagram, we can start discussing with the interviewer how the system will work from the client’s perspective.
Now it’s time to go into detail about the major components of the system we designed. As always discuss with the interviewer which component may need further improvements.
Here is a good opportunity to demonstrate your experience in the areas of your expertise. Present different approaches, advantages, and disadvantages. Explain your design decisions, and back them up with examples. This is also a good time to discuss any additional features the system might be able to support, though this is optional.
- “How should we partition our data?”
- “What about load distribution?”
- “Should we use cache?”
- “How will we handle a sudden spike in traffic?”
Also, try not to be too opinionated about certain technologies, statements like “I believe that NoSQL databases are just better, SQL databases are not scalable” reflect poorly. As someone who has interviewed a lot of people over the years, my two cents here would be to be humble about what you know and what you do not. Use your existing knowledge with examples to navigate this part of the interview.
7. Identify and resolve bottlenecks
Finally, it’s time to discuss bottlenecks and approaches to mitigate them. Here are some important questions to ask:
- “Do we have enough database replicas?”
- “Is there any single point of failure?”
- “Is database sharding required?”
- “How can we make our system more robust?”
- “How to improve the availability of our cache?”
Make sure to read the engineering blog of the company you’re interviewing with. This will help you get a sense of what technology stack they’re using and which problems are important to them.
8. Most Frequently asked Problems for System Design
Below, are some question which is most frequently asked in system design for designing purpose:
9. Quick Tips and Strategies for Succeding in System Design Interview Round:
Try to follow the 80-20 rule during your interview, where 80% of the time you will be speaking and explaining everything and 20% of the time your interviewer. Don’t use buzzwords and pretend to be an expert if you don’t know something.
- You read some blog posts or a few topics today and tomorrow is your interview, during your interview if you throw some buzzwords like “No-SQL”, “Mongo DB” and “Cassandra” then it may backfire on you.
- You can’t make a fool of the interviewer who is an industry expert, always consider that your interviewer may ask for more details and justification so if you are using technology X or database Y then “why?”, prepare yourself for this kind of question.
- Do not go into detail prematurely.
- Many times it happens when a candidate starts explaining one part of the system, they go into too much detail about the component and forget about the strict timeframe and other components.
- Maybe the interviewer wants you to stop somewhere where they don’t need too much detail. So to avoid this mistake wait for the interviewer’s feedback or response.
- They will give you some hints or will direct you to whatever part of the system they want you to explain further.
- Don’t have a set architecture in mind
- Like MVC or event-driven and try to fit the requirement somehow in that architecture. Maybe it’s not suitable as per the requirement. Requirements may change during the interview to test your flexibility so try to avoid this mistake.
- Be honest during your interviews
- If you have never used technology X then you don’t need to be fake in that situation. Try to find common solutions and show them your honesty, confidence, and willingness to learn something. That will make a good impression on the interviewer.
- Your practical experience, your knowledge, your understanding of modern software systems, and how you express yourself clearly during your interview matter a lot to designing a system successfully.
10. Importance of Communication in System Design Interview Round
In the system design interview round, effective communication plays a crucial role in demonstrating your understanding of the problem, your approach to solving it, and your ability to collaborate with others. Here are some key reasons why communication is important in the system design interview:
- Clarifying Requirements: Communication skills allow you to ask insightful questions to clarify requirements and ensure you have a clear understanding of the problem statement. This helps you avoid making assumptions and ensures that your design aligns with the interviewer’s expectations.
- Explaining Design Choices: During the interview, you’ll need to articulate your thought process and rationale behind the design choices you make. Effective communication allows you to explain your decisions clearly, demonstrating your expertise and reasoning abilities to the interviewer.
- Collaborating with the Interviewer: The system design interview often involves a collaborative discussion where you work with the interviewer to refine your design. Strong communication skills enable you to engage in constructive dialogue, solicit feedback, and incorporate suggestions into your design iteratively.
- Presenting Complex Ideas: System design problems can be complex, involving multiple components, trade-offs, and considerations. Effective communication skills enable you to break down complex concepts into digestible explanations, making it easier for the interviewer to follow your thought process.
- Handling Technical Challenges: Inevitably, you may encounter technical challenges or ambiguities during the interview. Strong communication skills allow you to articulate your understanding of the problem, discuss potential solutions, and collaborate with the interviewer to overcome obstacles effectively.
- Demonstrating Soft Skills: Beyond technical expertise, the system design interview assesses soft skills such as teamwork, adaptability, and problem-solving. Effective communication allows you to showcase these skills by actively listening, empathizing with the interviewer, and adapting your approach based on feedback.
11. Do’s and Dont’s in System Design Interview Round
Let’s try to make it simple and discuss some key points before you start your preparation for this round.
- Consider your interviewer as a team member and take this round as an opportunity to work with him where you both are supposed to solve a real-world problem related to your company’s goal but here you need to take ownership and lead everything.
- The main purpose of this round is to understand how capable you are of building a large-scale system and your thought process behind designing a service. Clarity of thoughts matters a lot because if you can explain it to the interviewer, you can do this in your team as well.
- One of the good things for you in this round is that you are supposed to come up with the best solution for all kinds of open-ended problems instead of accurate solutions. Your ability to articulate your thoughts matters more than the final design you present to them.
We hope that from the above points, we have simplified a few things for you and made this round a little bit easier for you.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...