How to Calculate Statistical Significance?
Last Updated :
16 Mar, 2022
In research surveys, statistical significance is an important metric for determining the validity of hypotheses. Every day, a variety of people conduct a variety of tests and surveys, but not all of them are useful. What is the reason behind this? It’s because a survey must have statistical significance or a low likelihood that the hypothesis is false, in order to be regarded as valuable. In other words, a statistically significant survey will have a high likelihood of confirming a theory.
Example
If our survey indicates that 86 percent of respondents have toast and fruit juice as breakfast, we may claim that the survey is statistically significant since the hypothesis that most people have the said meals as breakfast has a higher chance of being correct based on the survey results. When it comes to statistical significance, though, you won’t see the percentage.
Small discrepancies in study findings can be minor if you have a big sample size and are certain that the differences are not due to chance. This formula aids in determining whether or not there is a link between the differences or variations. Statistical significance is used to determine how moderate, weak, or strong a relationship is based on the sample size.
Formula
The statistical significance formula is given as follows:
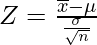
where,
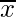 is the sample mean
is the sample mean- μ is population mean
- σ is standard deviation
- n is the number of items
Sample Problems
Question 1. Find the statistical significance given that sample mean, the population mean, standard deviation and sample size are 16, 13, 5, 31.
Solution:
Given: x = 16, μ = 13, σ = 5 and n = 31
Since, 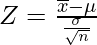
⇒ Z = 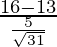
= 3/0.89802
Z = 3.34068
Question 2. Find the statistical significance given that sample mean, the population mean, standard deviation and sample size are 15, 12, 4, 30.
Solution:
Given: x = 15, μ = 12, σ = 4 and n = 30
Since, 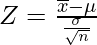
⇒ Z = 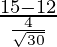
= 3/0.73
Z = 4.10
Question 3. Find the statistical significance given that sample mean, the population mean, standard deviation and sample size are 15, 11, 4, 30.
Solution:
Given: x = 15, μ = 11, σ = 4 and n = 30
Since, 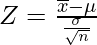
⇒ Z = 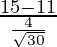
= 4/0.73
Z = 5.47
Question 4. Find the statistical significance given that sample mean, the population mean, standard deviation and sample size are 14, 11, 4, 30.
Solution:
Given: x = 14, μ = 11, σ = 4 and n = 30
Since, 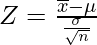
⇒ 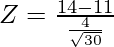
= 3/0.73
Z = 4.10
Question 5. Find the statistical significance given that sample mean, the population mean, standard deviation and sample size are 12, 11, 5, 30.
Solution:
Given: x = 12, μ = 11, σ = 5 and n = 30
Since, 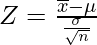
⇒ 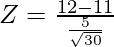
= 1/0.91
Z = 1.098
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...