Hardy’s Rule
Last Updated :
12 Dec, 2021
Hardy’s Rule is an extension of Newton–Cotes formulas. Consider a function, f(x), tabulated at points 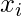 equally spaced by
equally spaced by 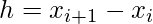 such that
such that 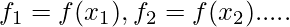
Given the following inputs
1. A function 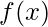 , whose integrand has to be computed.
, whose integrand has to be computed.
2. The upper and lower limits 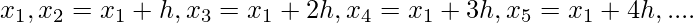

Hardy’s rule can be derived by approximating the integrand f(x)
Example :
The task is to find the integrand of the function using Hardy’s Rule
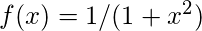 upper limit, b = 6,
lower limit a = 0 .
upper limit, b = 6,
lower limit a = 0 .
Approach :
Hardy’s Rule is a numerical integration technique to find the approximate value of the integral.

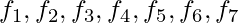 are the values of f(x) at their respective intervals of x.
are the values of f(x) at their respective intervals of x.
In order to integrate any function f(x) in the interval (a, b), follow the steps given below:
1.the value of n=6, which is the number of parts the interval is divided into.
2.Calculate the width, h = (b-a)/6
3.Calculate the values of x0 to x6 as 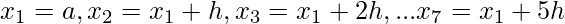
Consider y = f(x). Now find the values of 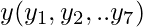 for the corresponding
for the corresponding 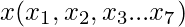 values.
values.
4. Substitute all the above-found values in the Hardy’s rule to calculate the integral value.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
float y(float x)
{
return (1 / (1 + x));
}
float Hardyrule(float a, float b)
{
int n = 6;
int h;
h = ((b - a) / n);
float sum = 0;
float hl = (28* y(a) + 162 * y(a + h)
+ 220 * y(a + 3 * h)
+ 162* y(a + 5 * h)
+28* y(a + 6*h))*h/100
;
sum = sum + hl;
return sum;
}
int main()
{
float lowlimit = 0;
float upplimit = 6;
printf("f(x) = %.4f",
Hardyrule(0, 6));
return 0;
}
|
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...