Handoff in Cellular Telecommunications
Last Updated :
09 Jul, 2023
In cellular telecommunications, the terms handover or handoff refers to the process of transferring an ongoing call or data connectivity from one Base Station to another Base Station. When a mobile moves into a different cell while the conversation is in progress then the MSC (Mobile Switching Center) transfers the call to a new channel belonging to the new Base Station.
When a mobile user A moves from one cell to another cell then BSC 1 signal strength loses for the mobile User A and the signal strength of BSC 2 increases and thus ongoing calls or data connectivity for mobile users goes on without interrupting.
Types of Handoff
- Hard Handoff
- Soft Handoff
- Delayed Handoff
- Mobile-Assisted Handoff
Hard Handoff
When there is an actual break in the connectivity while switching from one Base Station to another Base Station. There is no burden on the Base Station and MSC because the switching takes place so quickly that it can hardly be noticed by the users. The connection quality is not that good. Hard Handoff adopted the ‘break before make’ policy.
It is generally implemented in Time Division Multiplexing and Frequency Division Multiplexing when a user connects to the base station with a fluctuating radio frequency.
- Hard Handoff is cheaper in cost as compared to soft Handoff because only one channel needs to be active at a time.
- It is more efficient than soft handoff, that’s why hard handoffs are widely implemented.
- Sometimes, a delay can be experienced while switching base stations.
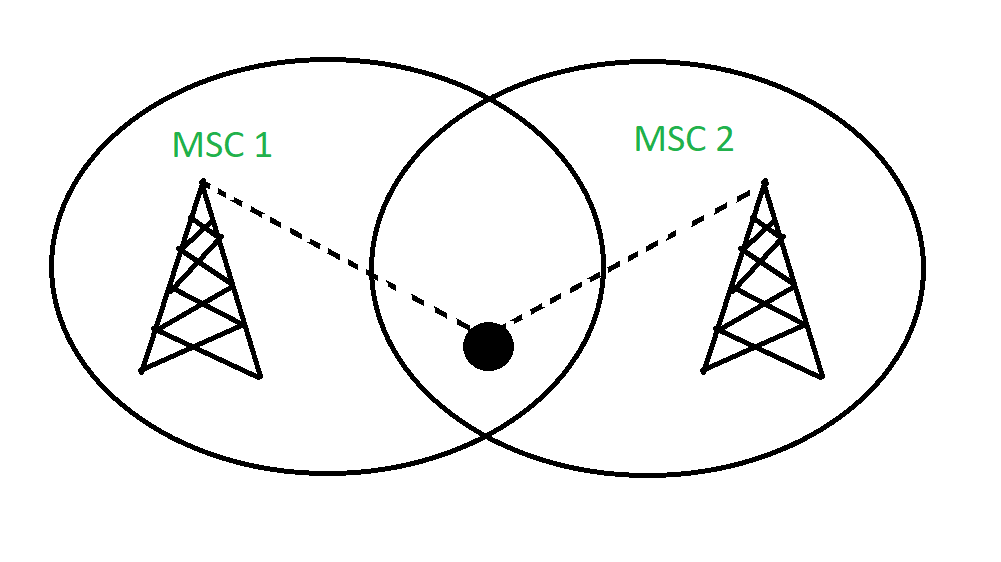
Soft Handoff
Soft Handoff is a mechanism in which the device gets connected with two or more base stations at the same time. At least one of the links is kept when radio signals are added or removed to the Base Station. Soft Handoff adopted the ‘make before break’ policy. If a channel is in power loss then another channel will always be on standby mode so this makes it best in terms of quality as compared to Hard handoff. Soft handoffs are used in devices supporting CDMA/WDMA networks
- High Transmission speed as more than one repeater can transmit signals.
- It has a very low delay in signals.
- It can’t be implemented on devices supporting GSM or LTE networks.
Delayed Handoff
Delayed handoff occurs when no base station is available for accepting the transfer. The call continues until the signal strength reaches a threshold, and after that, the call is dropped. Generally, it happens when the user is out of the network coverage area, or at some dead spots where network reach is very low.
Mobile-Assisted Handoff
Mobile-Assisted handoff is generally used when a mobile phone helps a base station to transfer the call to another base station with better-improvised connectivity and more signal strength. This handoff is used in TDMA technique-based GSM devices.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...