What is Fragmentation?
Last Updated :
08 Aug, 2023
Fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction in which the organism’s body breaks into pieces that further develop into new organisms that develop and mature to show the same process of reproduction. In this process, the organism may break into two or more fragments that will grow into a complete clone. This process is usually seen in favorable conditions with ambient conditions and nutrient availability.
What is Asexual Reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is the type of reproduction in which only one parent gives rise to offspring that are genetically similar to the parent itself i.e. a clone. This type of reproduction does not require two parents of the opposite sex or a male or female gamete to take place. The offspring produced are clone to the parent i.e. they don’t show any form of variation. This process is common in lower organisms. The different types of asexual reproduction are; vegetative propagation, sporogenesis, fragmentation, binary fission, and budding.
What is Fragmentation?
In reproductive biology, fragmentation takes place in multicellular organisms only as the body has to break into two or more pieces for the process to take place. These pieces which are called fragments later grow into individual organisms that are exact copies of the parent organisms without any variation, thus showing the asexual mode of reproduction. This process can be intentional or unintentional i.e. the organism can perform this process to reproduce or any environmental change that induces stress to the organism can also force the organism to undergo fragmentation. Some of the common examples of organisms performing this process are spirogyra, flatworms, sponges, fungi, sea stars, etc.
Steps of Fragmentation
Following are the steps of fragmentation;
- Amputation of body parts from the parent body or breaking down of the parent body into two or more parts.
- The fragments will then start developing into a new organism.
- The development fragments will mature into a new individual that is capable of reproduction.
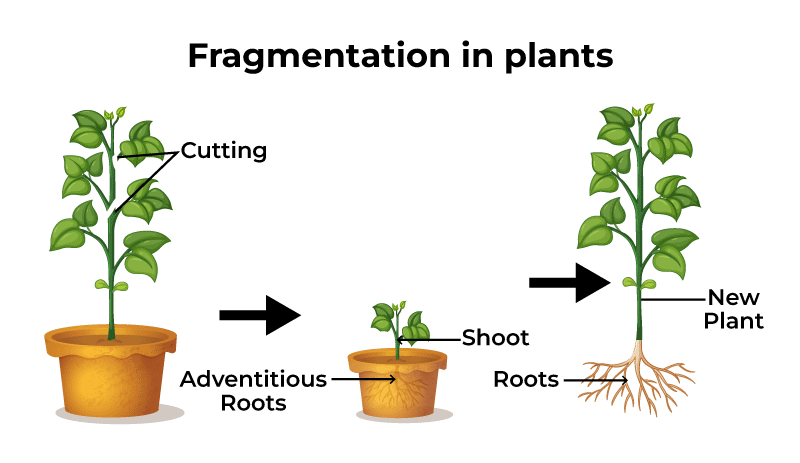
Fragmentation in Plants
In certain plants like mosses, liverworts, and certain higher plants the plant’s body may form fragments which are capable of forming adventitious roots and grow in a different region with suitable conditions a copy of the original plant. This is a very common form of vegetative reproduction in plants in which the detached parts are usually modified forms like bulbils, turions, etc. Various processes like division, cutting, layering, grafting, etc. are types of fragmentation that help in growing plants on a large scale commercially.
Fragmentation in Animals
In lower animals like sponges, coral colonies, sea stars, etc. fragmentation is seen. In these animals either the whole body will split into fragments that will give rise to a new organism (paratomy) or an organ from the body will split to give rise to a new organism (architomy). The point at which splitting will take place will start developing a furrow that will completely detach the part or side of the body.
Fragmentation in Spirogyra
In Spirogyra, the filamentous thallus is broken into multiple fragments by the dissolution of the middle lamella between cells which will undergo multiple mitotic divisions that will give rise to new filaments that will mature to form adult filaments.

Fragmentation in Planaria
In Planaria (a flatworm) the body splits into different fragments and when these fragments receive an appropriate environment they will grow and mature into new adults.

Advantages of Fragmentation
The advantages of fragmentation are as follows:
- Helps in the reproduction of the organism from a single parent only.
- DNA cloning takes place and thus forms clones.
- The extensive and energy-consuming process of mating is avoided.
- Large numbers of offspring can be produced in a very short amount of time.
- No genetic variation is seen i.e. the parental traits are preserved.
- Helps maintain environmental equilibrium by maintaining a large number of smaller or lower-level organisms.
Disadvantages of Fragmentation
The disadvantages of fragmentation are as follows:
- As no genetic variation is seen inbreeding depression or transfer of genetic diseases can be seen.
- As no genetic variation is seen adaptation to changes in the environment is very slow or not seen which may result in the elimination of the entire species.
- The clones are usually weak and have very less defense capabilities against new predators or parasites.
- As a large number of offspring can be produced in a smaller amount of time overpopulation can be seen.
FAQs
Q: Are fragmentation and regeneration the same process?
Answer:
Fragmentation and regeneration are not the same. Regeneration is a form of healing whereas fragmentation is a form of asexual reproduction.
Q: What is cladoptosis? How does it help in fragmentation?
Answer:
Cladoptosis is the process by which woody plants like willow on a regular basis sheds twigs and branches. Through this process, these twigs and branches which are capable of growing adventitious roots develop into a new plant just like in the process of fragmentation.
Q: Other than Spirogyras name some species of algae that shows fragmentation.
Answer:
Some other species of algae that shows fragmentation are; Ulothrix, Zygnema, Oscicillatoria, etc.
Q: In fungi the fragment that takes part in fragmentation are known as?
Answer:
In fungi, the fragments that may grow into new individuals are known as oidium or arthrospore.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...