Explain the concept of RESTful APIs in Express.
Last Updated :
12 Feb, 2024
RESTful APIs are a popular way of creating web applications that exchange data over the internet in a standardized manner. These APIs follow specific principles such as using resource-based URLs and HTTP methods to perform various operations like creating, reading, updating, and deleting data. ExpressJS is a powerful framework that allows developers to easily create routes, handle requests, and send responses, making it a versatile choice for building APIs that are robust and scalable.
Understanding the concept of RESTful APIs in Express JS:
- REST Architecture: REST, which stands for Representational State Transfer, is an architectural style for designing networked applications.
- Resource-Based: RESTful APIs in ExpressJS are designed around resources, which are identified by unique URLs. These resources represent the entities (e.g., users, products, articles) that the API manipulates.
- HTTP Methods: RESTful APIs use standard HTTP methods to perform CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations on resources:
- GET: Retrieves data from a resource.
- POST: Creates a new resource.
- PUT: Updates an existing resource.
- DELETE: Deletes a resource.
- Statelessness: RESTful APIs are stateless, meaning that each request from a client contains all the information needed to process the request. Servers do not maintain a session state between requests.
- Uniform Interface: RESTful APIs have a uniform interface, which simplifies communication between clients and servers. This interface typically involves the use of standard HTTP methods, resource identifiers (URLs), and representations (e.g., JSON, XML).
- ExpressJS and Routing: In ExpressJS, you define routes to handle incoming requests for specific resources and HTTP methods. Each route specifies a callback function to process the request and send an appropriate response.
- Middleware Integration: ExpressJS middleware can be used to handle tasks such as request validation, authentication, and response formatting, enhancing the functionality and security of RESTful APIs.
- Response Codes: RESTful APIs use standard HTTP status codes to indicate the success or failure of a request. Common status codes include 200 (OK), 201 (Created), 400 (Bad Request), 404 (Not Found), and 500 (Internal Server Error).
Example: Below are the example of RESTful APIs in ExpressJS.
- Install the necessary package in your application using the following command.
npm install express
Example: Below is the basic example of the RESTful API in ExpressJS.
Javascript
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const PORT = 3000;
let books = [
{
id: 1,
title: 'The Great Gatsby',
author: 'F. Scott Fitzgerald'
},
{
id: 2,
title: 'To Kill a Mockingbird',
author: 'Harper Lee'
},
];
app.get('/api/books',
(req, res) => {
res.json(books);
});
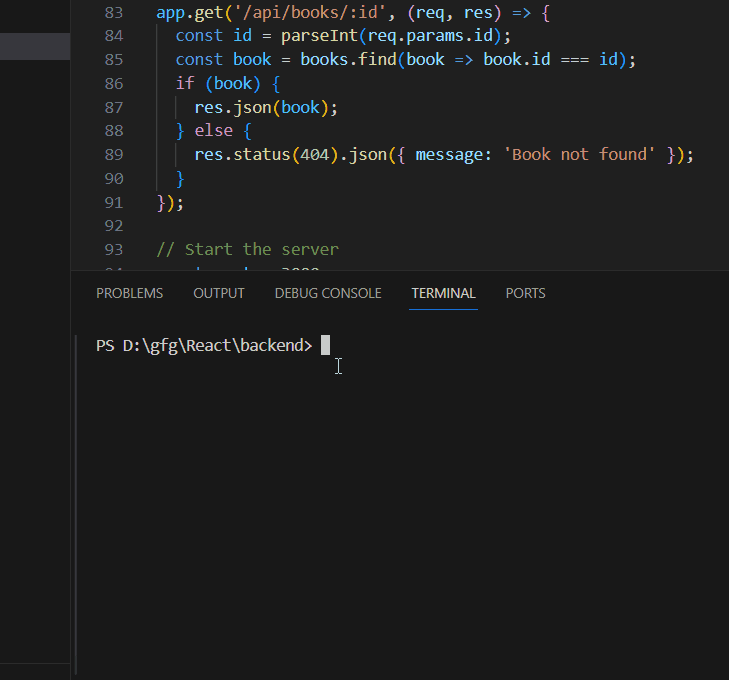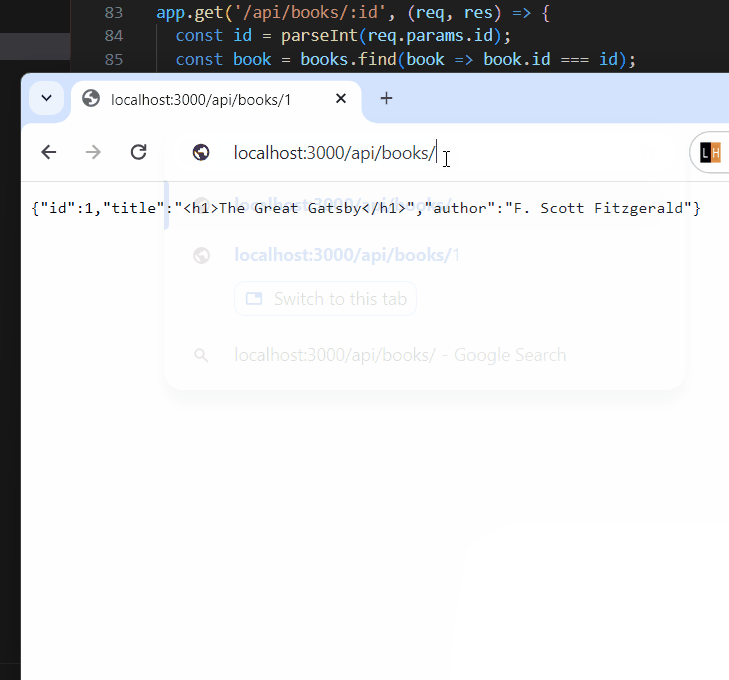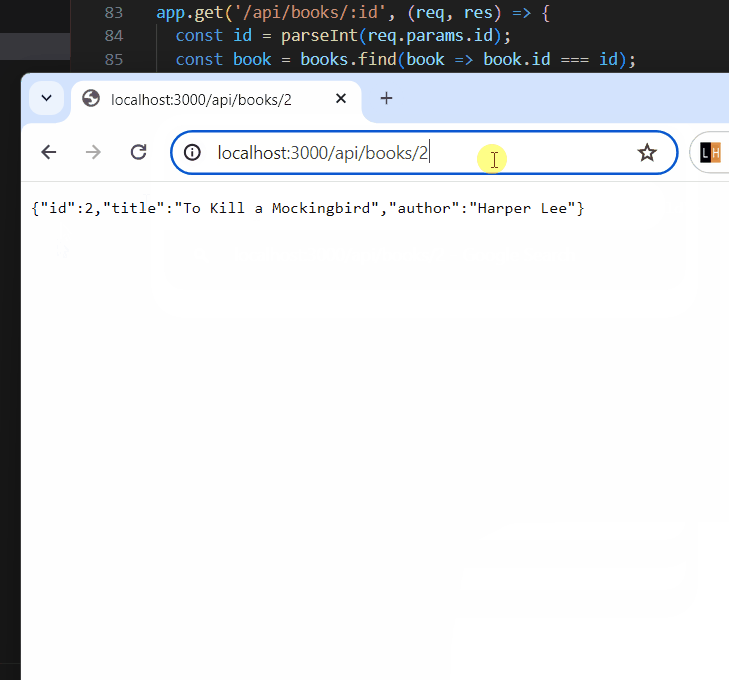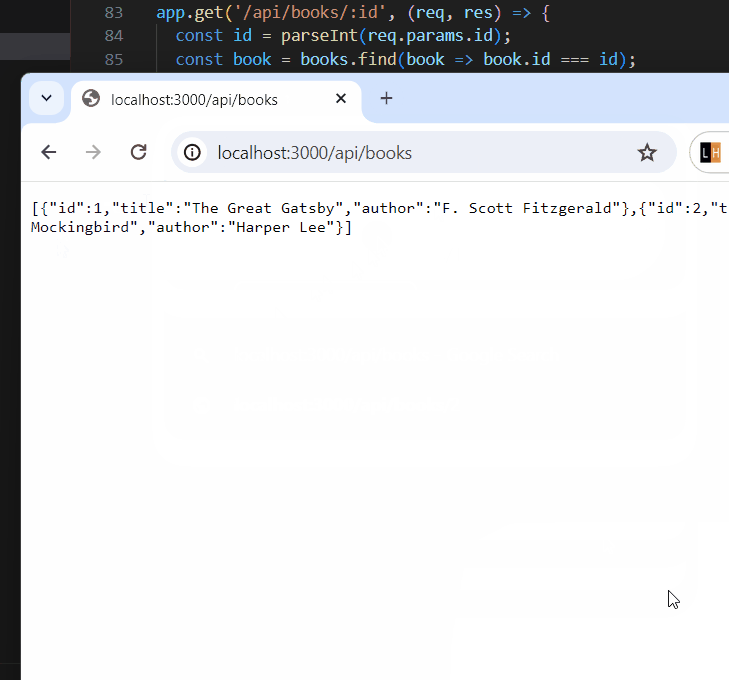
app.get('/api/books/:id',
(req, res) => {
const id =
parseInt(req.params.id);
const book =
books.find(book => book.id === id);
if (book) {
res.json(book);
} else {
res.status(404)
.json({ message: 'Book not found' });
}
});
app.listen(PORT,
() => {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${PORT}`);
});
|
Start your application using the following command.
node server.js
Output:
Output
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...