What is Dumping?
Dumping refers to the practice of selling goods or services in a foreign market at a price lower than their domestic market value. This can be a strategic business move to gain a competitive advantage, increase market share, or eliminate competitors. Dumping can have economic and trade implications and is subject to international trade regulations. This practice can harm local businesses because it makes it hard for them to compete.
Geeky Takeaways:
- Dumping is essentially a strategy where companies intentionally set their prices lower than what other businesses in the market are charging.
- Dumping often involves producing a lot of goods all at once. When companies make things in large quantities, they can save money because the cost of making each item goes down.
- The main goal of dumping is to take over as much of the market as possible.
How Dumping Works?
Dumping typically involves selling goods or services in a foreign market at a price that is below their fair market value or below the cost of production. Here’s how the process of dumping generally works,
1. Identifying Target Markets: Companies or countries may identify target markets where they believe they can sell their goods or services at a profit, even if it means pricing them below market value.
2. Setting Low Prices: The dumping entity sets prices for their products or services at a level significantly lower than what is charged in their domestic market or what would be considered fair market value.
3. Exporting Goods: The goods or services are then exported to the target market at the low prices set by the dumping entity. This often involves significant quantities of goods being exported to maximize market penetration.
4. Undercutting Competitors: In the target market, the dumped goods or services undercut prices offered by domestic producers or other foreign competitors. This can lead to a rapid increase in market share for the dumping entity.
5. Market Penetration: Through aggressive pricing and marketing strategies, the dumping entity aims to gain a significant share of the target market, potentially driving out competitors or severely limiting their market opportunities.
6. Consequences and Responses: Once dumping is detected, the importing country may take various measures to address it, such as imposing anti-dumping duties or tariffs to level the playing field for domestic producers.
7. Long-Term Implications: While dumping may provide short-term benefits for the dumping entity, such as increased market share or immediate profits, it can have negative long-term consequences. These can include trade disputes, retaliatory actions from affected countries, damage to domestic industries in the importing country, and potential harm to international trade relations.
Examples of Dumping
1. Steel Industry: A country might export steel to another nation at a price below its production cost, making it difficult for local steel producers to compete. the scenario is a country exports steel to another nation at a price significantly below its production cost. Impact of Local steel producers struggle to compete due to the artificially low prices, potentially leading to job losses and industry decline.
2. Electronic Goods: Companies might sell electronic devices in a foreign market at lower prices, intending to dominate the market and push local competitors out. let’s take the scenario that companies export electronic devices to a foreign market at prices considerably lower than their domestic market value. Impact is the goal to dominate the foreign market by undercutting local competitors, potentially leading to reduced innovation and market diversity.
3. Textile Industry: The scenario is exporting textiles at prices lower than production costs to secure a larger market share in a foreign country. Impact Local textile producers may struggle to compete, leading to economic challenges and potential job losses in the domestic industry.
4. Pharmaceuticals: Companies might be selling pharmaceutical products in a foreign market at prices well below those charged domestically. The impact of this can undermine local pharmaceutical industries, hinder research and development, and compromise the quality of healthcare products.
Types of Dumping
1. Predatory Dumping: Predatory dumping aims to eliminate competition by selling products at a loss for a specific time. This strategy allows the dumping company to drive competitors out of the market. Once competitors are gone, the company can raise prices, recover losses, and possibly establish a monopoly. Companies engaging in predatory dumping might use tactics like pricing below production costs, utilizing subsidies from their government, or employing aggressive marketing strategies to undercut competitors. The primary goal is to gain control over the market. By eliminating rivals through low prices, the dumping company seeks to become the dominant player. Once it achieves dominance, it can raise prices and potentially reap significant profits.
2. Persistent Dumping: Persistent dumping involves consistently selling goods or services at prices below what’s considered fair market value for an extended period. Unlike predatory dumping, the goal here isn’t just to eliminate competition but to maintain dominance over time. Companies practicing persistent dumping aim to secure a strong position in the market. By continuously offering lower prices, they discourage new competitors from entering and ensure they maintain a significant share of the market. This type of dumping can have long-lasting effects on the market dynamics. It creates barriers for new entrants and makes it difficult for existing competitors to compete effectively, potentially leading to market stagnation or reduced consumer choice.
3. Intermittent Dumping: Intermittent dumping involves sporadic instances of selling products below their actual cost. Unlike persistent dumping, this strategy isn’t about maintaining consistently low prices but rather about disrupting the market periodically. Companies may resort to intermittent dumping to create instability in the market. By periodically undercutting prices, they make it challenging for competitors to predict pricing trends or plan their strategies effectively. Intermittent dumping can lead to uncertainty and volatility in the market. Competitors may struggle to adjust their pricing strategies or invest in long-term planning, potentially weakening their position over time.
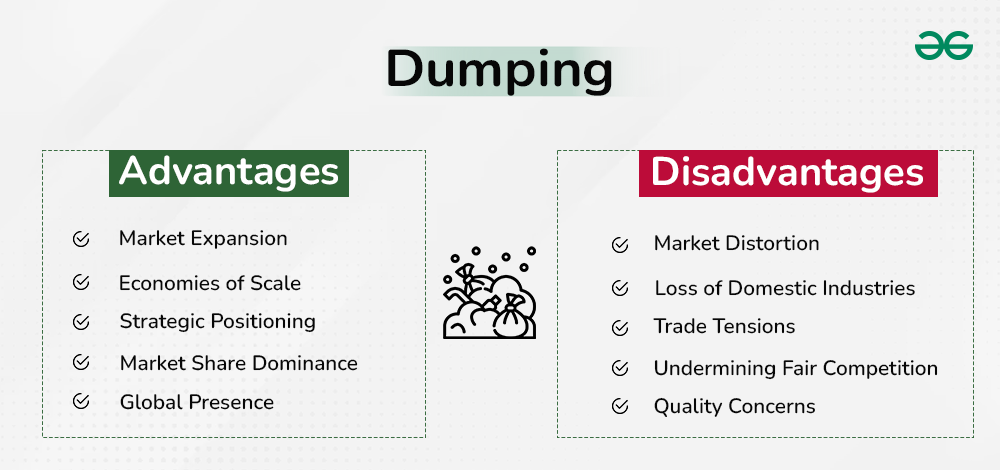
Advantages of Dumping
1. Market Expansion: Dumping can help companies expand their market share in foreign countries. This expansion can provide opportunities for economic growth, job creation, and increased revenue for the exporting company.
2. Economies of Scale: Large-scale production allows for cost efficiencies that enable lower prices. Lower production costs facilitate competitive pricing, making products more affordable for consumers in the target market.
3. Strategic Positioning: Dumping can strategically position a company as a price leader, gaining a competitive advantage over local rivals. This strategic positioning may contribute to brand recognition and loyalty, enhancing the company’s long-term market position.
4. Market Share Dominance: Dumping aims to capture a significant share of the foreign market by offering products at more attractive prices. Achieving dominance can create barriers for new competitors and solidify the exporting company’s market influence.
5. Global Presence: Dumping facilitates the establishment of a global presence, allowing companies to diversify their operations and reduce dependence on a single market. A global footprint can provide resilience against economic downturns in specific regions, ensuring a more stable revenue stream.
Disadvantages of Dumping
1. Market Distortion: Dumping can distort the market by artificially lowering prices below what would occur in a competitive market. This can harm domestic industries in the importing country by making it difficult for them to compete.
2. Loss of Domestic Industries: Dumping can lead to the decline or even collapse of domestic industries in the importing country. If foreign goods are consistently sold at lower prices, domestic producers may struggle to compete, leading to job losses and economic dislocation.
3. Trade Tensions: Dumping often leads to tensions between trading partners. The importing country may retaliate by imposing tariffs or other trade barriers on the dumping country’s goods, leading to trade disputes and potentially escalating into trade wars.
4. Undermining Fair Competition: Dumping undermines the principles of fair competition by allowing companies to gain an unfair advantage in foreign markets through artificially low prices. This can discourage innovation and investment in domestic industries.
5. Quality Concerns: In some cases, dumped goods may be of inferior quality compared to domestically produced goods. This can lead to consumer dissatisfaction and concerns about product safety and standards.
Dumping – FAQs
Is dumping illegal?
Dumping itself is not illegal, but it becomes a concern when it violates fair trade practices. Countries have anti-dumping laws to address such practices.
Can dumping benefit consumers?
Initially, consumers may benefit from lower prices, but the long-term consequences, such as reduced competition, may outweigh the short-term advantages.
How do countries prove dumping allegations?
Countries investigate dumping allegations by examining evidence of below-cost pricing and its impact on the domestic industry.
How do dumping practices affect the environment?
Dumping practices can have adverse environmental effects. To cut costs and offer products at lower prices, companies may compromise on environmental standards. This could lead to increased pollution, resource depletion, and unsustainable practices, negatively impacting ecosystems and contributing to environmental degradation.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...