Converters convert electrical energy which can be used with our devices. And dual converter is an electronic device that regulates two directions of electrical power flow. Also, to switch between AC and DC, we can use a dual converter. In this article, we will be going through what are Dual Converters, We will start our article with the definitions of Converters, We will see in short different types, then we will move to our Topic Dual Converters, We will go through their working and Different types and See their Individual Working, At last, we will conclude our Article with its Applications and Some FAQs.
What are Converters?
Converters function as power interpreters, that convert electrical energy which can be used with our devices. The dual converters can control the flow of electricity in two directions. Considering our power outlets as doors that only permit electricity to flow in one direction. Dual converters act as traffic controllers, which send electricity where it is needed for specific industrial processes requiring bidirectional power flow.
Dual converters act like super-smooth operators, turning jumpy AC into steady DC by straightening out its wiggles. In reverse-blocking mode, they perform the opposite function, converting DC back into AC, which is necessary for systems such as high-voltage transmission lines.
Regenerative mode is similar to how a car recharges its battery when it reduces speed. These converters help in the effective recycling of energy, guaranteeing smooth operation even in the face of difficulties such as commutation errors.
Types of Converters
Converters are essential components in the field of electricity due to their capacity to convert energy. They allow energy to be used for a wider variety of applications and more skillful management. There are various types of converters, each having its own needs:
- Rectifiers: These are the devices that convert AC to DC. They are commonly found in power supplies for electronic equipment and ensure a steady, one-way flow of electricity.
- Inverters: They convert DC to AC in order to carry out the opposite transformation. They are used in devices like uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and solar energy systems require them.
- Converters: They change the AC power’s amplitude or frequency. They are also referred as frequency changers or cyclic converters. When it’s necessary to modify the characteristics of AC power, such as controlling the speed of AC motors, they come in handy.
- DC to DC Converters: DC to DC converters control the voltage of direct current. Electric cars, renewable energy systems, and battery-operated devices all use them to optimize and regulate power flow.
What is Dual Converter ?
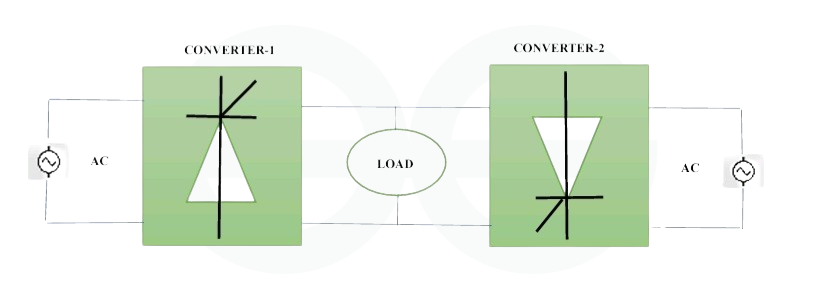
Dual Converter
- Electronic device that regulates two directions of electrical power flow is called a dual converter.
- It allows us to switch between AC and DC. Dual converters are useful in applications where bidirectional power transfer is necessary because of their bidirectional functioning.
- Dual converters are advantageous in situations requiring bidirectional power transfer because of their bidirectional functioning.
- In its forward-blocking mode, the dual converter acts as rectifier, converting AC to DC, which is necessary for applications such as motor drives. However, in reverse-blocking mode, it transforms DC back into AC, which is crucial in high-voltage transmission systems. Helps in increased power control.
- Additionally, dual converters can operate in regenerative mode, which recovers energy in a manner similar to that of electric car regenerative braking systems. Despite their utility, these devices may experience issues such as commutation failures.
- When all factors considered, the ability of the dual converter to regulate the direction of electrical power flow is critical for several industrial applications and improves the adaptability and effectiveness of modern power systems.
Modes of Operation of Dual Converter
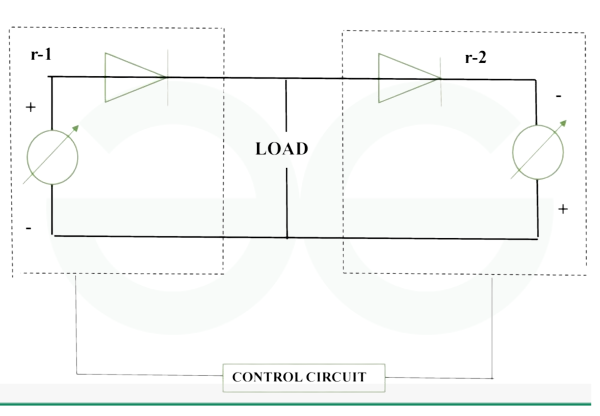
Modes of operation – Dual Converters
Dual converters are power electronic devices that allow power transfer between two AC systems in both directions. They are widely used in high-power applications such as HVDC transmission systems. There are two distinct modes of operation for dual converters:
Mode of Circulating Current
- The rectifier and inverter of the dual converter can operate simultaneously in this mode. Because of the way the converter works, a certain amount of current flows between the AC systems through the converter bridges.
- This circulating current allows for both bidirectional power flow and the upkeep of the DC link voltage.
- The system requirements can be taken into account when controlling and adjusting the circulating current.
- This mode helps to stabilize the DC link voltage and is frequently used in applications that require a continuous bidirectional power flow.
Non-Circulating Current Mode
- The rectifier and inverter operate independently, not in combination, when operating in the non-circulating current mode.
- The rectifier is active when rectifying, and the inverter is active when inverting. The dual converter alternates between rectification and inversion when the system needs power. When bidirectional power flow is not continuous and control over the direction of the power flow is required, this mode is used.
Four Quadrant Significance in Dual Converter
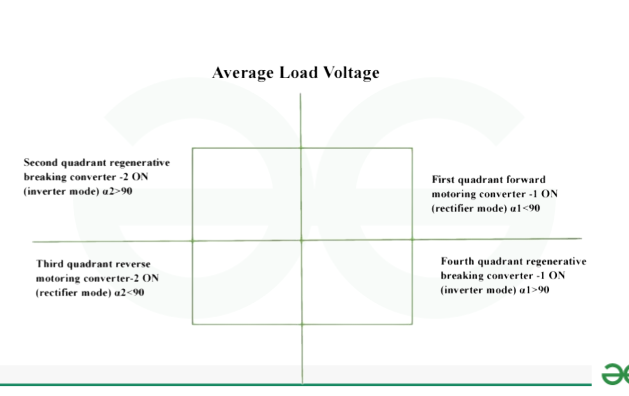
Graph for modes of operation
Ist quadrant: voltage and current both positive.
IInd quadrant: voltage is positive and current is negative.
IIIrd quadrant: voltage and current both negative.
IVth quadrant: voltage is negative and current is positive.
The first of these two converters operates in two quadrants, depending on the firing angle α. This converter acts as a rectifier when α is less than 90˚. When operating in the first quadrant, the converter produces a positive average load voltage and load current.
When α is more than 90°, this converter performs the duties of an inverter. During this operation, the converter produces an average output voltage that is negative, and the current flow remains constant. The current under load stays positive as a result. Energy travels from the source to the load in the first quadrant operation, and from the load back to the source in the fourth.
Thus, the second converter either rectifies or inverts, depending on its firing angle (α). When a rectifier is employed, power moves from the source to the load, reversing the motor, and both the average output voltage and current are negative while operating in the third quadrant. When an inverter is used, power flows from the source to the load and turns the motor in the opposite direction. Its positive output operates in the second quadrant. When regenerative braking is applied, the motor becomes a generator as power moves from the source to the load.
Types of Dual Converters
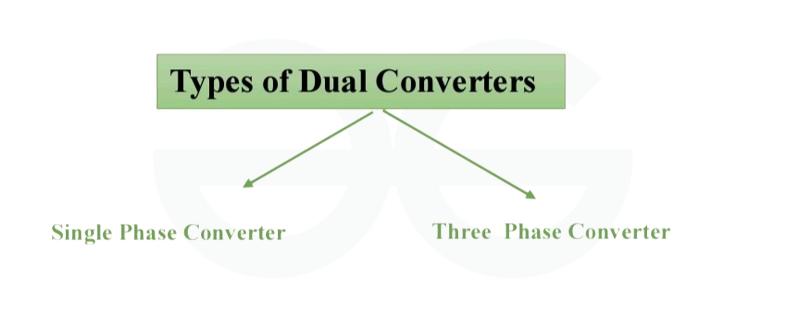
Types of Dual Converters
A dual converter can be classified based on the number of phases it can handle
Single Phase Dual Converter
- The single-phase dual converter’s objective is to control the power flow in a single-phase AC system. It is made up of two structures that are usually placed opposite to one another to allow power to flow in both directions.
- Single-phase dual converters are widely used in applications where the power flow is primarily single-phase, such as in systems that convert DC to AC or single-phase AC to DC.
Three-Phase Dual Converter
- A three-phase dual converter is used in three-phase AC systems to control power flow.
- It consists of up of six bridges, two sets of three bridges each, that are arranged to control the three phases of the AC system.
- Like single-phase dual converter, the three-phase dual converter allows bidirectional power flow and is commonly used in three-phase AC to DC or DC to AC conversion systems.
The choice between using a single-phase or three-phase dual converter depends on the particular requirements of the application as well as the features of the AC power system in question. Three-phase dual converters are more common in industrial and high-power applications where three-phase AC systems are typical. Single-phase dual converters are used when there are applications with lower power requirements or when the power system is primarily single-phase.
Ideal Dual Converter
Ideal inverter is the inverter with ripple free output voltage. Between the converters, two diodes (D1 and D2) are included to allow for the unidirectional flow of DC current. On the contrary hand, the current may move in any direction. Converters 1 and 2 have average output voltages of V1 and V2, respectively. Controlling the transistor firing angles is required in order that the output voltages of the two converters have the same polarity and magnitude.
Average output voltage (Single-phase converter) =[Tex]\frac{2V_mcos\alpha}{\pi}
[/Tex]
Average output voltage (Three-phase converter) = [Tex]\frac{3V_mcos\alpha}{\pi}
[/Tex]
[Tex]V_1=V_{max}cos\alpha_1
[/Tex]
[Tex]V_2=V_{max}cos\alpha_2
[/Tex]
Output voltage, [Tex]V_{out}= V_1= -V_2
[/Tex]
[Tex]V_{max}cos\alpha_1= -V_{max}cos\alpha_2
[/Tex]
[Tex]cos\alpha_1= cos(180°- α2) or cos\alpha_1= cos(180°+ α2)
[/Tex]
Therefore, [Tex]\alpha_1{+\alpha}_2=180° or \alpha_1{-\alpha}_2=180°
[/Tex]
The firing angle is always ≤ 180°. So,[Tex] \alpha_1{+\alpha}_2=180°
[/Tex]
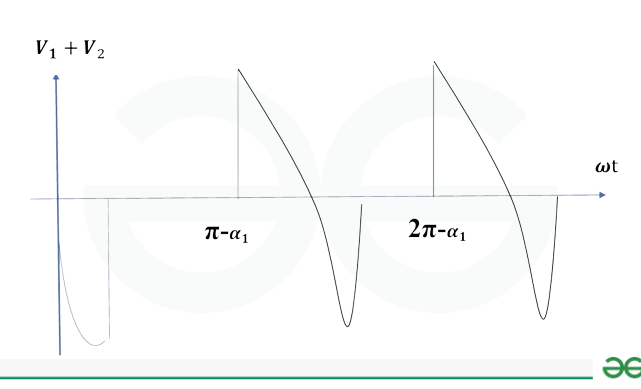
waveform of output voltage
Three Phase Dual Converter
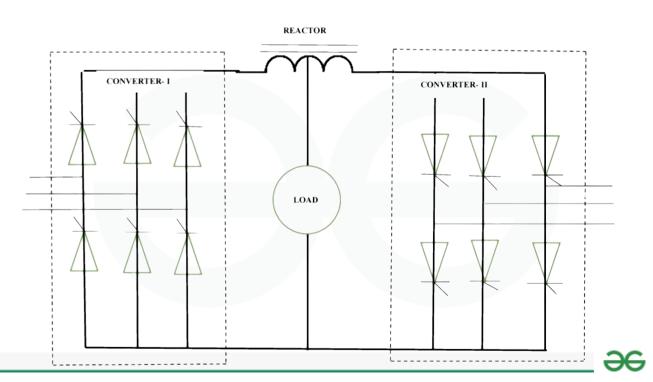
Three phase dual converter
A three-phase dual converter is an electrical device created for enabling bidirectional transfer of power between two three-phase AC systems. In general, there are two groups of three bridges each, totaling six bridges. By managing power flow in both directions, these switches allow for conversion of AC to DC or DC to AC. In high-power applications where three-phase AC systems are common, like industrial settings and HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) transmission systems, the three-phase dual converter is frequently used. It provides the adaptability to change the power flow’s direction as necessary for certain applications.
Single Phase Dual Converter
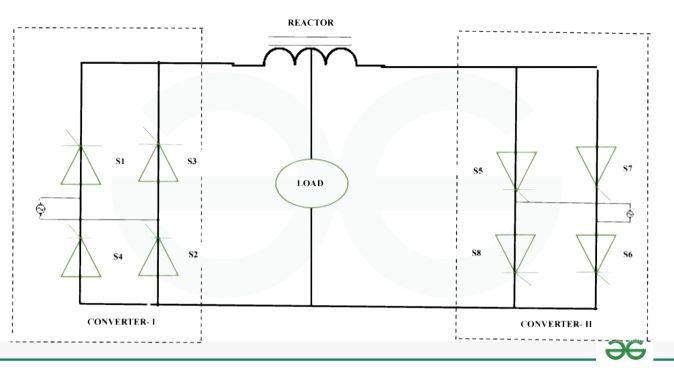
Single Phase Dual Converter
A power electronic device called a single-phase dual converter is made to manage bidirectional power flow in single-phase AC systems. Usually, it is made up of two bridges placed opposite to one another. With this arrangement, power flow direction can be controlled as AC power can be converted to DC and vice versa. Single-phase dual converters are useful in systems where the predominant power flow is single-phase, like in some single-phase DC to AC or AC to DC conversion scenarios.
Direction and Speed Control of DC Motors using Dual Converter
A bidirectional power electronic device controls the direction and speed of DC motors when they are operated with a dual converter.
Direction Control
- The dual converter’s capacity to produce bidirectional power flow allows the DC motor’s current to be reversed.
- The direction of the DC motor can be easily changed by varying the firing angle of the thyristors.
Speed Control
- Dual converters allow variable speed control by altering the thyristors’ firing angles.
- This speed can be changed without any external mechanical component.
- A higher angle of fire results in higher voltage to the motor, which increases its speed.
- When the firing angle decreases, the motor speed decreases along with the voltage.
Bidirectional Power Flow
- The dual converter is especially appropriate for applications requiring fast changes in motor speed and direction because of its capacity for bidirectional energy flow.
Smooth Control
- Precise control of the firing angles allows smooth, continuous adjustments that enable accurate control over the motor’s direction and speed.
Applications of Dual Converter
- They are used by HVDC systems to efficiently move power across large distances between AC lines.
- They enable variable speed control in motor control by regulating the speed and torque of electric motors.
- During blackouts, UPS systems effortlessly switch between battery power and AC mains using two converters, guaranteeing a steady supply of electricity.
- They regulate the power transfer between the traction motor and the power supply in electric trains to ensure smooth motion.
- They are necessary to ensure that the proper voltage and frequency are maintained when AC power from renewable energy sources is integrated into the grid.
Conclusions
In power electronic , dual converters are helpful and necessary components as they come in single- as well as three-phase designs, they can be easily customized to fit a range of needs. Since they can regulate power flow in both directions, they are crucial to electric traction, motor drives, uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), high voltage direct current (HVDC) transmission systems, and renewable energy plants. When used for specific purposes, they effectively regulate the power flow in systems that require single-phase power. However, three-phase dual converters are often used in industrial settings that use three-phase AC systems. The adaptability, effectiveness, and bidirectional power control of Dual converters show how vital role they have played in the advancement of power electronics and a wide range of technological applications.
FAQs on Dual Converters
How does a dual converter regulate power flow?
A dual converter adjusts with the firing angles of the thyristors in order to regulate the power flow. Since DC motors can transfer power both from AC to DC and from DC to AC, they have precise control over both direction and speed.
Can dual converters handle both single-phase and three-phase power systems?
The power system in which dual converters are employed may have single- or three-phase settings, based on its specifications.
Differentiate between single-phase converters and three-phase dual converters?
- Single-phase dual converters control power flow in single-phase AC systems, whereas three-phase dual converters are designed for three-phase AC systems and provide flexibility in responding to various industrial and power system requirements.
- Single-phase dual converters are commonly used in residential and small-scale industries whereas three phase dual converters in large scale industries.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...