C – Pointer to Pointer (Double Pointer)
Last Updated :
08 Nov, 2023
Prerequisite: Pointers in C
The pointer to a pointer in C is used when we want to store the address of another pointer. The first pointer is used to store the address of the variable. And the second pointer is used to store the address of the first pointer. That is why they are also known as double-pointers. We can use a pointer to a pointer to change the values of normal pointers or create a variable-sized 2-D array. A double pointer occupies the same amount of space in the memory stack as a normal pointer.
Declaration of Pointer to a Pointer in C
Declaring Pointer to Pointer is similar to declaring a pointer in C. The difference is we have to place an additional ‘*’ before the name of the pointer.
data_type_of_pointer **name_of_variable = & normal_pointer_variable;
int val = 5;
int *ptr = &val; // storing address of val to pointer ptr.
int **d_ptr = &ptr; // pointer to a pointer declared
// which is pointing to an integer.
The above diagram shows the memory representation of a pointer to a pointer. The first pointer ptr1 stores the address of the variable and the second pointer ptr2 stores the address of the first pointer.
Example of Double Pointer in C
C
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int var = 789;
int* ptr2;
int** ptr1;
ptr2 = &var;
ptr1 = &ptr2;
printf("Value of var = %d\n", var);
printf("Value of var using single pointer = %d\n", *ptr2);
printf("Value of var using double pointer = %d\n", **ptr1);
return 0;
}
|
Output
Value of var = 789
Value of var using single pointer = 789
Value of var using double pointer = 789
How Double Pointer Works?
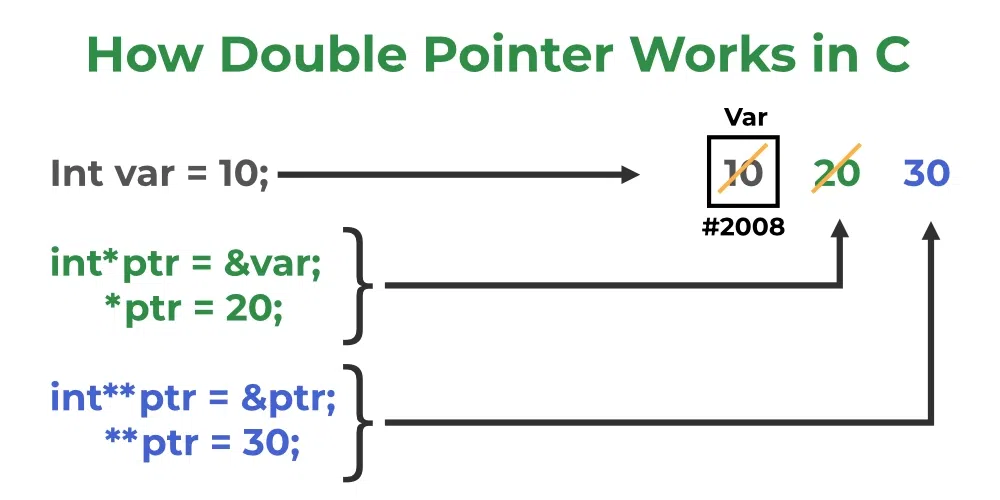
The working of the double-pointer can be explained using the above image:
- The double pointer is declared using the syntax shown above.
- After that, we store the address of another pointer as the value of this new double pointer.
- Now, if we want to manipulate or dereference to any of its levels, we have to use Asterisk ( * ) operator the number of times down the level we want to go.
Size of Pointer to Pointer in C
In the C programming language, a double pointer behaves similarly to a normal pointer in C. So, the size of the double-pointer variable is always equal to the normal pointers. We can verify this using the below C Program.
Example 1: C Program to find the size of a pointer to a pointer.
C
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a = 5;
int* ptr = &a;
int** d_ptr = &ptr;
printf(" Size of normal Pointer: %d \n", sizeof(ptr));
printf(" Size of Double Pointer: %d \n", sizeof(d_ptr));
return 0;
}
|
Output
Size of normal Pointer: 8
Size of Double Pointer: 8
Note: The output of the above code also depends on the type of machine which is being used. The size of a pointer is not fixed in the C programming language and it depends on other factors like CPU architecture and OS used. Usually, for a 64-bit Operating System, the size will be 8 bytes and for a 32-bit Operating system, the size will be 4 bytes.
Application of Double Pointers in C
Following are the main uses of pointer to pointers in C:
- They are used in the dynamic memory allocation of multidimensional arrays.
- They can be used to store multilevel data such as the text document paragraph, sentences, and word semantics.
- They are used in data structures to directly manipulate the address of the nodes without copying.
- They can be used as function arguments to manipulate the address stored in the local pointer.
Multilevel Pointers in C
Double Pointers are not the only multilevel pointers supported by the C language. What if we want to change the value of a double pointer?
In this case, we can use a triple pointer, which will be a pointer to a pointer to a pointer i.e, int ***t_ptr.
Syntax of Triple Pointer
pointer_type *** pointer_name;
Similarly, to change the value of a triple pointer we can use a pointer to a pointer to a pointer to a pointer (Four level Pointer). In other words, we can say that to change the value of a ” level – x ” variable we can use a ” level – x+1 ” pointer. And this concept can be extended further.
Note: We can use any level pointer in C. There is no restriction about it but it makes the program very complex and vulnerable to errors.
Must Read – Function Pointer in C
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...