Difference between APC and MPC
Last Updated :
21 Jul, 2023
The functional relationship between consumption and national income is known as Consumption Function. It represents the willingness of households to purchase goods and services at a given income level during a given period of time. It is represented as C = f(Y). The consumption function is a psychological concept that shows consumption levels at different income levels in an economy. Besides, it is influenced by subjective factors like consumer habits, preferences, etc. The two technical aspects of Propensity to Consume are Average Propensity to Consume (APC) and Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC).
Average Propensity to Consume (APC)
It is the ratio of consumption expenditure to the corresponding income level. The formula to determine Average Propensity to Consume (APC) is:
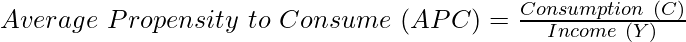
APC can be equal to one, less than one, and more than one, but can never be zero. According to the formula, APC can be zero when the consumption level is zero, which is not possible at any income level because even at zero income level, there is autonomous consumption  .
.
Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
It is the ratio of the change in consumption expenditure to the change in total income. In simple terms, MPC explains the proportion of change income that is spent on consumption. The formula to determine Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) is as follows:
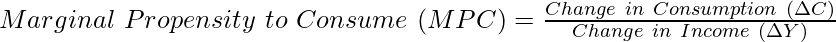
The value of MPC varies between 0 and 1. Besides, the Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) of the poor is more than the MPC of the rich. It is because the poor spend most of their increased income on consumption as most of their basic needs are not yet fulfilled. However, rich people spend less of their increased income on consumption as they are already enjoying a high living standard.
Difference between Average Propensity to Consume (APC) and Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
Basis
| Average Propensity to Consume (APC)
| Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC)
|
|---|
| Meaning | It is the ratio of consumption expenditure to the corresponding income level. | It is the ratio of change in consumption expenditure to the change in total income. |
| Value more than one | As long as the consumption level is more than national income (till the break-even point), the Average Propensity to Consume (APC) can be more than one. | As the change in consumption cannot be more than the change in income, the Marginal Propensity to Consume cannot be more than one. |
| Response to Change in Income | When the income increases, the Average Propensity to Consume falls. However, the rate of fall is less than that of MPC. | When the income increases, the Marginal Propensity to Consume also falls. However, the rare of fall is more than that of APC. |
| Zero Value | APC can never be zero. | MPC can be zero. |
| Formula | 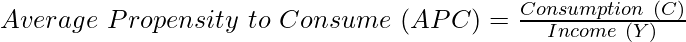 | 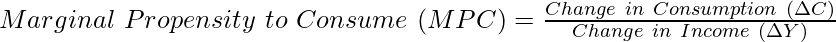 |
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...